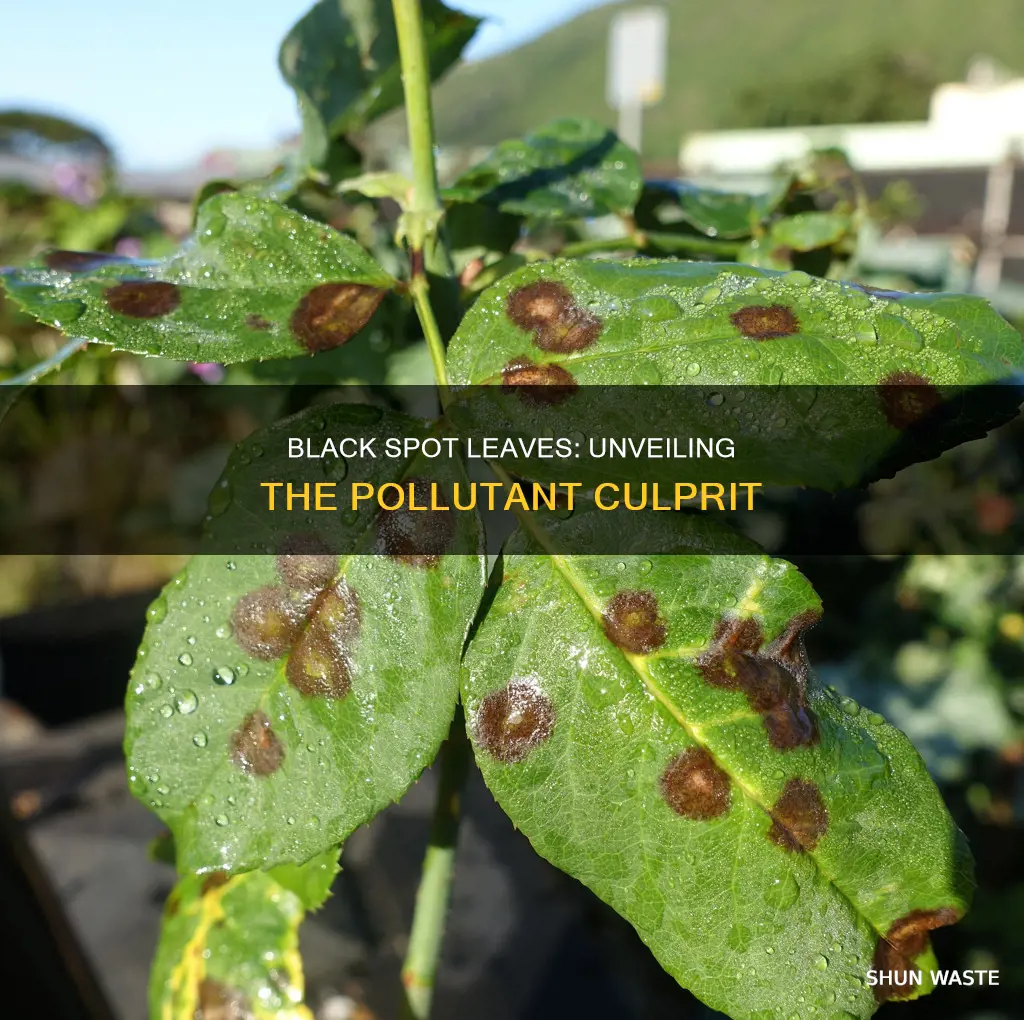
Black spots on leaves are a common concern for gardeners and plant enthusiasts. While there are various causes, from insect infestations to fertiliser overuse, the most common cause is a fungal infection. This is known as black spot fungus, or Diplocarpon rosae, and it affects a range of plant species, including roses. It appears as tiny black spots, which develop into larger blotches, and can cause leaves to turn yellow and fall prematurely. The spores of the fungus are spread by water, wind, and human activity, and thrive in cool, wet weather. While black spot fungus rarely kills the host plant, it can cause stress and vulnerability to other diseases and pests.
What You'll Learn

