Sulfuric acid is the world's largest volume industrial chemical, with applications in the production of phosphate fertilizers, explosives, other acids, dyes, glue, and automobile batteries, among other things. It is a corrosive substance that can cause severe burns and blindness if it comes into contact with the skin or eyes. It is well known that exposure to sulfuric acid mist can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, and that it can also increase asthmatics' airway resistance. Given the dangers it poses, is sulfuric acid a hazardous air pollutant?
What You'll Learn
- Sulfuric acid is a corrosive chemical that can burn skin and eyes, and cause blindness
- It is carcinogenic to humans, according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer
- Sulfuric acid can be found in cleaning products and car batteries
- Industrial emissions of sulfuric acid can cause acid rain
- Asthmatics are particularly vulnerable to the effects of sulfuric acid

Sulfuric acid is a corrosive chemical that can burn skin and eyes, and cause blindness
Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive chemical that poses a serious threat to human health and the environment. It is a colourless, oily liquid with powerful oxidizing and dehydrating properties, making it extremely hazardous. The main hazards associated with sulfuric acid include the risk of severe burns to the skin and eyes, as well as the potential for blindness.
When sulfuric acid comes into contact with the skin, it can cause severe chemical burns, ranging from mild to third-degree burns. These burns can lead to permanent scarring, and in some cases, may even be fatal. The risk of burns is higher with more concentrated forms of sulfuric acid, and safe handling procedures must be followed to prevent accidental exposure. This includes wearing protective gloves and eye protection when using products containing sulfuric acid, especially when there is a risk of splashing.
The corrosive nature of sulfuric acid also poses a significant risk to the eyes. Even short-term exposure to sulfuric acid vapour or liquid can cause eye irritation, burning, swelling, tearing, and blurred vision. In more severe cases, sulfuric acid can lead to permanent blindness if it comes into contact with the eyes. Therefore, it is crucial to take precautionary measures, such as wearing eye protection, to minimize the risk of eye exposure.
In addition to the risks associated with direct contact, sulfuric acid can also cause harm through inhalation and ingestion. Inhalation of sulfuric acid mist can irritate the respiratory system, nose, throat, and lungs, with asthmatics being particularly vulnerable to pulmonary irritation. Higher levels of exposure can lead to a buildup of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary oedema) and potentially result in chronic bronchitis. Ingesting sulfuric acid causes immediate burning in the mouth and throat, followed by severe pain, nausea, and vomiting. Ingestion of concentrated solutions can also lead to holes in the oesophagus and irreversible damage to internal organs.
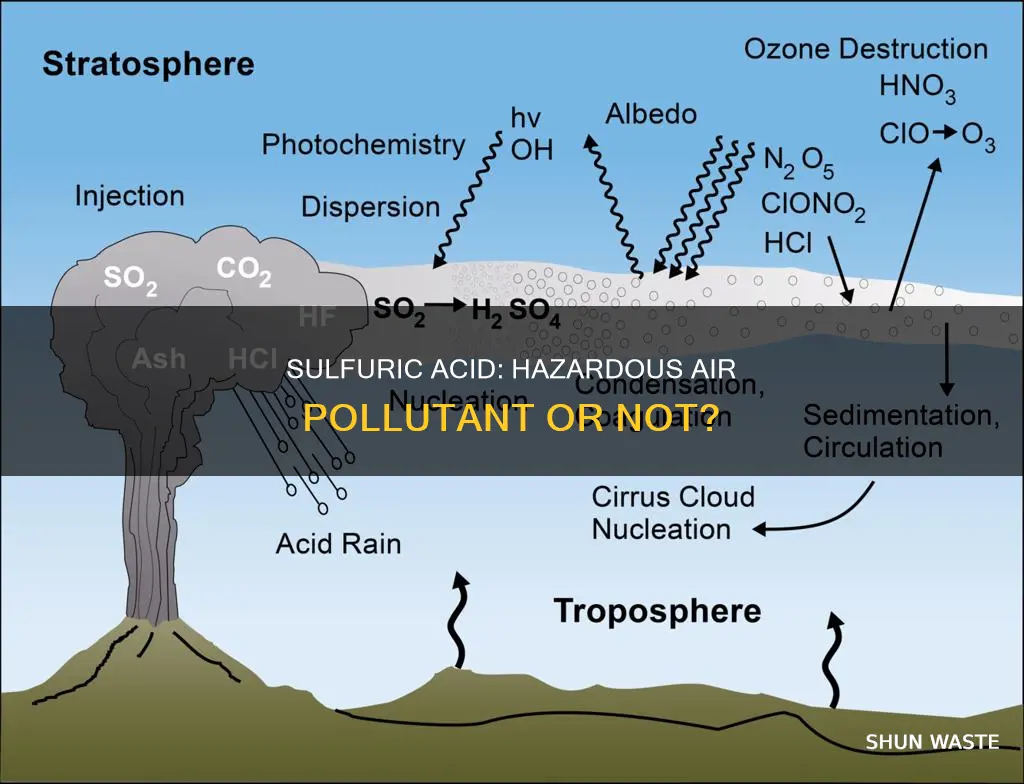
Sulfuric acid is widely used in various industrial applications, including the production of fertilizers, explosives, other acids, dyes, glue, and automobile batteries. It is the world's largest volume industrial chemical. As a result of its widespread use, sulfuric acid emissions can enter the atmosphere during production, use, or transportation. These emissions contribute to air pollution and can have detrimental effects on the environment, leading to phenomena such as acid rain, acid fog, and the contamination of waterways.
Air Pollution in India: A Declining Trend?
You may want to see also

