Ozone is a gas composed of three atoms of oxygen. It can be found in the Earth's upper atmosphere and at ground level. Ozone is both beneficial and harmful to humans and the environment. Ozone in the stratosphere is beneficial because it filters out incoming radiation from the Sun in the cell-damaging ultraviolet (UV) part of the spectrum. Without this ozone layer, life on Earth would not have evolved in the way it has. However, ground-level ozone is harmful because it can trigger a variety of health problems, particularly for children, the elderly, and people of all ages who have lung diseases such as asthma.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Ozone in the stratosphere | Filters out incoming radiation from the Sun in the cell-damaging ultraviolet (UV) part of the spectrum |
| Ozone pollution | Harmful to people and the environment; the main ingredient in smog |
| Ozone in the stratosphere | Protects living things from ultraviolet radiation from the sun |
| Ozone pollution | Can trigger a variety of health problems, particularly for children, the elderly, and people of all ages who have lung diseases such as asthma |
| Ozone in the stratosphere | Exists in the lower part of the stratosphere |
| Ozone pollution | Exists at ground level |
What You'll Learn

Ozone is both beneficial and harmful to us
Ozone is a gas composed of three atoms of oxygen. It occurs both in the Earth's upper atmosphere and at ground level.
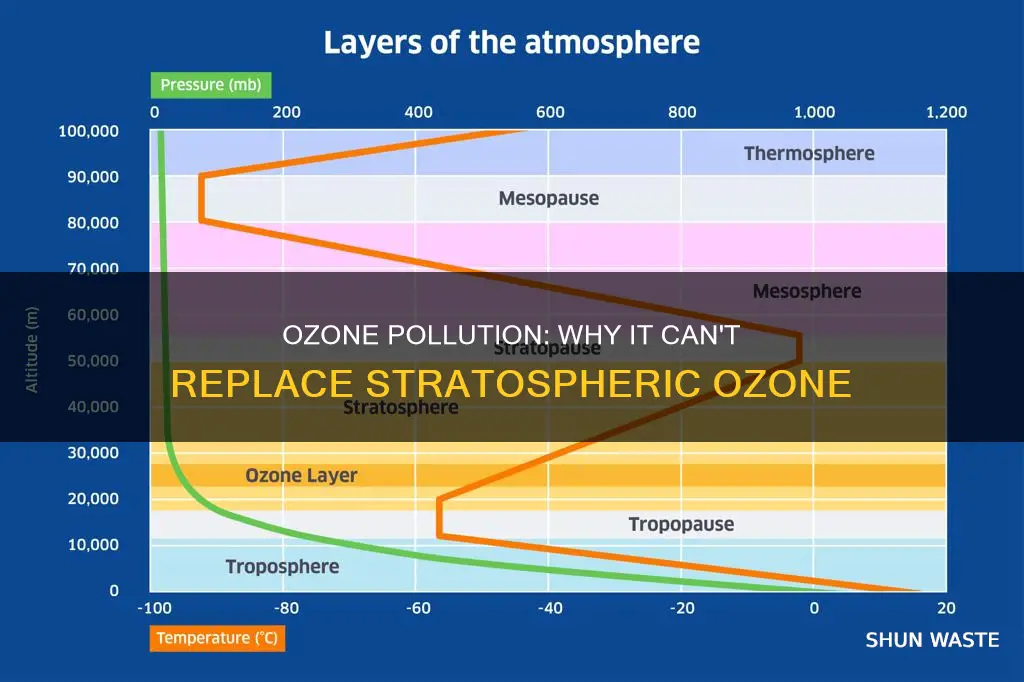
Stratospheric ozone is "good" because it protects living things from ultraviolet radiation from the sun. The stratosphere is the second major layer of the atmosphere and lies above the troposphere, the lowest layer. It occupies the region of atmosphere from about 12 to 50 km above the Earth's surface, although its lower boundary tends to be higher nearer the equator and lower nearer the poles. The highest ozone concentrations are found in the lower part of the stratosphere, from about 12 to 30 km. Without this ozone layer, life on Earth would not have evolved in the way it has.
Ground-level ozone, on the other hand, is "bad" because it can trigger a variety of health problems, particularly for children, the elderly, and people of all ages who have lung diseases such as asthma. Ground-level ozone is created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC). This happens when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, chemical plants, and other sources chemically react in the presence of sunlight. Ground-level ozone is the main ingredient in "smog".
Carbon Monoxide: A Silent, Deadly Health Hazard
You may want to see also

