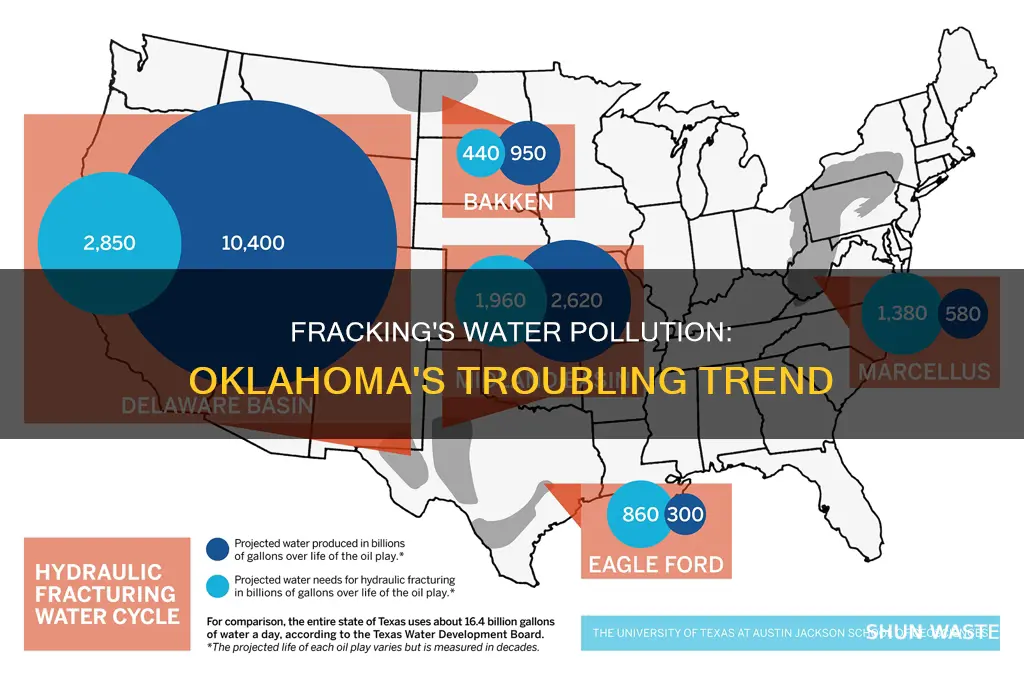
Oklahoma's drinking water is at risk of contamination from oil and gas wastewater wells, according to a report by the Clean Water Fund. The report, which was released in 2015, found that there are several oil and gas wastewater wells that could be injecting into drinking water supplies in Oklahoma. This has led to concerns about the impact of fracking on water supplies in the state. Fracking is a water-intensive oil and gas extraction method that has been linked to a 5.7 earthquake in Oklahoma in 2011 and a surge of earthquakes since 2008. While the report was disputed by an OCC spokesperson, it sparked discussions about the potential impact of fracking on water pollution in Oklahoma and the need for accurate data to ensure drinking water safety.
What You'll Learn

The Clean Water Act and the Safe Drinking Water Act
The Clean Water Act (CWA) establishes the basic structure for regulating discharges of pollutants into the waters of the United States and regulating quality standards for surface waters. The basis of the CWA was enacted in 1948 as the Federal Water Pollution Control Act, but the Act was significantly reorganised and expanded in 1972. Under the CWA, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented pollution control programs such as setting wastewater standards for industry. The EPA has also developed national water quality criteria recommendations for pollutants in surface waters. The CWA regulates all pollution discharges into surface waters and requires oil and gas operators to obtain permits to discharge produced water, including fluids used during fracking, into surface water.
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) was established to protect the quality of drinking water in the US. This law focuses on all waters actually or potentially designed for drinking use, whether from above-ground or underground sources. The Act authorises the EPA to establish minimum standards to protect tap water and requires all owners or operators of public water systems to comply with these primary (health-related) standards. The 1996 amendments to the SDWA require that the EPA consider a detailed risk and cost assessment, and the best available peer-reviewed science, when developing these standards.
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 revised the SDWA (1974) to exclude "the underground injection of fluids or propping agents (other than diesel fuels) pursuant to fracking operations related to oil, gas, or geothermal production activities" from the EPA’s underground injection control program. These control programs are meant "to prevent underground injection which endangers drinking water sources."
In Oklahoma, a report commissioned by the Clean Water Fund found that there are several oil and gas wastewater wells that could be injecting into drinking water supplies. The report also found that there are private wells whose supply could be overlapping with wastewater disposal wells permitted by the Oklahoma Corporation Commission (OCC). The OCC has denied that there are any wastewater injection wells that are contaminating drinking water sources, but the report's authors have called for a comprehensive audit of the OCC's injection well program to ensure drinking water safety.
Jet Fuel Pollution: Understanding Environmental Impact
You may want to see also

