Water pollution is the contamination of water sources, including rivers, seas, oceans, canals, lakes, and reservoirs, by substances that impair the water's quality and interfere with its beneficial use. These substances, known as contaminants, can be chemical, such as toxic waste, petroleum, and disease-causing microorganisms, or physical, such as plastic and electronic waste. Water pollution has severe consequences for the environment, human health, and economic structures worldwide. It is caused by a range of human activities, including industrial processes, agricultural practices, and improper waste disposal, threatening the health of aquatic ecosystems and millions of people who depend on clean water sources.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Water pollution is the release of substances (such as chemicals or microorganisms) or energy (in the form of radioactivity or heat) into surface and subsurface waters to the point that the substances interfere with beneficial use of the water or with the natural functioning of ecosystems. |
| Impact on Humans | Water pollution is endangering the health of millions of people around the world. 80% of diseases and 50% of child deaths worldwide are related to poor water quality. |
| Impact on the Environment | Water pollution can lead to the destruction of biodiversity, contamination of the food chain, and damage to aquatic ecosystems. |
| Causes | Oil spills, sewage discharge, industrial waste, agricultural activities, plastic pollution, radioactive waste, and natural factors such as extreme weather events. |
| Prevention | Strengthening water intervention management, carrying out intervention measures, improving plumbing and septic systems, reducing oil, fat, and grease disposal in sinks, and proper waste management. |
| Treatment | Wastewater treatment facilities, reed beds for filtering groundwater, and advanced sewage treatment processes for removing personal care products. |
| Global Statistics | In 2020, no river in England and Wales was classed as being in good overall health. According to the UN, more than 80% of the world's wastewater is released into the environment without treatment, and this figure tops 95% in the least developed countries. |
| Regional Statistics | In the US, wastewater treatment facilities process about 34 billion gallons of wastewater per day. |

Plastic pollution
Water pollution is the release of substances into bodies of water that make the water unsafe for human use and disrupt aquatic ecosystems. Plastic pollution is a significant contributor to water pollution, affecting every continent on Earth. Plastics are the most prevalent type of marine debris found in waterways today, with microplastics and macroplastics originating from larger pieces of plastic trash that have broken down or from manufactured microplastics called nurdles, which are used to make plastic products.
Plastic water pollution can enter bodies of water through various pathways, including storm drains, stormwater runoff, wind, and human intervention. Stormwater runoff carries debris, trash, oils, and sediments from impermeable surfaces into waterways, ultimately leading to plastic-filled water in large bodies of water and rivers that flow into the ocean. Additionally, land pollution can become water pollution when trash or debris is carried by animals, wind, or rainfall into bodies of water.
The presence of plastic in water bodies has severe ecological and health consequences. Plastics break down into microplastics, which are then consumed by marine organisms, from zooplankton to large marine predators. These microplastics have been detected in seafood, indicating their potential to enter the human food chain. The health effects of consuming microplastics are currently unknown.
To address plastic water pollution, various solutions have been proposed and implemented. One approach is to use debris booms, large containment barriers that float on the water's surface, to corral and contain floating marine debris. Additionally, storm drain grate filters can be used to catch plastics, trash, oils, and sediments before they enter storm drains. Reducing the production of single-use plastics and promoting reusable alternatives are also essential strategies to mitigate plastic water pollution.
While recycling is often viewed as a solution, it is important to note that only a small fraction of plastic globally makes it to a recycling plant. Therefore, reducing plastic consumption and properly disposing of plastic waste are crucial in preventing plastic water pollution.
Water Pollution's Environmental Impact: Understanding the Devastating Effects
You may want to see also

