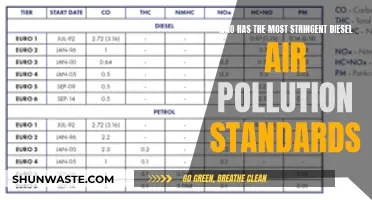
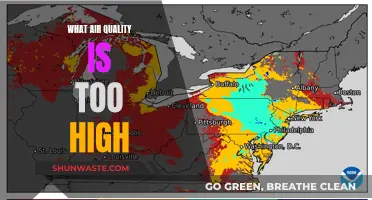
The fuel that produces the least air pollution is a topic of ongoing debate, with various factors influencing the environmental impact of different energy sources. Air pollution from energy production, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, contributes to acid rain, excess greenhouse gases, and adverse health effects. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are significant contributors to air pollution when extracted and burned, releasing nitrogen oxides and other harmful compounds. Natural gas, primarily composed of methane, has lower CO2 emissions relative to its energy content. However, its production and transportation can lead to air pollution and the release of contaminated water. To reduce air pollution, individuals and businesses can conserve energy, improve energy efficiency, and transition to renewable energy sources.
What You'll Learn

Natural gas has lower CO2 emissions relative to its energy content
Natural gas is primarily methane (CH4), which has a higher energy content compared to other fuels. This means that burning natural gas produces less CO2 relative to the energy content of the fuel. In other words, natural gas is a relatively clean-burning fossil fuel.
When comparing emissions across fuels, it is important to consider the amount of CO2 emitted per unit of energy output or heat content. Natural gas, for example, produces fewer emissions of nearly all types of air pollutants and carbon dioxide (CO2) than coal or petroleum products when generating an equal amount of energy. Specifically, for every 1 million BTUs consumed, coal produces over 200 pounds of CO2, while fuel oil produces over 160 pounds.
However, it is important to note that natural gas production and use have some environmental and safety considerations. For instance, some natural gas leaks into the atmosphere from oil and gas wells, storage tanks, pipelines, and processing plants. Additionally, while natural gas flaring reduces the amount of gas released directly into the atmosphere, it still produces CO2, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other compounds.
To fully realize the climate benefits of natural gas, technologies and policies must be implemented to minimize methane leaks throughout the production, gathering, processing, transmission, distribution, and LNG shipping processes. Furthermore, natural gas plants will need to adopt carbon capture, utilization, and storage technologies to achieve mid-century net-zero emission goals.
Cleanse Your Lungs: Breathe Easy and Fight Air Pollution
You may want to see also

Fossil fuels burned for energy produce harmful emissions
Fossil fuels are non-renewable energy sources formed from the decomposition of carbon-based organisms that died millions of years ago. They are primarily made up of coal, oil, and natural gas. The burning of fossil fuels releases harmful emissions into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to air pollution and climate change.
The combustion of fossil fuels emits large quantities of carbon dioxide (CO2), a potent greenhouse gas. In 2018, 89% of global CO2 emissions were attributed to the burning of fossil fuels. CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion increased by 8% in 2022 compared to 2020, showcasing an upward trend. The amount of CO2 produced is directly linked to the carbon content of the fuel, with coal being the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel.
In addition to CO2, fossil fuel combustion releases other harmful substances. Coal-fired power plants, for example, are responsible for generating a significant portion of mercury, sulfur dioxide, and soot emissions. Sulfur dioxide contributes to acid rain, which contaminates freshwater sources and harms aquatic ecosystems. Soot and sulfate aerosols increase the reflectivity of the atmosphere, influencing cloud formation and reflectivity.
The transportation sector, including cars, trucks, ships, trains, and planes, relies heavily on fossil fuels. Fossil fuel-powered vehicles are major contributors to carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide emissions, which lead to smog formation and respiratory illnesses. Additionally, the industrial sector's use of fossil fuels for energy and industrial processes further exacerbates air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
The combustion of natural gas, a fossil fuel, accounts for a fifth of the world's total carbon emissions. However, it is often promoted as a cleaner energy source compared to coal and oil due to its higher energy content and relatively lower CO2 emissions per unit of energy produced. Nevertheless, natural gas still contributes significantly to global carbon emissions and remains a non-renewable resource.
Lichen's Sensitivity: Air Pollution's Impact
You may want to see also

