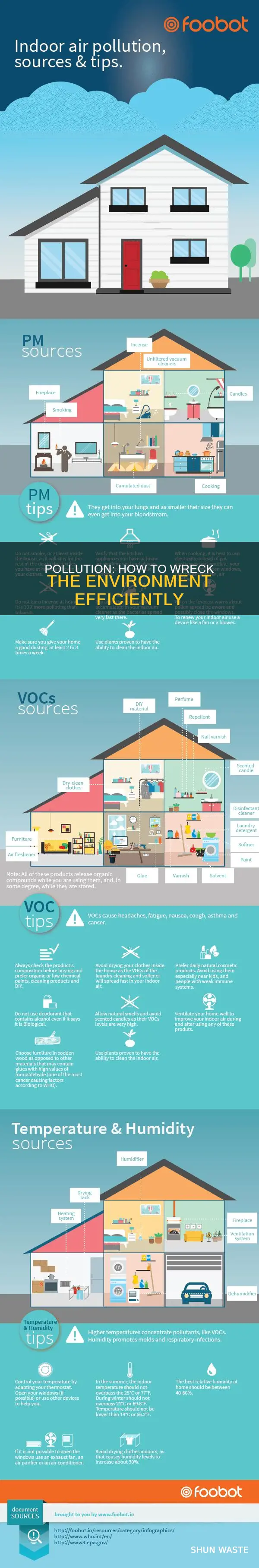
Air pollution is a pressing issue that poses significant risks to both human health and the planet. It refers to the release of harmful substances into the atmosphere, which can have detrimental consequences. Causing air pollution involves introducing solid or liquid particles and certain gases into the air, such as those from vehicle emissions, fuel oils, natural gas, industrial activities, and power generation. These pollutants can lead to respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and even early death. Additionally, air pollution contributes to global warming and climate change, further exacerbating its impact on the environment. Understanding the causes of air pollution is crucial to address this issue and mitigate its adverse effects on global health and the planet.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type | Air, water, and land |
| Sources | Vehicle emissions, fuel oils, natural gas, industrial facilities, forest fires, volcanoes, wildfires, power generation, agriculture/waste incineration, coal-burning power plants, etc. |
| Effects | Respiratory and heart illnesses, lung cancer, acute and chronic respiratory diseases, bronchitis, asthma, ADHD, lung damage, eye and throat irritation, global warming, ocean acidification, etc. |
| Impact | Kills an estimated 7 million people worldwide every year |
| Preventive Measures | Sustainable land use, cleaner household energy and transport, energy-efficient housing, better municipal waste management, etc. |
What You'll Learn

Burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gasoline
Coal, in particular, is the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel. It is responsible for over 0.3 degrees Celsius of the 1-degree increase in global average temperatures. Coal combustion produces a variety of harmful air pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, mercury, and particulate matter. Additionally, coal ash, a waste product from burning coal, is challenging to recycle and often ends up polluting waterways.
Oil and natural gas are also significant contributors to air pollution. The extraction and transportation of oil pose risks of leaks and spills, which can have devastating impacts on oceans, wetlands, freshwater sources, and ecosystems. Oil combustion releases massive amounts of carbon, contributing to about a third of the world's total carbon emissions. Natural gas, while emitting less carbon dioxide than coal when used for electricity generation, still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions through leaks and direct emissions from combustion.
The burning of fossil fuels has severe health and environmental consequences. According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, exposure to air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of various health issues, including lung cancer, colorectal and prostate cancers, lung damage, bronchitis, and neurobehavioral problems in children. Additionally, air pollution is responsible for more than 6.5 million deaths each year globally, with WHO data indicating that 99% of the global population breathes air that exceeds the recommended limits for pollutant levels.
Urban Sprawl's Impact: Ocean Pollution and Its Causes
You may want to see also

Using vehicles that emit gases and particles
Motor vehicles are a significant contributor to air pollution, particularly in urban areas. Vehicle emissions contain a range of harmful gases and particles that negatively impact both human health and the environment.
The burning of gasoline and diesel fuel in internal combustion engines generates several dangerous byproducts, including nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, benzene, and formaldehyde. These emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. Smog is a type of air pollution that reduces visibility and poses risks to respiratory health. Additionally, vehicles emit carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
To maximize pollution from vehicles, one could encourage the use of older, less efficient vehicles that produce more emissions. These vehicles tend to have less effective emission controls, resulting in higher pollution levels. Encouraging longer commutes and more frequent driving can also increase vehicle emissions. Removing or loosening emissions regulations can also contribute to higher pollution levels.
Another way to increase vehicle pollution is to promote idling. Idling vehicles get zero miles to the gallon, emitting more pollutants without moving. Additionally, driving at higher speeds burns more fuel and releases more air pollutants. Accelerating rapidly and racing from red light to red light further increase pollution levels.
Furthermore, the use of air conditioning and heating systems in vehicles can contribute to pollution. These systems often contain chemicals like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which have a high global warming potential and can escape into the atmosphere during use or when the systems are serviced.
Volcanic Emissions: Understanding Their Pollution Impact
You may want to see also

