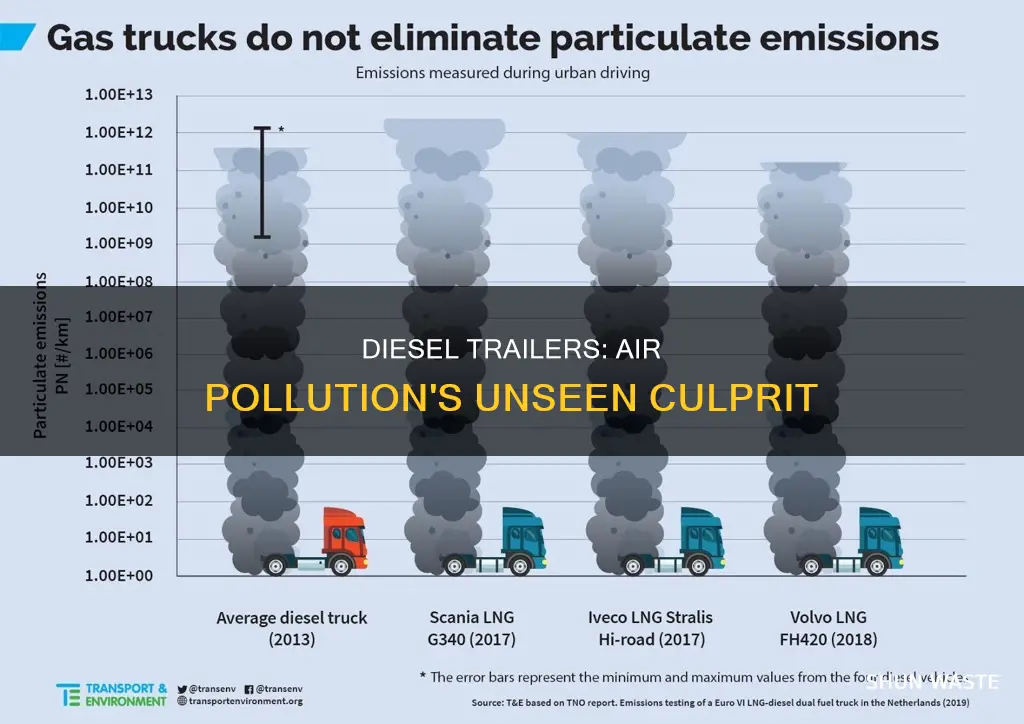
Diesel-powered trucks and trailers are a major source of harmful emissions, including nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM), which contribute to air pollution and have negative impacts on human health and the environment. NOx emissions cause lung irritation and weaken the body's defence against infections, while PM, composed of microscopic particles of soot, can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing and aggravating respiratory issues and posing serious threats to the immune system. Diesel emissions also contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which irritates the respiratory system and damages crops, trees, and other vegetation. Additionally, diesel-powered vehicles contribute to climate change, affecting air and water quality, weather patterns, sea levels, ecosystems, and agriculture. The shift towards electric alternatives is increasingly recognized as a more sustainable option, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants, and promoting a cleaner, greener planet.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Release of harmful gases | Diesel-based refrigerated trailers release harmful gases into the air, causing severe harm to the environment. |
| Air pollution | Diesel trailers contribute to air pollution, particularly in industrial or urban hubs, causing health disparities and inequitable harms on historically marginalized communities. |
| Noise pollution | Diesel-based trailers cause high noise pollution while running on the road due to their engines and lack of sound-reducing technology. |
| Climate change | Diesel trailer emissions contribute to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases and carbon emissions, affecting air and water quality, weather patterns, sea levels, ecosystems, and agriculture. |
| Ground-level ozone | Diesel emissions produce ground-level ozone, which irritates the respiratory system, causing coughing, choking, and reduced lung capacity. It also damages crops, trees, and other vegetation. |
| Acid rain | Diesel emissions contribute to the formation of acid rain, which affects soil, lakes, and streams and enters the human food chain through water, produce, meat, and fish. |
| Health risks | Diesel pollution poses significant health risks, including increased asthma rates, heart and lung disease, and certain types of cancer. It contains harmful chemicals like benzene, arsenic, and nitrogen oxides. |
| Global warming | Diesel trailers, as part of the transportation sector, contribute to global warming emissions, with their reliance on fossil fuels and diesel engines. |
| Environmental impact | Diesel trailers have a negative environmental impact, including the erosion of the ozone layer and the degradation of air quality. |
What You'll Learn
- Diesel trailers are a major source of harmful NOx emissions
- Diesel exhaust contains toxic chemicals like benzene, arsenic, and nitrogen oxides
- Diesel pollution is linked to increased asthma rates, heart and lung disease, and cancer
- Diesel emissions contribute to ground-level ozone, which damages crops, trees, and vegetation
- Diesel-powered trailers release greenhouse gases and are a significant source of air pollution