Ground-level ozone is a harmful air pollutant
Ground-level ozone is particularly harmful to children, the elderly, and people of all ages with lung diseases such as asthma. It can cause a variety of respiratory problems and trigger health issues.
The concentration of ozone in the atmosphere decreases as you go higher. The lower down in the atmosphere you go, the more oxygen the ultraviolet radiation has to pass through, and the greater the chance it has already been absorbed to create ozone higher up. This is why ozone concentrations tend to be lower very low down and higher in the stratosphere.
The stratosphere is the second major layer of the atmosphere, lying above the troposphere (the lowest layer). It occupies the region from about 12 to 50 km above the Earth's surface, with the lower boundary higher near the equator and lower near the poles. The ozone layer exists in the lower part of the stratosphere, where it filters out incoming radiation from the Sun in the cell-damaging ultraviolet (UV) part of the spectrum. Without this protective layer, life on Earth would not have evolved as it has.
Biotechnology Solutions for Pollution Control and a Green Future
You may want to see also

Ozone amounts decrease as you go higher in the atmosphere
The ozone layer exists in the lower part of the stratosphere, from about 12 to 50 km above the Earth's surface. The stratosphere is the second major layer of the atmosphere and lies above the troposphere, the lowest layer. The ozone layer filters out incoming radiation from the Sun in the cell-damaging ultraviolet (UV) part of the spectrum. Without this ozone layer, life on Earth would not have evolved in the way it has.
Ozone is both beneficial and harmful to us. Ozone in the stratosphere is 'good' because it protects living things from ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. However, ground-level ozone is 'bad' because it can trigger a variety of health problems, particularly for children, the elderly, and people of all ages who have lung diseases such as asthma. Ground-level ozone is created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC) when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, and chemical plants react in the presence of sunlight.
Ozone that occurs in the troposphere is a much smaller proportion of the total planetary ozone and is regarded as 'bad' ozone since it reacts easily with other molecules, making it highly toxic to living organisms.
Technology's Role in Solving Water Pollution
You may want to see also

The ozone layer exists in the lower part of the stratosphere
The ozone layer is found in this region because, as you go lower in the atmosphere, the more oxygen the ultraviolet has to pass through to get there, and the greater the chances are that it has already been absorbed to create ozone somewhere higher up. This means that very low down, the ozone concentrations tend to be lower. From roughly 12 to 30 km, the two tendencies balance out, and the highest ozone concentrations are found there, in what is called the "ozone layer".
Ozone in the stratosphere is considered "good" ozone because it filters out incoming radiation from the Sun in the cell-damaging ultraviolet (UV) part of the spectrum. Without this ozone layer, life on Earth would not have evolved in the way it has.
In contrast, ground-level ozone is considered "bad" because it can trigger a variety of health problems, particularly for children, the elderly, and people of all ages who have lung diseases such as asthma. Ground-level ozone is created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC) when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, and chemical plants react in the presence of sunlight.
Pollution Masks: Suffocating Amidst Protection
You may want to see also

A diminished ozone layer allows more radiation to reach the Earth's surface
Ozone is both beneficial and harmful to humans and the environment. Ground-level ozone is a harmful air pollutant, which is created by chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen and volatile organic compounds. This occurs when pollutants emitted by cars, power plants, industrial boilers, refineries, and chemical plants react in the presence of sunlight.
However, in the stratosphere, ozone is beneficial as it filters out incoming radiation from the Sun in the cell-damaging ultraviolet (UV) part of the spectrum. The stratosphere is the second major layer of the atmosphere and lies above the troposphere, the lowest layer. It occupies the region of atmosphere from about 12 to 50 km above the Earth's surface. The highest ozone concentrations are found in the lower part of the stratosphere, from about 12 to 30 km.
Ozone that occurs in the troposphere is a much smaller proportion of the total planetary ozone and is regarded as 'bad' ozone since it reacts easily with other molecules, making it highly toxic to living organisms. Therefore, while ground-level ozone pollution is harmful, it cannot replace the beneficial ozone in the stratosphere, as it is created by different chemical reactions and exists in a different part of the atmosphere.
Electric Energy's Pollution Paradox: Clean Power, Dirty Secrets?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Ozone pollution is bad for us because it can trigger a variety of health problems, particularly for children, the elderly, and people of all ages who have lung diseases such as asthma.
Stratospheric ozone is "good" because it protects living things from ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Ground-level ozone is "bad" because it can cause a number of respiratory problems, particularly for young children.
The ozone layer is the region of the stratosphere where the highest ozone concentrations are found. It occupies the region of the atmosphere from about 12 to 50 km above the Earth's surface.
A diminished ozone layer allows more radiation to reach the Earth's surface. Excessive exposure to UV-B at the surface of the earth has been shown to cause harmful effects in plants and animals.



















