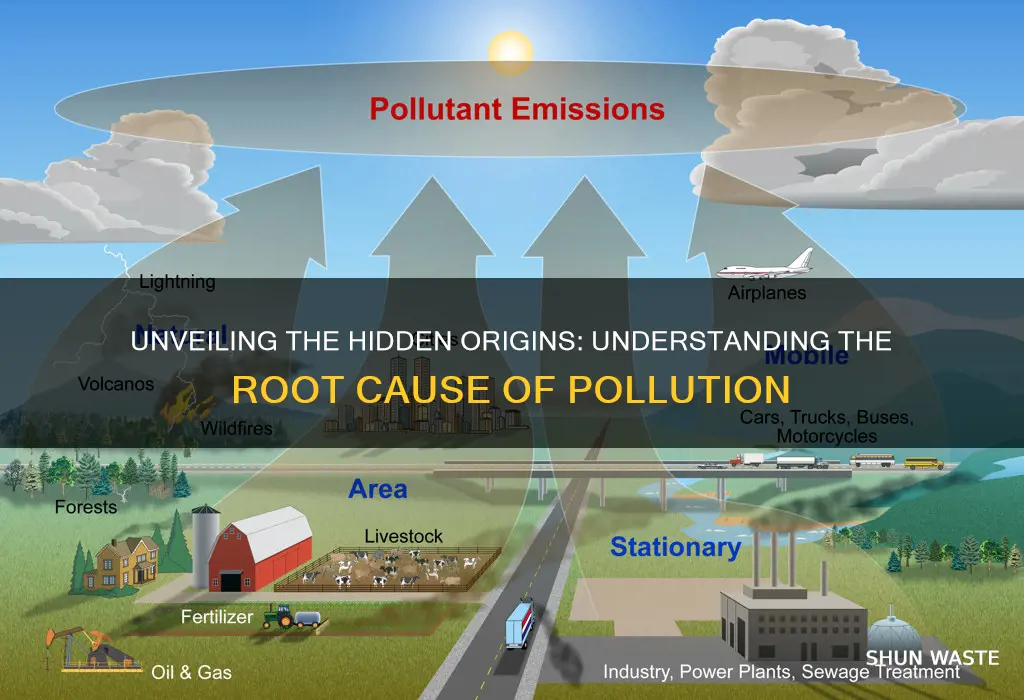
Pollution is a complex environmental issue with multiple causes, and understanding its root causes is essential for developing effective solutions. The primary sources of pollution include industrial activities, vehicle emissions, and improper waste disposal. Industrial processes often release toxic chemicals and pollutants into the air, water, and soil, leading to air and water pollution. Vehicle emissions, particularly from older models, contribute to air pollution by releasing harmful gases and particulate matter. Improper waste disposal, such as the dumping of plastic and other non-biodegradable materials, results in soil and water pollution, affecting ecosystems and human health. Addressing these root causes requires a multifaceted approach, including stricter regulations, sustainable practices, and public awareness to mitigate the harmful impacts of pollution on our planet.
What You'll Learn
- Industrial Emissions: Factories release pollutants into air and water, causing environmental degradation
- Vehicle Exhaust: Cars and trucks emit harmful gases, contributing to air pollution and climate change
- Agricultural Runoff: Pesticides and fertilizers in farming lead to water pollution and soil contamination
- Waste Disposal: Improper waste management creates landfill pollution and releases toxic gases
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture and urbanization increases air and water pollution

Industrial Emissions: Factories release pollutants into air and water, causing environmental degradation
The root cause of pollution, as identified through extensive research, is primarily human activity, with industrial emissions from factories being a significant contributor. These emissions have a profound impact on both the environment and human health. Factories, as part of the industrial sector, play a crucial role in the global economy, but their operations often come at a cost to the natural world. The primary pollutants released by industrial activities include sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and various toxic chemicals. These emissions are a direct result of the manufacturing processes, energy production, and waste management practices employed by factories.