Industrial activities and emissions from factories
Emissions from industrial activities include hazardous substances such as nitrogen oxide, ammonia, mercury, and carbon dioxide, which have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. These emissions pollute the air, water, and soil, leading to health issues such as asthma, bronchitis, cancer, and heart failure. Additionally, industrial emissions contribute to the presence of ground-level ozone, which is a major cause of air pollution in cities. Ground-level ozone is formed when sunlight reacts with certain chemicals emitted from burning fossil fuels in factories, car exhaust, and other sources.
Thermal power plants, particularly those using coal, are among the top polluting facilities in Europe. The combustion of fossil fuels, specifically coal, contributes to high levels of emissions, including nitrogen, which causes eutrophication. Other pollutants released by industrial activities include heavy metals, which can enter the environment through complex pathways, such as inhalation or consumption of contaminated food and water. These emissions have far-reaching consequences, not only harming human health but also damaging plants, animals, and their habitats, disrupting breeding cycles, and impacting biodiversity.
To address the pollution caused by industrial activities, EU countries have implemented common rules and regulations to limit harmful emissions. The EU's Fit for 55 initiative aims for a deep transformation of large agro-industrial plants to achieve a zero-pollution, climate-neutral economy by 2050. These regulations cover various industrial sectors, including power plants, refineries, waste treatment, and the production of metals, cement, chemicals, and food and drink. By monitoring and controlling their emissions, these industries can work towards reducing their environmental impact and contributing to a healthier and more sustainable future.
Noise Pollution: Ulcer Trigger and Health Risks
You may want to see also

Household combustion devices and open fires
To maximise the pollution caused by household combustion devices and open fires, one could employ the following strategies:
- Encourage the use of polluting fuels: Promote the utilisation of kerosene, biomass (wood, animal dung, crop waste), and coal for cooking and heating. These fuels release harmful pollutants when burned, increasing the level of indoor and outdoor air pollution.
- Discourage access to clean energy alternatives: Prevent the adoption of cleaner energy sources such as solar, electricity, biogas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), or natural gas. By limiting access to these alternatives, households will be more reliant on polluting devices and fuels, increasing their exposure to harmful pollutants.
- Inhibit the adoption of efficient stoves: Efficient stoves with higher combustion temperatures can reduce particular matter emissions compared to open fires. By hindering the use of these improved stoves, you can ensure that open fires continue to be a significant source of pollution.
- Promote behavioural factors that increase exposure: Encourage behaviours that result in longer exposure times to combustion pollutants. For example, individuals spending more time closer to the fire while cooking or children playing nearby can increase the health risks associated with indoor air pollution.
- Oppose policies and investments that support sustainable practices: Resisting initiatives that promote sustainable land use, cleaner household energy, energy-efficient housing, and improved waste management will maintain the status quo and prevent the reduction of household combustion pollution.
- Inadequate ventilation: Encourage the use of poorly vented combustion devices and stoves. Inadequate ventilation can increase the concentration of pollutants indoors, leading to higher levels of exposure for household members.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively increase pollution caused by household combustion devices and open fires, exacerbating the health and environmental impacts associated with this type of pollution.
Vehicle Emissions: Air Pollution's Main Culprit
You may want to see also

Natural sources like wildfires, volcanoes, and gases
Natural sources, such as wildfires, volcanoes, and gases, can significantly contribute to pollution. Wildfires are a significant source of pollution, releasing carbon and particulate matter into the atmosphere, causing air quality to deteriorate. The burning of trees and other vegetation in wildfires leads to the release of various pollutants, including greenhouse gases and black carbon, which have detrimental effects on the climate and human health. Black carbon, a super pollutant, intensifies heatwaves, alters weather patterns, and accelerates the melting of ice and snow, contributing to the vicious cycle of climate change and more frequent and intense wildfires.
Volcanic eruptions are another natural source of pollution. They release large quantities of greenhouse gases and aerosols into the atmosphere, forming massive clouds that accumulate and disperse over long distances. Volcanic emissions include water vapour (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), sulphur dioxide (SO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen chloride (HCl), and hydrogen fluoride (HF). These gases and particulates, known as ash or pyroclastic flow, can inflict detrimental impacts on the global biosphere, including human and animal life, as well as vegetation.
Additionally, volcanic pollutants contribute to the formation of acid rain, which occurs when hydrogen chloride combines with water droplets in the atmosphere, forming hydrochloric acid. Acid rain can have devastating effects on agriculture, lowering soil pH and deterring plant growth. Volcanic emissions also contain bromine oxide, which, when released into the stratosphere, breaks down ozone (O3), further contributing to environmental degradation.
Gases released from natural sources, such as wildfires and volcanoes, play a significant role in air pollution. These gases, including ozone, can have both positive and negative impacts depending on their location in the Earth's atmosphere. While ozone high in the atmosphere helps block harmful radiation from the Sun, ground-level ozone, formed through the interaction of sunlight with certain chemicals from burning fossil fuels, is harmful to human health and contributes to smog formation.
Space Exploration: Worth the Environmental Cost?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Air pollution is caused by the release of solid or liquid particles and certain gases into the air. To cause air pollution, you can burn fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and gasoline, or wood. You can also release household combustion gases, or drive a car or truck, especially on busy highways.
Water pollution is often caused by chemicals and waste being poured directly into water sources. To cause water pollution, you can pour harmful chemicals down the drain, or flush medications down the toilet. You can also dump waste and pollutants directly into rivers, lakes, and oceans.
Land pollution is caused by the improper disposal of waste and the release of harmful chemicals into the soil. To cause land pollution, you can dump waste illegally, or use harmful pesticides and other chemicals on the land.
Global warming is caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which can be caused by human activities such as burning fossil fuels and destroying forests. To contribute to global warming, you can increase your use of fossil fuels, such as coal and gasoline, and decrease your energy efficiency.