Air pollution
Fungi can lead to blackened leaves, and one common example is black spot, caused by the fungus Diplocarpon rosae. Black spot is a widespread disease that affects a range of plant species, including roses, and appears as black spots on leaves, resulting in discoloration and leaf drop. It is favoured by extended periods of cool, wet weather in the spring and can be spread by splashing water, dew, or sprinklers. While black spot does not directly kill plants, it weakens them and makes them more susceptible to other diseases and pests, such as aphids.
Another leaf spot fungus that can cause black spots is anthracnose, caused by several closely related fungi species that produce brown or black lesions on leaves. Trees that are already stressed, such as those that have been recently transplanted or are growing under drought conditions, are more susceptible to serious injury from leaf spot fungi.
To prevent and control leaf spot diseases, gardeners can take several measures. Firstly, regular inspection of plants is crucial, especially in the spring when fungi are most active. Preventative treatment with fungicides can be applied as soon as buds begin to swell and break in spring, and it should be repeated every seven to 14 days until conditions no longer favour the disease. Proper pruning and disposal of affected plant parts can also help control the spread of the disease.
While there is no effective way to treat leaf spots caused by air pollution, gardeners can take preventive measures by transplanting plants from outdoors to indoors and avoiding exposure to polluted air. Additionally, providing plants with a balanced fertiliser that includes essential nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and magnesium can help promote overall plant health and reduce their susceptibility to diseases.
Car Pollution and Asthma: Is There a Link?
You may want to see also

Insect infestations
Black spots on leaves can be caused by various factors, including environmental conditions, pathogens, and insect infestations. While insect infestations are more commonly associated with indoor plants, certain insects can also affect outdoor plants, leading to leaf discolouration and damage.
One of the most common insects that cause black spots on leaves is the scale insect. These insects feed on plant sap, weakening the plant and causing discolouration. Scale insects often cluster together on leaves, and their presence is indicated by a sticky residue called honeydew, which promotes the growth of sooty mould. Sooty mould is a dark-coloured fungus that hinders photosynthesis and further contributes to leaf discolouration.
Another insect that can cause black spots is the flea beetle. Flea beetles swarm over leaves, leaving numerous holes that can result in wilted or stunted plants. While they do not directly cause black spots, the damage they inflict can lead to leaf discolouration and overall plant decline.
Additionally, spider mites and aphids are tiny insects that feed on plant sap and can cause leaf discolouration. These pests also secrete honeydew, which encourages the growth of sooty mould. In severe cases, the mould can cover the entire leaf surface, hindering the plant's ability to photosynthesize effectively.
To prevent and control insect infestations, regular inspection of plants is crucial. Removing infested leaves and disposing of affected plant debris can help reduce the insect population. Insecticidal soaps, horticultural oils, and neem oil are also effective treatments. Neem oil, in particular, is a natural, organic option that can help manage both insects and fungal growth.
Pollution's Role in Invasive Species: A Complex Relationship
You may want to see also

Bacterial infections
Bacterial leaf spots initially appear as small, dark brown to black spots, which can merge to form larger black blotches or turn the entire leaf black. These spots are often surrounded by a yellow halo, and the centre of the spot may dry up and fall out, resulting in a "shot hole" appearance. The spots can also be speckled and may enlarge and run together in wet conditions. As the infection progresses, the leaves may yellow, wither, and drop.
Bacterial leaf spot can affect a wide range of plants, including annual and perennial flowering plants such as geraniums, zinnias, purple cone flowers, and black-eyed Susans. It is also common in stone fruit trees, such as cherry, plum, almond, apricot, and peach trees. Additionally, vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and lettuce are susceptible to bacterial leaf spot.
There is currently no cure for plants infected with bacterial leaf spot. However, preventive measures can be taken to manage the disease. These include spraying plants with a baking soda solution or neem oil. Baking soda can be prepared by mixing one tablespoon of baking soda, 2.5 tablespoons of vegetable oil, one teaspoon of liquid soap, and one gallon of water. It is important to test this solution on a small area of the plant first, as baking soda may burn some plant leaves. Neem oil, an oil pressed from an evergreen tree, is another effective organic treatment. Additionally, sulfur sprays or copper-based fungicides can be applied when the first signs of the disease appear to prevent its spread. While these fungicides will not kill the leaf spot, they can prevent the spores from germinating.
Diseases from Polluted Water: 10 Devastating Illnesses
You may want to see also

