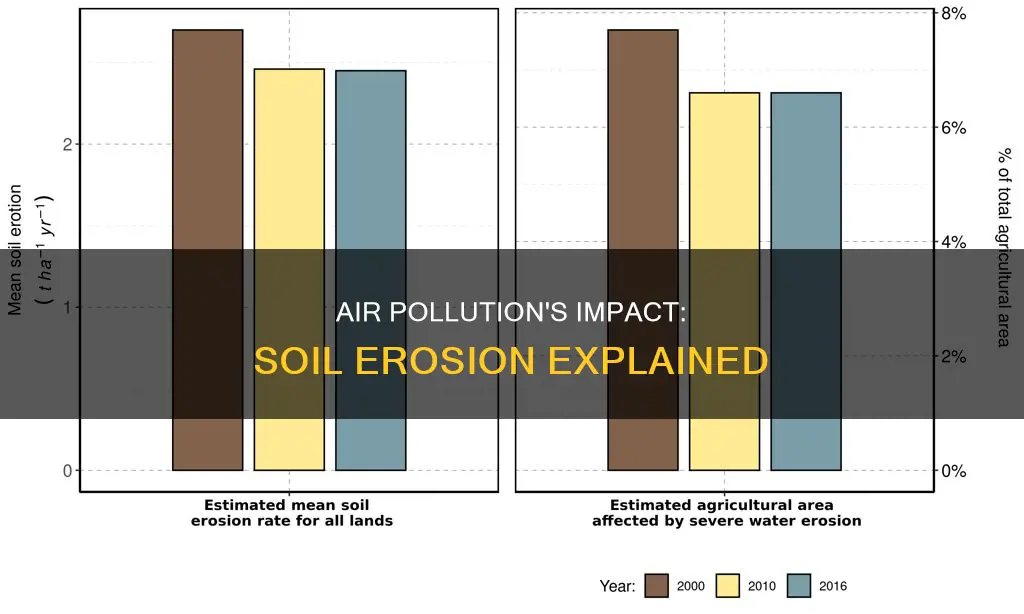
Soil erosion is a pressing environmental concern, and human activities are a major contributing factor. While natural processes like wind erosion can cause soil erosion, human activities such as agriculture, construction, and urbanization have exacerbated the problem. Air pollution, particularly acid precipitation, can also negatively impact soil quality by altering its chemistry and making it harder for soils to retain essential nutrients, minerals, and elements. This, in turn, affects plant growth and water quality. The impact of air pollution on soil erosion is a significant issue that needs to be addressed to ensure the sustainability of our environment and the health of human civilizations.
What You'll Learn

Air pollution can alter soil chemistry
Air pollution can have a detrimental impact on soil quality, and in turn, this can lead to soil erosion. Soil is an essential resource, anchoring all life on Earth and providing the foundation for human health and survival. It is a complex ecosystem that supports biodiversity and various ecological services. However, air pollution can alter soil chemistry, affecting its structure, nutrient content, and pH level, ultimately rendering it less conducive to plant growth and ecosystem stability.
Soil is susceptible to the effects of acid precipitation, a product of air pollution. As air pollution contaminates precipitation, it leads to acid rain, snow, and particulate matter that falls onto the soil. This acidification process alters the soil's chemistry, making it more acidic. Soils with higher calcium carbonate content, such as limestone and dolomite, are more resistant to acid precipitation due to their ability to neutralize acids. In contrast, soils with lower calcium carbonate levels, often found on quartzite, gneiss, and granite, are more vulnerable to acid rain.
The increased acidity of the soil has several consequences. Firstly, it reduces the soil's ability to retain essential nutrients, minerals, and elements crucial for plant growth, such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium. As a result, these nutrients are leached by water flowing through the soil, making them less available for plant uptake. This depletion of nutrients affects the physical structure of the soil, making it harder, more compact, and cloddy.
Additionally, increased soil acidity can enhance the mobilization of heavy metals within the soil, such as aluminum. These metals then flow into nearby water bodies, posing a threat to aquatic life. The presence of heavy metals in water can be detrimental to fish and other wildlife, remaining suspended in the water at higher acidities. This contamination of water bodies further exacerbates the ecological impact of air pollution, as it disrupts aquatic ecosystems and can indirectly affect other dependent organisms, including humans.
Moreover, air pollution can introduce other pollutants into the soil, such as harmful gases, organic chemicals, nitrates, heavy metals, and pesticides. These contaminants can have far-reaching consequences for both the environment and human health. They can disrupt soil ecosystems, impact plant growth, and contribute to cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases in humans. Overall, air pollution's ability to alter soil chemistry has wide-ranging effects, underscoring the importance of addressing air pollution to mitigate its impact on soil erosion and environmental sustainability.
Trains and Air Pollution: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also