When factories release these pollutants into the air, they contribute to air pollution, which has far-reaching consequences. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, for instance, are major contributors to acid rain, a phenomenon where rainfall becomes acidic due to the presence of these gases. This not only harms aquatic ecosystems but also damages forests, soils, and even buildings. Particulate matter, a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets, can be inhaled and cause respiratory issues in humans, leading to increased healthcare burdens.
Water pollution is another critical issue stemming from industrial emissions. Factories often discharge untreated or inadequately treated wastewater, which contains a variety of contaminants. These include heavy metals, organic compounds, and toxic chemicals that can have devastating effects on aquatic life. The release of such pollutants into water bodies can lead to the destruction of aquatic ecosystems, making waters unsafe for drinking and recreational use.
The environmental degradation caused by industrial emissions is a complex issue. It involves not only the immediate release of pollutants but also the long-term consequences of these emissions. Over time, the accumulation of pollutants in the environment can lead to soil degradation, reduced crop yields, and the loss of biodiversity. Furthermore, the impact on human health is significant, with air and water pollution contributing to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and various other health issues.
Addressing the root cause of pollution requires a multifaceted approach. It involves implementing stricter regulations and standards for industrial emissions, encouraging the adoption of cleaner production methods, and promoting sustainable practices. Factories can play a vital role in mitigating pollution by investing in pollution control technologies, improving waste management systems, and adopting renewable energy sources. By taking these steps, industries can reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a healthier, more sustainable future.
Unraveling the Complex Web: Causes of Pollution
You may want to see also

Vehicle Exhaust: Cars and trucks emit harmful gases, contributing to air pollution and climate change
Vehicle exhaust is a significant contributor to air pollution and climate change, and understanding its root causes is essential for developing effective solutions. The primary issue lies in the combustion process within internal combustion engines, which powers most cars and trucks. When gasoline or diesel is burned to propel vehicles, it releases a complex mixture of pollutants into the atmosphere. These emissions include carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM).
The combustion process itself is inherently inefficient and incomplete, leading to the formation of these harmful byproducts. Carbon monoxide, for instance, is a toxic gas that can be deadly in high concentrations. It is produced when there is an insufficient supply of oxygen during combustion, causing unburned hydrocarbons to remain in the exhaust stream. Nitrogen oxides, on the other hand, are formed through high-temperature combustion and the interaction of nitrogen and oxygen in the air. These gases contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog, which has detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
Volatile organic compounds are another critical concern. These compounds are released from the evaporation of gasoline and the incomplete combustion of fuel. VOCs contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and can also have direct health impacts, including eye, nose, and throat irritation, headaches, and even more severe respiratory issues. Particulate matter, often referred to as soot, is a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. It is classified based on its size, with PM10 and PM2.5 being the most common. These particles can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, causing various health problems, especially for vulnerable populations like children and the elderly.
The root cause of these emissions is the design and operation of internal combustion engines. These engines are inherently inefficient, especially when compared to electric or fuel cell-powered vehicles. The combustion process, as mentioned earlier, is not optimized for complete fuel burning, leading to the release of unburned hydrocarbons and the formation of harmful byproducts. Additionally, the high temperatures and pressures within the engine create conditions that favor the production of nitrogen oxides.
To address this issue, a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation methods is necessary. Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles offer a cleaner alternative, as they produce fewer emissions during operation. The use of advanced combustion technologies, such as lean-burn engines and direct injection, can also help improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Furthermore, implementing stricter emission standards and regulations for vehicle manufacturers can drive the development and adoption of cleaner technologies, ultimately contributing to a significant reduction in vehicle exhaust pollution.