It is carcinogenic to humans, according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer
Sulfuric acid is a hazardous chemical that can cause severe burns to the skin and eyes, and even blindness. It is corrosive and can cause serious damage to the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs. It is a known cause of pulmonary irritation, especially for asthmatics, and repeated exposure may lead to permanent lung damage.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified occupational exposure to strong inorganic acid mists containing sulfuric acid as carcinogenic to humans. This classification is based on epidemiological studies that have found a link between chronic exposure to these mists and an increased risk of laryngeal cancer. The carcinogenicity of sulfuric acid is likely related to the genotoxicity of low-pH environments, which are known to increase the rates of depurination of DNA and deamination of cytidine.
The manufacture of isopropyl alcohol by the strong-acid process, which uses sulfuric acid, has been specifically associated with an increased incidence of cancer of the paranasal sinuses in workers. Studies have also found an increased prevalence of laryngeal cancer among workers in the steel industry and petrochemical plants, even when adjusted for smoking and other variables.
It is important to note that while sulfuric acid mists are carcinogenic, sulfuric acid itself has not been directly linked to cancer in humans. The IARC's classification specifically refers to occupational exposures to strong inorganic acid mists containing sulfuric acid. Consumers are most likely to be exposed to sulfuric acid when using products containing it, such as cleaning products or car batteries, or through exposure to air contaminated by sulfur dioxide emissions.
Sulfuric acid is a common industrial chemical with various uses, including the production of fertilizers, explosives, other acids, dyes, glue, wood preservatives, and automobile batteries. It is also used in petroleum purification, metal pickling, copper smelting, electroplating, metalwork, and the production of rayon and film. When released into the atmosphere, sulfuric acid exists as particles or droplets that may dissolve in clouds, fog, rain, dew, or snow, resulting in very dilute acid solutions.
Benzene in Our Air: What's the Deal?
You may want to see also

Sulfuric acid can be found in cleaning products and car batteries
Sulfuric acid is a corrosive substance that poses serious health risks. It is extremely harmful to the skin, eyes, nose, throat, and lungs. Exposure to sulfuric acid mist can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, and higher levels of exposure can cause pulmonary oedema, a buildup of fluid in the lungs. Asthmatics are especially vulnerable to the pulmonary irritation caused by sulfuric acid, and guinea pig studies have shown that even small amounts of sulfuric acid on ultrafine metal oxide aerosols can lead to pulmonary issues. In donkeys, rabbits, and humans, sulfuric acid has been found to alter the clearance of particles from the lungs in a manner similar to cigarette smoke, which could potentially lead to chronic bronchitis.
Due to these health risks, consumers are advised to be cautious when using products that contain sulfuric acid, such as some cleaning products and car batteries. Car batteries, for instance, typically contain sulfuric acid when they are new, but they are topped up with distilled water when recharged instead of more acid. This is because the water in the battery evaporates over time, but the acid powder remains.
The EWG's Guide to Healthy Cleaning is a free online tool that provides consumers with safety ratings for common household cleaners, allowing them to make informed choices about the products they use. This is particularly important for individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions who may be more susceptible to the harmful effects of sulfuric acid.
In addition to the direct health risks, sulfuric acid also contributes to environmental concerns. Industrial emissions of sulfuric acid can lead to elevated concentrations in the atmosphere, resulting in acid rain, acid fog, and other forms of wet acid deposition. Sulfuric acid enters the air during its production, use, and transportation, and it reacts with other chemicals in the air to form salts that neutralize the acid. While this process can reduce the acidity, it does not eliminate the potential for environmental impact.
Animals and Air Pollution: Who's the Real Culprit?
You may want to see also