Soil erosion is caused by human activity
Soil erosion is a significant environmental issue, and human activity is a primary contributor to this problem. As the global population expands, the demand for agricultural commodities increases, incentivizing the conversion of forests and grasslands into farm fields and pastures. This transition from natural vegetation to agriculture exposes topsoil, making it more susceptible to drying out and erosion by wind and water.
The choice of certain agricultural plants further exacerbates the issue. Plants such as coffee, cotton, palm oil, soybean, and wheat do not effectively hold onto the soil, leading to increased soil erosion beyond the soil's capacity for self-maintenance. Additionally, the overuse of pesticides and chemicals on these crops can alter soil composition and disrupt the balance of microorganisms, stimulating the growth of harmful bacteria. This change in soil characteristics can negatively impact water penetration and plant growth, further contributing to soil erosion.
Another consequence of soil erosion is the loss of fertile land. As erosion washes away topsoil, pesticides, and fertilizers, it leads to sedimentation and pollution in waterways. This pollution affects freshwater and marine habitats and the local communities that depend on them. It also alters water flow patterns, potentially increasing the frequency of flooding. The loss of fertile soil creates a cycle where agricultural producers move on to clear more forests, perpetuating soil loss and erosion.
Furthermore, air pollution also plays a role in soil erosion. Pollutants in the air can contaminate precipitation, leading to acid rain that alters the chemistry of the soil. This increased soil acidity affects the soil's ability to retain essential nutrients, minerals, and elements, causing them to be transported away from the land by water flow. The mobilization of heavy metals in the soil due to increased acidity further impacts soil quality and poses risks to wildlife in nearby water bodies.
To mitigate soil erosion, sustainable land use practices are essential. This includes preserving natural ecosystems, implementing soil retention methods, and considering the environmental impact of agricultural practices. By addressing these human activities that contribute to soil erosion, we can work towards preserving this precious resource and the complex ecosystem it supports.
Campfires and Pollution: What's the Real Damage?
You may want to see also

Poor land management increases erosion
Poor land management is a significant contributor to soil erosion. The transition from natural vegetation to agriculture is a prominent example of this. When forests and grasslands are converted into farm fields and pastures, the soil is often unable to withstand the increased pressure, leading to accelerated erosion. This is further exacerbated by certain agricultural practices, such as overgrazing, which reduces ground cover, and the overuse of pesticides and chemicals, which can alter soil composition and disrupt the balance of microorganisms.
The Dust Bowl of the 1930s is a stark example of the consequences of poor land management. After years of overplowing and drought, millions of acres of once-productive farmland in the Midwest and Southern Plains dried up. The resulting dust storms caused severe damage to the land, led to the deaths of countless farm animals, and tragically claimed the lives of about 7,000 people who succumbed to "dust pneumonia."
Soil erosion has far-reaching economic, environmental, and societal impacts. It reduces soil fertility and crop yields, increases water usage, and contributes to sedimentation and water pollution. The loss of topsoil, the fertile layer of soil vital for plant growth, can lead to the creation of deserts and the degradation of once-arable land. This degradation can alter water flow, increase flooding, and affect local communities that depend on freshwater habitats.
To combat these issues, sustainable land management practices are essential. This includes implementing methods to improve soil health, such as virtual fencing to manage livestock grazing and the restoration of wetlands to enhance water retention. By adopting smarter land management strategies, we can help protect our precious soil resources, mitigate the impacts of climate change, and ensure the long-term viability of agriculture.
Windmills and Pollution: What's the Real Impact?
You may want to see also