Sewage and sludge
Water pollution is the release of substances into bodies of water, which makes the water unsafe for human use and disrupts aquatic ecosystems. Sewage and sludge are by-wastes of municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. Sewage pollution is a global crisis threatening human health and biodiversity. It is caused by untreated or poorly treated wastewater, which elevates concentrations of nutrients, pathogens, endocrine disruptors, heavy metals, and pharmaceuticals in natural habitats.
Sewage can promote algae growth, which can eventually result in eutrophic "dead zones" where aquatic life cannot survive due to a lack of oxygen. This process is known as eutrophication and is caused by an increase in the biological oxygen demand of the water. Sewage sludge, the solid component produced during wastewater treatment, can contain dangerous contaminants, including heavy metals and pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella and Escherichia coli.
In Europe, the Sewage Sludge Directive (86/278/EEC) (SSD) was established to regulate the use of sewage sludge in agriculture and prevent harmful environmental effects. The directive sets allowable limits for heavy metals and pathogens and allows for the recovery of sludge on land under sanitary and environmentally sound conditions. However, according to a 2010 report by the European Commission, only 39% of sewage sludge is recycled into agriculture in the European Union.
The presence of contaminants in sewage sludge is a growing concern. Studies have identified various chemicals and biologicals in sewage sludge, including perfluorinated chemicals, polychlorinated biphenyls, pharmaceuticals, and pathogenic bacteria. These contaminants can have serious effects on human health and ecosystems. Sewage sludge incineration with energy recovery has been proposed as an environmentally safer alternative to agricultural application, provided that emissions to air, soil, and water are adequately controlled.
The global extent of sewage pollution in and near natural habitats, such as coral reefs, salt marshes, and fish-rich river systems, highlights the need for cross-sector collaboration between conservation and public health sectors. New sewage management solutions, such as waste-free toilets and resource recovery, are emerging, but more innovation is needed to address this pressing issue effectively.
Sewage's Sinister Impact: Polluting Our Precious Waterways
You may want to see also

Oil spills
Water pollution is the release of substances into bodies of water, which makes the water unsafe for human use and disrupts aquatic ecosystems. Oil spills are a significant contributor to water pollution.
Cleanup and recovery from an oil spill are challenging and can take weeks, months, or even years. The process depends on several factors, including the type of oil spilled, the temperature of the water, and the types of shorelines and beaches involved. Physical cleanups of oil spills are also very expensive. After the Exxon Valdez oil spill in 1989, it was found that high-pressure, hot-water hoses used to clean up beaches caused more damage than the oil alone. As a result, sensitive habitats require extra consideration during oil spill cleanups.
While large oil spills often make the headlines, consumers account for the majority of oil pollution in our seas. Oil and gasoline that drips from cars and trucks, as well as oil from factories, farms, and cities, contribute to oil pollution. Additionally, oil can reach the oceans from land-based sources, such as oil on roads, which is then flushed into the oceans during rainstorms.
Water Pollution: Our Actions, Our Future
You may want to see also

Chemical pollutants
Water pollution is the release of substances into bodies of water, causing interference with the beneficial use of the water and disruption to aquatic ecosystems. Chemical pollutants are one of the main categories of water contaminants, encompassing a wide range of substances. These pollutants can originate from various sources and have significant impacts on both the environment and human health.
One significant source of chemical water pollution is industrial waste. Industrial activities, such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and petroleum production, often generate toxic chemicals that can find their way into water bodies. Improper waste disposal methods, including unlined landfills and leaking storage tanks, contribute to this issue. Additionally, wastewater discharged from industrial facilities can contain harmful chemicals, such as lead, mercury, and chromium, which, if not properly treated, can contaminate water sources.
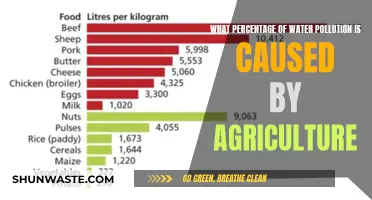
Agricultural practices also contribute to chemical water pollution. The use of fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste in farming can result in nutrient pollution, specifically from excess nitrogen and phosphorus. When it rains, these nutrients are washed into waterways, leading to algal blooms that are harmful to both people and wildlife. This type of pollution is known as nutrient pollution and is considered the number one threat to water quality worldwide.
Another source of chemical water pollution is solid waste or land pollution. This includes garbage, rubbish, electronic waste, and construction debris generated by individual, residential, commercial, and industrial activities. When solid waste is not properly disposed of, it can be carried by animals, wind, or rainfall into bodies of water. Plastics and electronic waste, for example, can break down and release harmful chemicals, posing a threat to aquatic life and potentially entering the human food chain through the consumption of seafood.
Oil pollution is another critical form of chemical water pollution. While oil spills from tankers and shipping operations attract significant attention, land-based sources, such as factories, farms, and cities, contribute nearly half of the estimated 1 million tons of oil that enters marine environments each year. Additionally, the transportation and storage of oil are subject to leakage, further exacerbating the problem. Oil pollution has devastating consequences for marine ecosystems, killing and endangering various species.
Radioactive waste is another severe form of chemical pollution, persisting in the environment for thousands of years. It is generated by uranium mining, nuclear power plants, military weapons production, and certain scientific and medical activities. Radioactive waste emits radiation beyond natural levels and poses significant challenges for disposal, threatening groundwater, surface water, and marine resources.
Fast Fashion's Water Pollution: Understanding the Toxic Truth
You may want to see also

