Air pollution is caused by the release of pollutants into the Earth's atmosphere, which are detrimental to human health and the planet as a whole. The major man-made cause of air pollution is the burning of fossil fuels, including coal, natural gas, and oil. This occurs across various sectors, such as transportation, power plants, manufacturing, and residential energy use. Mobile sources, such as cars, trucks, and planes, account for a significant portion of air pollution, with automobiles being the primary source in the United States. Additionally, industrial facilities, agricultural practices, and residential energy for cooking and heating also contribute significantly to air pollution.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Primary Source | Burning fossil fuels, including coal, natural gas, and oil |
| Other Sources | Cigarette smoke, wildfires, volcanic ash, windblown dust, car exhaust, industrial emissions, agricultural emissions, etc. |
| Effects | Haze, difficulty breathing, irritation in eyes, nose, and throat, skin allergies, asthma, respiratory issues, lung disease, heart issues, cancer, stroke, premature death |
| Impact | Harmful to humans, animals, plants, natural environment (climate change, ozone depletion, habitat degradation), and built environment (acid rain, building decay) |
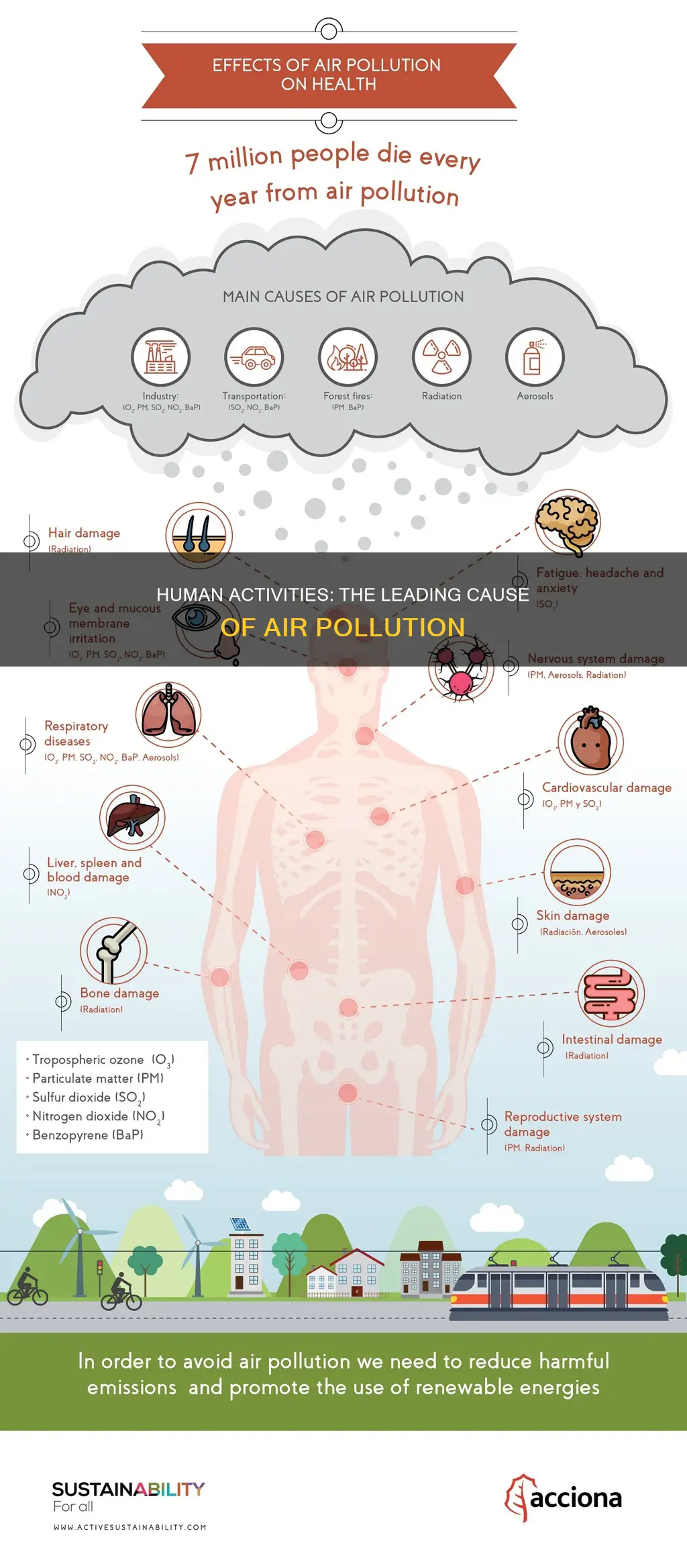
| Statistics | 7-8 million deaths annually; 99% of humans breathe air that exceeds WHO guideline limits |
| Mitigation | Sustainable land use, cleaner household energy, energy-efficient housing, better waste management, etc. |
What You'll Learn