Tape and Velcro: Environmental Impact and Sustainable Alternatives
You may want to see also

Agricultural Runoff: Pesticides and fertilizers in farming lead to water pollution and soil contamination
Agricultural runoff is a significant contributor to water pollution and soil contamination, posing a critical environmental challenge. The excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers in farming practices is at the heart of this issue. Pesticides, designed to eliminate pests and protect crops, often contain toxic chemicals that can have detrimental effects on the environment. When these chemicals are applied to fields, they can easily wash off during rainfall or irrigation, creating a harmful runoff. This runoff carries pesticides into nearby water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater, leading to water pollution. The impact is not limited to surface water; pesticides can also infiltrate the soil, contaminating it and affecting its quality.
Fertilizers, primarily composed of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential for plant growth. However, when used in excess, they can have adverse effects. Similar to pesticides, fertilizers can be washed off fields during heavy rains or improper irrigation, resulting in agricultural runoff. This runoff carries excess nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, into water bodies. The high concentration of these nutrients causes eutrophication, a process where water bodies experience rapid algae growth. This not only disrupts the natural balance of aquatic ecosystems but also leads to the depletion of oxygen, creating 'dead zones' where aquatic life cannot survive.
The consequences of agricultural runoff extend beyond water pollution. Soil contamination is another critical issue. Pesticides and fertilizers can accumulate in the soil, affecting its structure and fertility. Over time, these chemicals can alter the soil's pH levels and disrupt the natural microbial balance, leading to soil degradation. Contaminated soil can then impact crop health, reducing yields and affecting the quality of produce. Furthermore, the chemicals in the soil can leach into groundwater, posing risks to human health and aquatic ecosystems.
Addressing agricultural runoff requires sustainable farming practices. Farmers can adopt methods such as precision agriculture, which involves using technology to optimize pesticide and fertilizer application. This ensures that chemicals are used only where and when needed, minimizing runoff. Implementing buffer zones, which are areas of natural vegetation along water bodies, can also help filter and absorb runoff, preventing pollutants from entering water sources. Additionally, farmers can utilize cover crops and crop rotation to improve soil health and reduce the reliance on excessive fertilizers.
In conclusion, the root cause of pollution in the context of agriculture lies in the improper use of pesticides and fertilizers, leading to agricultural runoff. This runoff contaminates water bodies and soil, causing significant environmental damage. By adopting sustainable farming practices and implementing measures to control chemical usage, it is possible to mitigate the impact of agricultural runoff and promote a healthier environment. Educating farmers and the public about the importance of responsible farming practices is crucial in addressing this critical environmental issue.
Industrial Pollution: A Necessary Evil or a Preventable Issue?
You may want to see also

Waste Disposal: Improper waste management creates landfill pollution and releases toxic gases
The improper disposal of waste is a significant contributor to pollution, particularly in the context of landfills. When waste is not managed correctly, it can lead to a range of environmental issues, including the creation of landfill pollution and the release of harmful gases. This problem is a critical aspect of understanding the root causes of pollution and its impact on our ecosystems.
Landfills are designed to contain and bury waste, but when they are not properly maintained or when waste is not sorted and managed effectively, they can become sources of environmental degradation. Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, is a major concern in landfills. When these materials decompose, they undergo anaerobic digestion, a process that produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Methane is approximately 25 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide, making it a significant contributor to climate change. The release of methane from landfills is a direct result of improper waste management, where organic waste is not composted or recycled and instead ends up in landfills.
In addition to methane, landfills can also release other toxic gases, such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia. These gases are produced during the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Hydrogen sulfide, for example, has a strong, unpleasant odor and can be harmful if inhaled in large quantities. It can also react with water to form sulfuric acid, which can contaminate groundwater and further exacerbate pollution. The improper disposal of certain types of waste, such as batteries, electronics, and chemicals, can also lead to the release of toxic substances like lead, mercury, and heavy metals into the soil and groundwater.