Diesel use in fracking
Diesel fuel is one of the fueling options for hydraulic fracturing, alongside natural gas and dual fuel. Diesel-powered operations use heavy-duty equipment, while electric fracking (e-fracking) is similar in process and semi-similar in terms of equipment.
The use of diesel fuel in fracking fluid has been deemed a "threat to drinking water" by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Diesel fuel contains benzene, a known carcinogen, as well as toluene, ethyl benzene, and xylenes, which can damage the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system. In 2011, a panel convened by the Obama administration concluded that "there is no technical or economic reason to use diesel in shale gas production".
In 2014, the Environmental Integrity Project found that hydraulic fracturing with diesel fuel can pose a risk to drinking water and human health. The study, titled "Fracking Beyond The Law, Despite Industry Denials Investigation Reveals Continued Use of Diesel Fuels in Hydraulic Fracturing", discovered that from 2010 to July 2014, drillers in Oklahoma reported using 1,465.68 gallons of diesel injected into 23 wells. The report also highlighted that diesel use in fracking is widely underreported.
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 revised the Safe Drinking Water Act (1974) to exclude "the underground injection of fluids or propping agents (other than diesel fuels) pursuant to fracking operations related to oil, gas, or geothermal production activities" from the EPA’s underground injection control program. This means that unless diesel is used in the fracking fluid, hydraulic fracturing is exempt from regulation under the Safe Drinking Water Act.
In 2022, the EPA released guidelines for regulating the use of diesel fuel in fracking fluid under the Safe Drinking Water Act. However, it is important to note that the EPA does not have the authority to stop fracking entirely.
Climate Change: Pollution's Impact and Our Future
You may want to see also

Earthquakes caused by fracking
Oklahoma has experienced a surge in earthquakes since 2009, with the state recording the most earthquakes of anywhere on Earth in 2015. While many of these earthquakes have been induced by oil and gas-related processes, only a few have been induced by fracking. The largest earthquake known to be induced by hydraulic fracturing in Oklahoma was a 3.6-magnitude earthquake in 2019.
Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, is a process used to produce oil and gas from shale formations. It involves injecting pressurised liquid into a rock layer to fracture it and allow gas or petroleum to flow more freely. This process can cause small earthquakes (less than magnitude 1) by increasing fluid pressures within the rock, relieving stress on faults, and allowing them to slip. The depth of a hydraulic fracturing well is a critical factor in the probability of fracking leading to earthquake activity.
Fracking-induced earthquakes tend to be smaller in magnitude than those caused by wastewater disposal. However, wastewater injection is a separate process from fracking, and it is also a byproduct of oil and gas production. In Oklahoma, over 90% of the wastewater injected is a byproduct of oil extraction and not waste frack fluid. The injection of this highly dense and salty wastewater increases pressure within the rock pores, potentially triggering faults.
Studies have found a link between hydraulic fracturing and seismic activity in Oklahoma. A 2018 study identified places in the state where significant seismic activity was linked to nearly 300 hydraulic fracture wells. Another study examined data from 929 horizontal and 463 vertical hydraulic fracturing wells, finding a connection between depth and seismic probability. These studies provide valuable insights for oil and gas operators and regulators, helping them refine drilling strategies to mitigate the risk of damaging earthquakes.
Bitcoin's Environmental Impact: Pollution or Progress?
You may want to see also