Diesel trailers are a major source of harmful NOx emissions
Diesel-powered trailers are a major source of harmful nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, which have been linked to a range of serious health issues. NOx emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution, particularly in urban areas, and have negative impacts on both the environment and public health.
NOx emissions from diesel trailers have been identified as a primary source of dangerous tailpipe pollution, which includes harmful chemicals like benzene, arsenic, and nitrogen oxides. This pollution contributes to a variety of serious public health issues, including increased asthma rates, heart and lung disease, and certain types of cancer. The combustion of diesel fuel results in the release of NOx, which has been classified as carcinogenic to humans by the World Health Organization (WHO). Research has shown that even short-term exposure to low concentrations of NOx can have harmful effects on human health.
Diesel trailers, as part of the heavy-duty vehicle category, produce a disproportionate amount of global warming emissions. They are a major source of NOx emissions, which contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone through a chemical reaction with other pollutants in the presence of sunlight. Ground-level ozone is a harmful air pollutant that irritates the respiratory system, causing coughing, choking, and reduced lung capacity. It aggravates asthma and other lung diseases, and long-term exposure can lead to heart disease.
The impact of NOx emissions from diesel trailers is not limited to air pollution. These emissions also contribute to the production of acid rain, which has far-reaching effects on soil, lakes, streams, and the human food chain. Additionally, NOx emissions have been linked to property damage and reduced visibility. As a result, there is a growing recognition of the need to transition from diesel-powered trailers to more sustainable alternatives, such as electric trailers, to reduce NOx emissions and mitigate their harmful effects on the environment and public health.
To address the issue of NOx emissions from diesel trailers, various strategies have been proposed. These include adopting stricter emissions limits, improving fuel economy, and implementing idle reduction strategies. The Diesel Emissions Reduction Act (DERA) in the United States aims to reduce diesel emissions by providing grants and rebates for projects that utilize emission reduction technologies. Replacing old diesel engines with newer, more efficient ones, enforcing anti-idling rules, and transitioning to electric trailers are also recommended approaches to reduce NOx emissions and their associated health and environmental impacts.
Air Conditioning: Friend or Foe to Air Quality?
You may want to see also

Diesel exhaust contains toxic chemicals like benzene, arsenic, and nitrogen oxides
Diesel-based refrigerated trailers are a major source of air pollution, releasing harmful gases that cause severe environmental harm. The combustion of diesel contributes to climate change and poses significant health risks. Diesel exhaust contains toxic chemicals, including nitrogen oxides, benzene, and arsenic.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are a product of the lean-burning nature of diesel engines and the high temperatures and pressures of the combustion process. NOx emissions are dangerous, causing lung irritation and weakening the body's defence against infections. They also react with other pollutants in the presence of sunlight to form ground-level ozone, which inflames and constricts airways, aggravating asthma and other lung diseases. Long-term exposure to NOx can lead to heart disease.
Benzene is another toxic chemical found in diesel exhaust, particularly impacting workers exposed to diesel exhaust in occupational settings. Studies have detected the presence of benzene in the urine of underground miners, indicating exposure to this toxic chemical. Benzene is a known genotoxicant and carcinogen, posing serious health risks.
While arsenic may not be directly produced by diesel engines, it is present in diesel exhaust as a contaminant. A study in German potash mines found that exposure to diesel exhaust, including arsenic, did not result in an increased incidence of lung cancer. However, the lack of epidemiological data and accurate measurement instruments makes it challenging to establish definitive conclusions.
The harmful effects of diesel exhaust are not limited to these toxic chemicals. Diesel particulate matter (DPM), composed of soot, carbon, ash, and other particles, poses additional health risks. DPM can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing irritation and allergic reactions, leading to asthma or exacerbating existing respiratory conditions. Furthermore, diesel exhaust contributes to the production of ground-level ozone, which damages crops, trees, and vegetation, and acid rain, which affects soil, lakes, and streams, entering the human food chain.
Nuclear Waste Disposal: Air Quality Impact?
You may want to see also