Transportation is a large source of nitrogen oxide emissions
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are a group of gases that contribute to air pollution and the formation of smog, acid rain, and tropospheric ozone. NOx gases are produced by the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, methane gas (natural gas), and diesel. While lightning is a natural producer of NOx, human-made sources, particularly in the transportation sector, are a significant contributor to NOx emissions.
Transportation is a major source of nitrogen oxide emissions, especially in urban areas with high motor vehicle traffic. Gasoline-powered vehicles, including cars, trucks, and buses, are the largest sources of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions. In the United States, gasoline-powered vehicles contribute to 32% of all NOx and 82% of transportation-related NOx emissions. Diesel-powered vehicles, such as trucks and non-road equipment, also produce significant NOx emissions.
The combustion of fossil fuels in transportation contributes significantly to NOx emissions. Fossil fuel combustion, including gasoline and diesel consumption, leads to the release of NOx gases into the atmosphere. In 2022, CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion increased by 8% compared to 2020 levels in the United States. While CO2 emissions from coal consumption decreased, emissions from natural gas consumption increased by 5% in the same period.
To mitigate the impact of transportation on nitrogen oxide emissions, various technologies have been implemented. The use of exhaust gas recirculation and catalytic converters in motor vehicle engines has significantly reduced vehicular NOx emissions. Additionally, advancements such as flameless oxidation (FLOX), staged combustion, and water injection technology have helped reduce thermal NOx emissions in industrial processes.
It is important to note that while transportation is a significant contributor to nitrogen oxide emissions, other sectors, such as industry, commercial, residential, and agriculture, also play a role in NOx emissions. Industrial activities, including burning fossil fuels for energy and certain chemical reactions, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Commercial and residential sectors emit NOx from burning fossil fuels for heat and using gases for refrigeration and cooling. Agriculture-related emissions arise from livestock, agricultural soils, and rice production.
Air Pollution: Where in the US is it a Problem?
You may want to see also

Renewable energy reduces environmental impact
Renewable energy is derived from sources that are continuously, sustainably, and naturally replenished. It is widely acknowledged as the key to countering climate change and achieving global climate goals. It is important to understand the environmental impact of energy resources and assess which solution is best for a given location, community, and stakeholders.
Renewable energy sources produce far fewer greenhouse gases (GHGs) than fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. In some cases, renewable sources produce no GHGs once they are up and running. For example, solar energy is converted into usable energy by photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal systems. Solar farms can also support agricultural uses, such as growing crops or grazing livestock. Similarly, wind energy sites produce no GHG emissions once established.
However, it is important to note that any human intervention will have some impact on the environment. Renewable energy projects often require energy-intensive processes for the manufacture of parts, such as iron, steel, glass, and composite materials for turbines. The construction of renewable energy systems can also impact native habitats, and the production and use of electricity contribute to environmental impacts on air, water, and land. Nevertheless, renewable energy projects can be designed to minimize these impacts. For instance, strategic placement of wind turbines can help minimize risks to bird populations, and the use of previously disturbed or degraded land for renewable energy projects can protect relatively untouched natural areas.
Overall, renewable energy plays a critical role in combating climate change and building resilience for both private organizations and communities. By transitioning to renewable energy, we can reduce environmental injustices and create a more sustainable future.
Air Pollution's Impact on Global Warming
You may want to see also

Conserving energy reduces air pollution
Conserving energy is beneficial for both financial and environmental reasons. Energy efficiency is about using less energy to accomplish the same tasks, thereby avoiding high energy bills and unnecessary pollution. For example, minor adjustments such as turning off the lights when not in use, using ceiling fans instead of air conditioning in the summer, and washing laundry in cold water can significantly reduce energy consumption and, consequently, lower your electricity bills.
The amount of carbon dioxide produced when a fuel is burned is directly related to its carbon content. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, have high carbon content and are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing our energy consumption, we can lower the demand for these fossil fuels and decrease the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere. This is particularly important as the combustion of fossil fuels for energy production and transportation are some of the largest sources of greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, the production and consumption of fossil fuels can lead to water contamination. Coal-burning power plants, for instance, release harmful chemicals that pollute aquatic ecosystems, affecting both human and animal life. By conserving energy, we can reduce the need for such power plants and mitigate water pollution.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offer lower-carbon alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. They have a reduced carbon impact on the environment, contributing less to climate change and air pollution. By conserving energy, we can accelerate the transition to these cleaner energy sources and further diminish air pollution.
Overall, conserving energy is a critical step towards reducing air pollution. By decreasing our energy consumption, we can lower carbon emissions, mitigate water pollution, and promote the adoption of cleaner energy sources. These collective efforts will help improve air quality and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Hot Air Balloons: Polluting the Skies?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Natural gas has lower CO2 emissions relative to its energy content.
The amount of CO2 produced when a fuel is burned depends on its carbon content. Fossil fuels, for instance, release nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere when burned, contributing to smog and acid rain.
To reduce airborne nutrient pollution, one can conserve energy by turning off electrical equipment when not in use, buying energy-efficient appliances, and limiting air conditioning.
Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture come from livestock, agricultural soils, and rice production. Indirect emissions from electricity use in agricultural activities also contribute.
Burning fossil fuels for cars, trucks, ships, and trains releases nitrogen oxides, contributing to air pollution. To reduce this, one can opt for public transportation, carpooling, or consolidating driving trips.