To mitigate these issues, effective waste management strategies are essential. This includes implementing proper waste sorting and recycling programs, encouraging composting of organic waste, and promoting the use of sustainable alternatives to reduce the amount of waste generated. Educating communities about responsible waste disposal practices can also significantly reduce the environmental impact of landfills. By understanding the root cause of pollution in the context of waste disposal, we can take targeted actions to minimize landfill pollution and the release of toxic gases, ultimately contributing to a healthier and more sustainable environment.
Unveiling Soil's Dark Secret: Causes of Pollution Revealed
You may want to see also

Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture and urbanization increases air and water pollution
Deforestation, the widespread clearing of forests, is a significant contributor to pollution and has far-reaching environmental consequences. The primary root cause of this issue lies in the conversion of forested lands into agricultural fields and urban developments. As human populations expand and demand for resources increases, the pressure to utilize forest areas for farming and construction intensifies. This process involves the removal of trees, which play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance.
Trees act as natural air purifiers, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, thus regulating the Earth's atmosphere. They also prevent soil erosion by holding the earth together with their roots. When forests are cleared, this delicate balance is disrupted. The absence of trees leads to increased soil erosion, especially on slopes, as the protective cover is removed. Eroded soil often ends up in nearby water bodies, causing sedimentation and water pollution. This pollution can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems and the organisms that depend on them.
Furthermore, the burning of trees and vegetation during deforestation releases vast amounts of carbon dioxide and other harmful gases into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute significantly to air pollution and global warming. The loss of forests also reduces the Earth's capacity to absorb and store carbon, a vital process in mitigating climate change. As a result, the increased concentration of greenhouse gases leads to rising temperatures, altered weather patterns, and the potential for more frequent and severe natural disasters.
The impact of deforestation on water pollution is equally concerning. Without trees, the natural filtration system provided by forests is lost. Rainwater, instead of being absorbed into the soil, runs off, carrying pollutants from agricultural activities and urban areas into rivers, lakes, and coastal regions. This runoff can include pesticides, fertilizers, heavy metals, and other toxic substances, posing risks to human health and aquatic life. The degradation of water quality due to deforestation has long-lasting effects on ecosystems and can disrupt the balance of entire food chains.
Addressing deforestation is crucial in the fight against pollution. Sustainable land-use practices, such as agroforestry and urban planning that prioritize green spaces, can help mitigate the impacts. Reforestation efforts are also essential to restore the lost habitats and their ecological functions. By understanding and tackling the root cause of deforestation, we can take significant steps towards reducing air and water pollution, preserving biodiversity, and ensuring a healthier environment for future generations.
Breathing Trouble: How Indoor Air Pollution Affects Your Health
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The primary root cause of pollution is human activity. Human actions, such as industrial processes, transportation, and energy generation, have led to the release of various pollutants into the air, water, and soil. These activities often involve the burning of fossil fuels, improper waste disposal, and the use of chemicals, which contribute significantly to environmental degradation.
Industrial processes are a major source of pollution. Manufacturing, mining, and other industrial activities release pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter into the atmosphere. These emissions can cause air pollution, leading to respiratory issues and environmental damage. Additionally, industrial waste, if not managed properly, can contaminate water bodies and soil, affecting ecosystems and human health.
Transportation systems, including cars, trucks, ships, and airplanes, are significant contributors to pollution. The burning of fossil fuels for propulsion releases greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, which contribute to climate change. Transportation also emits pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, which have adverse effects on air quality and human well-being.
Energy generation, particularly from non-renewable sources, is a critical factor in pollution. Power plants that burn coal, oil, or natural gas release a multitude of pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions not only cause local air pollution but also contribute to global environmental issues, such as acid rain and climate change.
While human activities are the predominant cause of pollution, natural processes can also contribute to environmental degradation. Volcanic eruptions, for example, release ash, sulfur dioxide, and other gases, causing air pollution and potential climate impacts. Wildfires, though often human-induced, can also release pollutants into the atmosphere. However, the scale and frequency of these natural events are generally much lower compared to human-induced pollution.