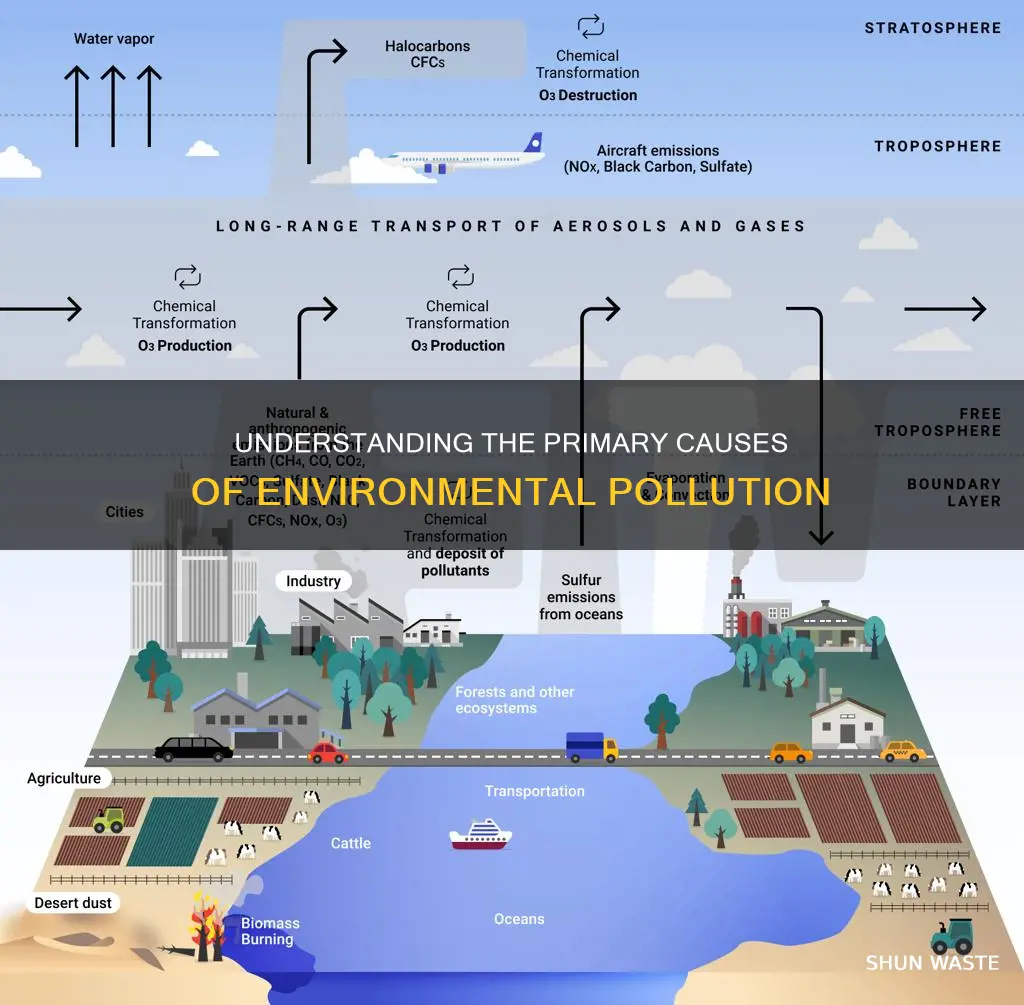
Environmental pollution is a critical issue that poses significant risks to both human health and the planet. While it is not a new phenomenon, it remains one of the most pressing challenges facing humanity. Various factors contribute to environmental pollution, with human activities such as urbanization, industrialization, mining, and exploration being primary drivers. Among the many causes, air pollution stands out as a significant concern, impacting communities worldwide and claiming an estimated seven million lives annually. This paragraph aims to introduce the topic of environmental pollution and highlight the urgent need to address its detrimental effects.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Environmental pollution causes | Urbanization, industrialization, mining, exploration, energy use and production |
| Types of pollution | Air, water, and soil |
| Causes of air pollution | Vehicle emissions, fuel oils, natural gas, manufacturing, power generation, chemical production, forest fires |
| Health effects of air pollution | Lung damage, asthma, emphysema, ADHD, skin allergies, eye irritation, blood disorders, respiratory diseases |
| Global impact of air pollution | 6.5-7 million deaths annually, 99% of the global population breathing air exceeding WHO guideline limits |
What You'll Learn