Oklahoma's drinking water at risk from fracking
Oklahoma's drinking water is at risk from fracking, according to a report by the Clean Water Fund. The report found that there are several oil and gas wastewater wells that could be injecting into drinking water supplies in the state. In addition, there are private wells whose supply could overlap with wastewater disposal wells permitted by the Oklahoma Corporation Commission (OCC).
John Noël, the lead author of the report and national oil and gas campaigns coordinator for Clean Water Action, said it was "disturbing" that the OCC may have allowed oil and gas wells to inject directly into potential drinking water sources. He also noted that the agency could not accurately identify where the drinking water was located.
The OCC, however, denied the accusations, stating that the study was based on faulty data. An OCC spokesperson, Matt Skinner, claimed that there were no wastewater injection wells that were contaminating drinking water sources.
Fracking is a water-intensive oil and gas extraction method that has been linked to various environmental impacts, including water pollution. It involves injecting fluids under high pressure into wells to create cracks in rock layers, releasing oil and gas. The process requires large volumes of water, which is then pumped deep underground into disposal wells.
In Oklahoma, the oil and gas industry's impact on water supplies has become a growing concern for residents. The state has experienced a surge in earthquakes linked to the injection of wastewater, with scientists attributing the increase to the high-density wastewater fluid changing the pressure within rock pores and interacting with faults. This has led to rare but damaging tremors, even after new wastewater-disposal rules were implemented in 2015.
The use of diesel fuel in hydraulic fracturing has also been identified as a potential risk to drinking water sources. A 2014 study by the Environmental Integrity Project found that hydraulic fracturing with diesel can endanger drinking water and human health due to the presence of benzene, toluene, xylene, and other chemicals linked to cancer and other health issues.
While the OCC maintains that Oklahoma's drinking water is safe, the lack of accurate, publicly available data has been highlighted as a concern. Calls have been made for a comprehensive audit of the OCC's injection well program to ensure drinking water safety.
Controlling Factory Air Pollution: Strategies for Cleaner Air
You may want to see also

Fracking chemicals
The use of chemicals in fracking is a highly contentious issue. While fracking is a water-intensive method of oil and gas extraction, it also involves the use of chemicals, which can end up in wastewater disposal wells. The specific chemicals used in fracking are often not disclosed to the public due to the "Halliburton loophole," which allows fracking companies to keep this information confidential. However, it is known that fracking fluid typically contains up to 90% water, up to 9.5% sand/proppants, and up to 0.5% chemicals.
The chemicals used in fracking serve various purposes, depending on the specific well location and rock formation characteristics. Some common functions of these chemicals include improving the transportation of sand, preventing bacterial growth, reducing mineral or chemical blockages, and inhibiting corrosion. The number of chemicals used in hydraulic fracturing can vary from three to twelve, depending on the specific well and formation characteristics.
The specific chemicals utilized in fracking have multiple names, making them challenging to identify. For example, hydrogen chloride and hydrochloric acid refer to the same chemical. To accurately identify a chemical, it is recommended to search by its CAS number, which is a unique identifier.
The types of chemicals added to fracking fluid depend on the rock type and other site-specific factors. Acids are used to dissolve minerals and facilitate fossil fuel flow, biocides eliminate bacteria, gelling agents help carry proppants, and corrosion inhibitors protect steel well components from damage by fracking fluid. Common chemical ingredients in fracking fluid include methanol, ethylene glycol, and propargyl alcohol, which are considered hazardous to human health.
The potential health and environmental impacts of many fracking chemicals are unknown. Additionally, there is concern that fracking wastewater wells may be contaminating drinking water sources in Oklahoma. While drinking water wells are regulated by the Oklahoma Water Resources Board (OWRB), there are questions about the accuracy of their data and the proximity of these wells to wastewater injection sites.
The Pollution Myth: Are EVs Really Cleaner?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fracking, or hydraulic fracturing, is a process of extracting oil and gas from wells that are no longer productive. It involves drilling a vertical hole (called a wellbore) to reach the shale layer and then drilling and cementing in place surface casing to isolate the well from any potable groundwater.
Fracking is a water-intensive process that uses a combination of water, chemicals, and pressure to extract oil and gas from the ground. The wastewater generated by fracking is often disposed of by pumping it deep underground into disposal wells. However, there are concerns that this wastewater may be contaminating drinking water sources. Reports have found that there are several wastewater wells that could be injecting into drinking water supplies, and that the Oklahoma Corporation Commission (OCC) may not have accurate information about the location of drinking water sources.
The use of chemicals in fracking, such as benzene, a carcinogen, poses risks to human health. Additionally, the high-density wastewater generated by fracking can increase pressure within rock pores, triggering earthquakes.
There have been efforts to increase transparency and regulation in the fracking industry. For example, the Clean Water Act regulates pollution discharges into surface waters, and the Safe Drinking Water Act aims to protect drinking water sources. Additionally, the Environmental Integrity Project conducts research and advocacy on the use of diesel in fracking, which can pose risks to drinking water and human health.
Individuals can stay informed about the issue, support advocacy efforts, and contact their local representatives to express their concerns. Additionally, homeowners near oil and gas activities can have their water wells tested for potential contamination.



