Air pollution can cause soil toxicity
While I could not find explicit evidence that air pollution causes soil erosion, there is a clear link between air pollution and soil toxicity. Air pollution can significantly harm soil quality, and by extension, water resources. When air is polluted, so too is the precipitation that falls into water bodies and soils. This is a significant concern, as soil and water are fundamental to all life on Earth, providing homes and nutrients for most organisms.
Acid precipitation, or acid rain, can alter the chemistry of the soil, affecting plant growth and water quality. Soils become less able to retain essential nutrients, minerals, and elements such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium. These nutrients are then leached by water flowing through the soil, making them less available for plant growth and agriculture. This can result in soil nutrient deprivation and degradation of land, leading to off-site environmental issues such as flooding, water siltation, and pollution.
Soil is a complex and dynamic ecosystem, and its quality is affected by various aspects of agriculture, including compaction, loss of soil structure, nutrient degradation, and salinity. Air pollution can introduce heavy metals and harmful chemicals into the soil, further disrupting the balance of microorganisms and stimulating the growth of harmful bacteria. This can have adverse effects on human health, as contaminated soil can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and other non-communicable diseases.
Additionally, airborne dust and particles can carry pathogens, harmful gases, organic chemicals, heavy metals, and even radioactive materials. These pollutants can have severe health impacts, including irritation of the respiratory tract and an increased risk of pulmonary diseases, such as pneumonia, chronic obstructive bronchitis, and lung cancer.
Overall, while the direct link between air pollution and soil erosion may be less clear, there is no doubt that air pollution contributes to soil toxicity and degradation, which can have far-reaching consequences for the environment, agriculture, and human health. Sustainable land use practices and ecological restoration methods are essential to mitigate these effects and preserve the fragile balance of our ecosystems.
Contrails: The Mystery of Pollution in the Sky
You may want to see also

Soil erosion impacts human health
Soil erosion has a profound effect on human health and well-being. Soil is the earth's fragile skin that anchors all life, and it is among the most precious resources to humans. Soil provides many of the nutrients we require, but it can also pass on harmful substances through the food we eat.
Soil erosion can have a direct impact on human health by reducing the ability for plants to grow and water to penetrate, which harms soil microbes and results in serious erosion of the land. This loss of fertile soil makes the land less productive for agriculture, creates new deserts, pollutes waterways, and can alter how water flows through the landscape, potentially making flooding more common. Desertification can be characterised by the droughts and arid conditions the landscape endures as a result of human exploitation of fragile ecosystems. Soil degradation, which includes soil erosion and the loss of soil structure and nutrient content, decreases crop production and threatens food security.
Soil erosion can also have indirect effects on human health. For example, it can lead to the spread of harmful substances, such as pesticides and fertilizers, into waterways, which can damage freshwater and marine habitats and the local communities that depend on them. Additionally, soil erosion can contribute to the spread of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) through a process called the grasshopper effect, which is of particular concern in the northern communities of the Arctic where these pollutants tend to concentrate.
Airborne dust generated from soil erosion can also impact human health, especially when the particles are less than 10 microns in size. Inhaling this dust can irritate the respiratory passages and lead to diseases such as lung cancer. Furthermore, airborne dust can carry additional materials, such as pathogens, harmful gases, organic chemicals, heavy metals, insects, pollen, and radioactive materials, which can cause a range of health problems. These toxicants may enter the bloodstream through the lungs.
Overall, soil erosion can have significant direct and indirect impacts on human health, affecting everything from the food we eat to the air we breathe and the water we drink.
Cars and Carbon Pollution: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Air pollution does not cause soil erosion, but it does negatively impact soil quality. Soil erosion is caused by natural agents or human activities such as unsustainable land use, poor land management, and agriculture.
Air pollution can alter the chemistry of the soil, making it more acidic. This reduced ability to retain essential nutrients, minerals, and elements can negatively affect plant growth and increase the mobilization of heavy metals, which can be harmful to wildlife.
Soil erosion can lead to land degradation, soil sterility, and a loss of biodiversity. It can also cause flooding, water siltation, and pollution, impacting both the environment and human health.
Soil pollution is a significant threat to human health, as it can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and other non-communicable diseases. It can also impact respiratory health, especially when polluted soil becomes airborne and is inhaled.



