Industrial facilities and manufacturing
The manufacturing industry, in particular, is responsible for emitting carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions contribute to the greenhouse effect and climate change, leading to global warming and altered weather patterns. Additionally, the production of goods, such as iron, steel, and rubber, results in the release of hazardous substances, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). PAHs are known carcinogens, posing serious health risks to those exposed.
Furthermore, industrial facilities often discharge untreated or partially treated wastewater into water bodies, contaminating them with heavy metals, chemicals, and other toxic substances. This pollution disrupts aquatic ecosystems, kills marine life, and can enter the food chain, ultimately affecting human health. The presence of pharmaceuticals in sewage effluent is also a growing concern, as their residues in aquatic systems can have detrimental ecological effects.
In addition to water pollution, industrial facilities generate significant amounts of solid waste. Poor waste management practices can lead to soil contamination, with toxic substances leaching into the ground and affecting soil fertility and nearby water sources. The accumulation of industrial waste in landfills also contributes to land degradation and air pollution, as waste burning releases harmful chemicals and particulate matter into the atmosphere.
To mitigate these issues, effective waste treatment strategies and pollution disposal facilities are essential. Implementing sustainable economic development practices, such as green technology and pollution-free environments, is crucial to reducing the impact of industrial facilities on the environment and human health. Additionally, the development of technology to convert industrial waste into reusable materials and clean air is vital to minimizing the detrimental effects of industrial pollution.
Apple's Pollution Problem: Environmental Impact of iPhones and Macs
You may want to see also

Vehicle emissions
Motor vehicles emit a range of harmful pollutants, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and benzene. These emissions have both environmental and health impacts. For example, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter can contribute to smog formation, leading to respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular disease, and even cancer.
One of the primary ways vehicles contribute to environmental pollution is through the release of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 is the main greenhouse gas produced by motor vehicles, and it plays a significant role in the 'greenhouse effect' and climate change. The more cars there are on the road, the higher the emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming.
To address the problem of vehicle emissions, individuals can take measures such as carpooling and using public transportation. Governments and organizations can also implement standards and regulations to reduce vehicular emissions. For example, Australia's emission standards mandate limits on carbon monoxide, hydrocarbon, and nitrogen oxide emissions for vehicles fuelled by petrol, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), or natural gas (NG).
Car Idling: A Major Contributor to Air Pollution and Climate Change
You may want to see also

Forest fires and wildfires
Human activities such as urbanization, industrialization, mining, and exploration are the main causes of environmental pollution. However, natural sources also contribute to environmental pollution, and forest fires or wildfires are a prime example of this.
The immediate consequences of wildfires are often felt in the form of reduced air quality. Smoke from wildfires can cause eye and respiratory illnesses, especially in children and the elderly. The emissions from wildfires affect not only the respiratory system but also the entire body. Research suggests that air pollution from wildfire smoke may contribute to the development of diabetes, dementia, and other illnesses. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) released during wildfires can have various health impacts, including lung damage and an increased risk of cognitive and emotional problems in children.
Wildfires also cause significant habitat damage by destroying vegetation and the homes and food sources of many animals. The loss of vegetation can lead to soil erosion, increased runoff, and flash floods, which introduce heavy metals and pollutants into waterways, affecting the physical, chemical, and biological qualities of water sources. Additionally, wildfires can melt plastic water pipes in residential areas, causing contamination of water systems with known carcinogens.
The impact of wildfires extends beyond the short term, and their long-term effects on human health and the environment are still being studied. While forest regeneration can offset some carbon dioxide emissions, wildfires are estimated to contribute five to ten percent of annual global CO2 emissions. They are also linked to a climate feedback loop, where wildfires and climate change fuel each other in a constant cycle.
Pollen's Air Pollution: Understanding the Impact of Pollen Grains
You may want to see also