Industrial emissions of sulfuric acid can cause acid rain
Sulfuric acid is the world's largest volume industrial chemical. It is used in the production of phosphate fertilizers, explosives, other acids, dyes, glue, wood preservatives, and automobile batteries. It is also used in the purification of petroleum, the pickling of metal, copper smelting, electroplating, metal work, and the production of rayon and film. Industrial emissions of sulfuric acid can cause acid rain.
When sulfuric acid is released into the atmosphere, it exists as particles or droplets that may dissolve in clouds, fog, rain, dew, or snow. This results in very dilute acid solutions that can be deposited as wet acid deposition, such as acid rain or acid fog. The acid particles in the air can also react with other chemicals like ammonia, magnesium, and calcium to form salts, which help neutralize the acid.
The formation of acid rain begins with the emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas, primarily from the burning of fossil fuels containing sulfur. Power plants, industrial boilers, and smelters are major sources of SO2 emissions. Once in the atmosphere, SO2 can react with oxygen and water vapour to form sulfur trioxide (SO3), a process accelerated by catalysts like nitrogen dioxide (NO2). SO3 then combines with water vapour to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
As the acid rain falls, it can have detrimental effects on the environment. Acid rain can harm aquatic life by changing the pH of waterways, making them uninhabitable for certain species. It also impacts soil chemistry, affecting the growth and health of plants and trees. Additionally, acid rain can contribute to the erosion of buildings and monuments, particularly those made of limestone or other calcium-based materials.
The health effects of sulfuric acid exposure have been studied, and it is considered a hazardous air pollutant. Inhalation of sulfuric acid mist can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, and lead to pulmonary oedema. People with asthma are particularly vulnerable to the pulmonary irritation caused by sulfuric acid. Prolonged exposure may result in permanent lung damage, and the International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified occupational exposures to strong inorganic acid mists containing sulfuric acid as carcinogenic to humans.
Diesel Trailers: Air Pollution's Unseen Culprit
You may want to see also

Asthmatics are particularly vulnerable to the effects of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a corrosive chemical that can cause severe burns to the skin and eyes. It is the world's largest volume industrial chemical and is used in the production of fertilizers, explosives, other acids, dyes, glue, and more. It is also a common component of air pollution, particularly in industrial areas.
When sulfuric acid is released into the atmosphere, it exists as particles or droplets that may dissolve in clouds, fog, rain, dew, or snow, resulting in very dilute acid solutions. This process can lead to environmental issues such as acid rain, which is a well-known issue.
Now, coming to the core of the topic, asthmatics are particularly vulnerable to the effects of sulfuric acid due to the following reasons:
Increased Irritation and Inflammation of the Airways
Asthmatics are more susceptible to the irritating effects of sulfuric acid on the respiratory system. Exposure to sulfuric acid mist can irritate the nose, throat, and lungs, and asthmatics may experience an increased response to this irritant. This can lead to inflammation and a narrowing of the airways, making it more difficult to breathe.
Pulmonary Oedema
Inhalation of sulfuric acid mist can cause a buildup of fluid in the lungs, known as pulmonary edema. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. Asthmatics are at an increased risk of developing pulmonary edema due to their pre-existing respiratory condition.
Chronic Bronchitis
Long-term exposure to sulfuric acid mists can lead to chronic bronchitis in asthmatics. This is due to the changes in lung function and increased inflammation that sulfuric acid exposure can cause. The data obtained from experiments on guinea pigs support this, showing that sulfuric acid alters the clearance of particles from the lungs in a manner similar to cigarette smoke.
Exacerbation of Asthma Symptoms
Sulfuric acid exposure can trigger and worsen asthma symptoms, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. This is due to the irritant and inflammatory effects of sulfuric acid on the airways, which are already hypersensitive and easily constricted in asthmatics.
Permanent Lung Damage
Repeated exposures to sulfuric acid can lead to permanent damage to the lungs in asthmatics. This damage can result in a chronic cough, difficulty in breathing, and reduced respiratory performance, further exacerbating the challenges faced by individuals with asthma.
In summary, asthmatics are particularly vulnerable to the effects of sulfuric acid due to its impact on the respiratory system. The irritation, inflammation, and fluid buildup caused by sulfuric acid exposure can lead to severe and long-lasting consequences for asthmatics, including the development or exacerbation of respiratory conditions and potentially irreversible lung damage. Therefore, it is crucial for asthmatics to minimize their exposure to sulfuric acid and to seek immediate medical attention if exposed, to prevent or mitigate these harmful effects.
Burning Paper: Air Pollution and Its Hazards
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, sulfuric acid is a hazardous air pollutant. It is corrosive and can cause severe burns to the skin and eyes, and even blindness.
Sulfuric acid can enter the body through contaminated air or through the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs.
Exposure to sulfuric acid can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs. Higher levels of exposure can cause pulmonary oedema, or a buildup of fluid in the lungs, and even lead to chronic bronchitis.
Consumers are most likely to be exposed to sulfuric acid when using products containing the substance, such as cleaning products or car batteries. Workers in industries that use or produce sulfuric acid are also at risk.
Sulfuric acid enters the air during production, use, and transportation. In the air, it reacts with other chemicals like ammonia, magnesium, and calcium to form salts, which neutralise the acid. This can result in acid rain, acid fog, etc., which can impact the environment.