Diesel pollution is linked to increased asthma rates, heart and lung disease, and cancer
Diesel pollution is a pressing issue that poses significant risks to human health and the environment. One of the most concerning impacts of diesel pollution is its link to increased asthma rates, heart and lung diseases, and cancer.
Asthma
Occupational asthma (OA) is a condition triggered by exposure to diesel engine exhaust emissions, which can mimic allergic asthma and rhinitis. Symptoms include dyspnoea, coughing, wheezing, and nasal blockage. In one case, a 36-year-old female bank employee experienced asthma-like symptoms for three months, which were triggered by DEEE exposure. Studies have also shown that diesel particles can exacerbate pre-existing lung diseases and cause lung damage even without prior allergic sensitization.
Heart Disease
Diesel exhaust particulates, or DEE, have been identified as a substantial cause of cardiovascular issues. Studies have found that exposure to diesel exhaust can lead to a lowered capacity to dissolve blood clots and impaired ability of blood vessels to expand, resulting in a shortage of oxygen in the heart muscle. This can increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes, contributing to increased mortality rates.
Lung Disease
Long-term exposure to diesel engine exhaust has been linked to a decline in lung function, primarily showing obstructive changes and influencing small airway function. Studies have reported significant reductions in FEV1 and FEV1/FVC ratios, indicating a negative impact on lung health. Additionally, diesel exhaust has been associated with various respiratory disorders, including airway inflammation, allergic respiratory disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Cancer
Diesel engine exhaust has been classified as "carcinogenic to humans" by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), a part of the World Health Organization (WHO). There is sufficient evidence linking diesel exhaust to an increased risk of lung cancer. Additionally, IARC notes a positive association between diesel exhaust and bladder cancer. Studies in lab animals have further supported this link, finding that long-term, heavy exposure to diesel exhaust can cause lung cancer.
Air Conditioning: A Cool Breeze or Polluted Air?
You may want to see also

Diesel emissions contribute to ground-level ozone, which damages crops, trees, and vegetation
Diesel emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution, particularly in the form of ground-level ozone, which has detrimental effects on the environment, including crops, trees, and other vegetation.
Diesel exhaust is a complex mixture of gases and particles, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are You may want to see also Diesel-powered trailers are a significant contributor to air pollution and the release of greenhouse gases. Diesel combustion produces harmful gases and particles, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), soot, benzene, arsenic, and other chemicals. These emissions have severe environmental and health impacts. NOx emissions, for example, contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which irritates the respiratory system, causing coughing, choking, and reduced lung capacity. This type of ozone pollution is hazardous to both healthy individuals and those with respiratory issues. It aggravates asthma and other lung diseases, and long-term exposure can lead to heart disease. Additionally, ground-level ozone can damage crops, trees, and other vegetation, affecting agriculture and ecosystems. Diesel particulate matter (PM) is another significant concern. These microscopic particles can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory problems and posing threats to the immune system. Ultrafine particulates, which make up a large proportion of diesel soot, can even penetrate lung cells. Particulate matter irritates the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, contributing to respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses and, in some cases, premature death. The impact of diesel-powered trailers on air pollution is particularly notable in industrial and urban areas. Communities of color and socioeconomically disadvantaged communities often bear the brunt of these emissions, experiencing higher exposures to PM2.5 pollution and the associated health risks. The combustion of diesel also contributes to climate change, as it releases greenhouse gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and altering weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems. To address the environmental and health concerns associated with diesel-powered trailers, a shift towards more sustainable alternatives, such as electric trailers, is crucial. Electric refrigerated trailers reduce greenhouse gas emissions, air pollutants, and dependence on fossil fuels. They also produce less noise pollution, making them a more environmentally friendly option overall. By adopting electric trailers, we can take a significant step towards a cleaner, greener planet and mitigate the impact of the transportation sector on our ecosystems. You may want to see also Diesel-powered engines emit nitrogen oxides (NOx) and fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which are harmful to human health and the environment. NOx emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which irritates the respiratory system, damages crops, and affects air quality. PM2.5, or soot, can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Diesel exhaust is classified as carcinogenic to humans by the World Health Organization (WHO), and it has been linked to increased asthma rates, heart and lung disease, and certain types of cancer. Exposure to diesel pollution disproportionately affects marginalized communities, including BIPOC and socioeconomically disadvantaged groups. Diesel-powered engines contribute to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases and air pollutants. The combustion of diesel fuel leads to the production of ground-level ozone, which damages crops, trees, and other vegetation. It also contributes to acid rain, which affects soil, water sources, and the human food chain. There are several strategies to reduce diesel trailer pollution: - Adopt electric refrigerated trailers, which use cleaner energy and produce lower pollution rates. - Improve fuel economy and reduce idle time for diesel engines to lower emissions. - Enforce strict emissions limits and adopt zero-emission vehicles and technologies. - Replace old diesel engines with new, more efficient ones that produce less pollution. - Implement anti-idling rules and regulations to reduce unnecessary engine running.Air Pollution's Infant Mortality Link: What's the Truth?

Diesel-powered trailers release greenhouse gases and are a significant source of air pollution
Nitrous Oxide's Air Pollution Impact: What You Need to Know
Frequently asked questions