Fossil fuels
The extraction and use of fossil fuels further exacerbate environmental issues. For example, coal mining can contaminate nearby water sources with toxic runoff and waste rock disposal. Oil extraction and transportation risk oil spills and leaks, which can have devastating effects on freshwater and marine ecosystems. Additionally, fracking, a controversial method of extracting oil and gas, has been linked to groundwater contamination and the release of toxic chemicals into the air and water.
The impact of fossil fuels on air pollution is significant. According to a 2017 study, millions of people are exposed daily to toxic air pollution from oil and gas wells, transport, and processing facilities. This includes harmful substances such as benzene and formaldehyde, which pose serious health risks. Fossil fuel combustion also releases particulate matter, which can have detrimental effects on respiratory health, particularly for vulnerable individuals and children.
Furthermore, the production and use of fossil fuels contribute to water pollution. The burning of fossil fuels releases nitrogen compounds, which can be deposited onto land and subsequently wash into water bodies. This excess nitrogen leads to harmful algal blooms, oxygen-deprived zones, and the toxicity of aquatic life. Additionally, wastewater generated during fossil fuel extraction and drilling contains heavy metals, radioactive materials, and other pollutants, which can leak into waterways, contaminating drinking water sources.
The transition to renewable energy sources is imperative to mitigate the environmental and health impacts of fossil fuels. Despite commitments made by governments and fossil fuel companies to reduce carbon emissions and promote cleaner alternatives, progress remains insufficient. It is crucial to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy, improve energy efficiency, and implement measures to conserve energy to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and minimize their detrimental effects on the environment and public health.
Air Pollution's Deadly Toll: Counting Last Year's Deaths
You may want to see also

Urbanization and industrialization
Beginning with the Industrial Revolution, societies transitioned from agrarian to industrial economies, leveraging new technologies to boost production and consumption. This shift led to the extensive use of fossil fuels, particularly coal, which became the primary energy source for factories and homes in industrializing cities. The burning of coal and other fossil fuels released unprecedented levels of carbon emissions into the atmosphere, driving climate change and global warming. This period also witnessed the emergence of large-scale manufacturing, with industries such as textiles, chemicals, and iron and steel production releasing harmful pollutants, including carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and organic compounds. These emissions contaminated the air and contributed to the formation of thick smog, which darkened the skies over industrial cities.
The Industrial Revolution also triggered a wave of urbanization as people migrated to cities in search of employment opportunities. This urbanization intensified the environmental strain, with cities becoming overcrowded and facing challenges such as poor sanitation, waste disposal issues, and insufficient water availability. The concentration of energy use and increased vehicle emissions in urban areas further exacerbated air pollution, affecting the health and well-being of residents.
As industrialization progressed, the exploitation and depletion of natural resources accelerated. Deforestation, driven by the need for wood and land, led to habitat destruction and the loss of biodiversity. Additionally, improper mining practices and industrial waste disposal contaminated waterways, polluting them with oil and debris and toxic pollutants. The environmental consequences of these actions were far-reaching, and signs of long-term damage became increasingly apparent.
Today, the impacts of urbanization and industrialization continue to be felt globally. While they have brought economic growth, improved living standards, and technological advancements, the environmental costs have been significant. Addressing these issues requires a concerted effort to reduce emissions, improve waste management, promote sustainable practices, and implement strong city planning to mitigate the negative effects of urbanization and industrialization on our environment.
Big Companies: Major Polluters or Saviors of the Environment?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Environmental pollution is caused by a variety of factors, both natural and human-made. The primary sources of human-made air pollution are vehicle emissions, fuel oils, natural gas, manufacturing, and power generation.
Environmental pollution has severe consequences for human health, causing an estimated seven million deaths worldwide each year. It is responsible for respiratory and other diseases and is a major threat to global health and prosperity.
Indoor air pollution is caused by household combustion devices, such as the use of gasoline and natural gas for cooking and heating, which release harmful chemicals and gases into the air.
Low-income communities, particularly communities of color, have historically been disproportionately affected by environmental pollution due to racist zoning policies and discriminatory lending practices. They experience higher health risks and economic harms as a result of living in areas with higher pollution levels.
Individuals can play a role in reducing environmental pollution by conserving energy, reducing consumption, reusing and recycling materials, and using public transportation whenever possible to decrease vehicle emissions.



