Fungal infections
Black spots on leaves are often caused by fungal infections. While some leaf spots are caused by air pollutants, insects, or bacteria, most are the result of infection by pathogenic fungi. These fungi grow and destroy leaf tissue, causing spots that vary in size and colour, from pinhead-sized black spots to large brown or black blotches.
Fungal leaf spots are favoured by cool, wet weather, particularly early in the growing season. They are rarely a problem following warm, dry weather in the spring. Many different types of fungi can cause leaf spots, and they can attack a wide range of plant species, including roses, trees, and shrubs. For example, black spot, caused by the fungus Diplocarpon rosae, can attack any plant with fleshy leaves and stems if the conditions are right. It typically appears as round black spots on leaves, and the leaves may turn yellow and fall early.
To prevent and control fungal leaf spots, gardeners can take several measures. Firstly, regular inspection of the garden is crucial, especially in the spring when fungi are more likely to develop. Preventative spraying with fungicides or homemade remedies can help, and it is important to start before temperatures hit sixty degrees Fahrenheit. During an outbreak, affected plant parts should be cut back and disposed of, and garden debris should be removed or burned in the fall. Bright sun and good air circulation are also essential for controlling fungal leaf spots.
In some cases, chemical control of leaf spots may be necessary, especially for trees under stress or susceptible varieties. Proper fungicides must be applied as a protectant before the fungus spore infects the leaf. This typically requires two to three spray applications, with the first spray at bud break and the second seven to fourteen days later.
Oil Pollution vs. Greenhouse Gases: Which Is Worse?
You may want to see also

Fertilizer issues
Black spots on leaves can be caused by various factors, and while fertilizer issues may be a contributing factor, it is important to consider other potential causes, such as fungal, bacterial, or pest infestations.
- Over-fertilization or incorrect fertilization: Excessive fertilizer application or using the wrong type of fertilizer can burn the leaves, resulting in blackened tips or spots. This is particularly true for indoor plants, which are more vulnerable to insect infestations that cause leaf discoloration.
- Nutrient deficiencies: A deficiency in key nutrients, especially nitrogen, can hinder the plant's ability to photosynthesize effectively, leading to leaf discoloration and the development of dark leaves.
- Improper fertilization timing: Applying fertilizer at the wrong stage of plant development can result in nutrient imbalances, affecting leaf health and making the plant more susceptible to diseases that cause black spots.
- Inadequate fertilizer application rates: Failing to follow the recommended application rates for different stages of plant growth can lead to nutrient deficiencies or excesses, impacting leaf health and making plants more prone to leaf spot diseases.
- Poor-quality fertilizer: Using low-quality or unbalanced fertilizer that does not provide essential nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and magnesium can result in nutrient deficiencies, causing leaf discoloration and making plants more susceptible to leaf spot pathogens.
To address fertilizer issues, it is important to select a high-quality, balanced fertilizer that meets the specific nutritional needs of your plants. Follow the recommended application rates and timing for the different growth stages of your plants. Additionally, regular inspection and maintenance of your plants are crucial to identify and address any fertilizer-related issues promptly.
Drilling for Oil: Pollution and Environmental Impact
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Black spots on leaves are commonly caused by fungal infections, such as the black spot fungus, or sooty mould. However, bacterial infections, like bacterial leaf spot, can also cause black spots. In addition, air pollution and incorrect fertilisation can cause leaf discolouration, resulting in black spots on leaves.
Black spot fungus, caused by the pathogen Diplocarpon rosae, appears as tiny black spots on leaves, which can grow and cause the entire leaf to turn yellow and fall.
To treat black spot fungus, you can use fungicides, such as Daconil® Fungicide, or natural alternatives like neem oil or a mixture of baking soda, water, and horticultural oil or soap. It is also important to dispose of affected debris and avoid watering plants on cloudy days.
Bacterial leaf spot, caused by Pseudomonas spp. or Xanthomonas spp., appears as small dark brown to black spots with a yellow halo. The centre of the spot may dry up and fall out, resulting in a "shot hole" appearance.
To treat bacterial leaf spot, you will need to use a fungicide that is effective against bacterial pathogens. Preventative measures include maintaining proper plant health and avoiding overwatering.



