Microorganisms
Water pollution is the release of substances, such as chemicals or microorganisms, or energy, in the form of radioactivity or heat, into surface and subsurface waters. This interferes with the beneficial use of the water and the natural functioning of ecosystems. Water pollution is endangering the health of millions of people around the world. According to the United Nations, one in every three people on the planet is affected by water pollution.
Bacteria, such as E. coli, are a common type of pathogen that can cause various illnesses, including cholera, typhoid fever, and bacillary dysentery. These bacteria can be found in drinking water and are a significant concern for human health, especially for vulnerable populations such as infants, children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. The presence of coliform bacteria in water is often used as an indicator of potential pathogen presence, and regular testing is required by organisations such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
In addition to bacteria, viruses can also contaminate water sources. Viruses can be transmitted through water and cause various diseases, leading to illnesses and deaths, particularly in areas with limited access to clean drinking water.
Parasites are another type of microorganism that can pollute water. They can be found in both human and animal faecal matter and can cause parasitic infections when ingested through contaminated water.
To address water pollution caused by microorganisms, it is essential to implement proper wastewater treatment and sanitation practices. This includes treating sewage and wastewater before releasing it back into the environment and ensuring that septic systems are well-maintained and do not leak. Additionally, natural processes such as using plants to filter pollutants from groundwater can also help reduce microbial pollution.
Preventing Water Pollution: Indonesia's Action Plan
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Environmental water pollution is the contamination of water bodies, including rivers, seas, oceans, and lakes, by various substances and energy forms. It occurs when harmful chemicals, waste, or microorganisms are released into these water bodies, rendering the water unsafe for human use and disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
Environmental water pollution has numerous causes, including:
- Industrial activities: Industries such as oil refineries, factories, and power plants release toxic chemicals, oils, and waste into water sources.
- Agricultural activities: Farming practices contribute pesticides, fertilizers, and organic waste, leading to nutrient pollution in water bodies.
- Sewage and wastewater: Untreated or partially treated sewage and wastewater discharge from homes, industries, and agricultural sources contain harmful microorganisms and chemicals, contaminating water.
- Solid waste: Trash, plastics, and electronic waste dumped into water bodies or carried by wind or rainfall contribute to solid waste pollution, harming aquatic life and leaching toxic chemicals.
- Natural factors: Oil seeps from the ocean floor, and natural events like rainfall, can contribute to water pollution.
Environmental water pollution has significant impacts on both human health and the environment:
- Human health: Polluted water can cause various diseases, with diarrhea being the most common. It is estimated that 80% of diseases and 50% of child deaths worldwide are linked to poor water quality.
- Environment: Water pollution destroys aquatic ecosystems, depletes biodiversity, and contaminates the food chain. It also affects economic growth and exacerbates poverty, as deteriorating water quality hinders development and increases costs.