Burning fossil fuels
The burning of fossil fuels has been a significant source of air pollution since the Industrial Revolution in the mid-1700s. During this period, the increased use of coal to power factories and engines led to a rise in air pollution. Today, the burning of fossil fuels in vehicles, airplanes, power plants, and factories continues to be a major contributor to air pollution.
Fossil fuel combustion releases a range of pollutants that reduce air quality and harm human health. These pollutants include greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O), as well as harmful substances like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and airborne particles such as soot. Poor air quality resulting from fossil fuel combustion can cause respiratory diseases and other serious health issues, including asthma, cancer, heart disease, and premature death.
In addition to the direct health impacts, burning fossil fuels also contributes to climate change, which further exacerbates air pollution. The release of greenhouse gases intensifies the greenhouse effect, leading to rising global temperatures and altering Earth's ecosystems. Climate change-fueled wildfires and extreme heat events also contribute to air pollution, creating a feedback loop that further degrades air quality.
The combustion of fossil fuels has disproportionate effects on vulnerable populations, particularly children, the poor, and certain minorities. These groups bear a heavier burden of disease and developmental impairments due to exposure to air pollutants and the impacts of climate change. Additionally, communities of color and low-income areas are more likely to be located near polluting industries and highways, subjecting them to increased health risks and economic consequences from breathing dirty air.
To address the major issue of air pollution caused by burning fossil fuels, a transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources is necessary. Mitigation efforts and comprehensive policies are crucial to reducing the health and environmental impacts of fossil fuel combustion and to ensuring a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Air Conditioners: Polluting Jupiter's Atmosphere?
You may want to see also

Industrial activities
Today, industrial facilities continue to release a variety of pollutants, including carcinogenic substances such as benzene, formaldehyde, 1,3-butadiene, and nickel. These emissions have detrimental effects on both human health and the environment. For instance, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide particles emitted from factories and power plants can create acid rain, which damages ecosystems, water sources, crops, and even buildings.
The Clean Air Council specifically highlights the impact of fracking-related infrastructure, steelmaking plants, petrochemical plants, and hazardous waste sites. These operations release pollutants at every stage, from production and extraction to processing and distribution. Similarly, the natural gas, plastic, chemical, electric generation, and waste disposal industries can generate hazardous waste that, if not properly disposed of, can lead to significant air pollution.
In addition to the direct emissions from industrial processes, the transportation and manufacturing sectors are also major contributors to air pollution. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and oil, in vehicles, airplanes, and factories remains a primary source of harmful substances in the air.
The Clean Air Act in the United States has helped reduce emissions from transportation, power plants, and manufacturing. However, it is important to acknowledge the existence of environmental racism, where communities of color are disproportionately affected by air pollution due to discriminatory policies and practices that locate polluting industries and highways closer to these communities.
Air Pollutants: Albedo's Warming and Cooling Effects Explained
You may want to see also

Vehicle emissions
The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of air pollution, and vehicles that run on fossil fuels are a primary contributor. Cars, trucks, buses, boats, ships, and locomotives are all significant sources of air pollution. Mobile sources, such as these vehicles, account for more than half of all air pollution in the United States, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
The link between air pollution and cars was first established in the early 1950s by a California researcher who attributed the smoggy skies over Los Angeles to pollutants from traffic. Since then, efforts to reduce vehicle emissions have been implemented, particularly by the EPA, which has set stringent emissions standards for various types of vehicles and engines. These standards include limits on the amount of sulfur in gasoline, which enhances the effectiveness of emissions reduction technologies. The EPA also has programs and standards that encourage investments in clean vehicle and engine technology.
The positive impact of these regulations is evident, as new cars, SUVs, and pickup trucks are now approximately 99% cleaner for common pollutants compared to 1970 models. Heavy-duty trucks and buses have also shown significant improvements, with a 99% reduction in pollutants. Additionally, the phase-out of lead in gasoline starting in the 1970s led to a 94% decrease in lead levels in the air between 1980 and 1999.
Despite these improvements, there is still work to be done, especially in reducing emissions from heavy-duty trucks, off-road vehicles, and equipment used in construction, agriculture, and cargo handling. These vehicles have varying applications and duty cycles, making emissions reduction more complex. However, with continued efforts and investments in clean vehicle technology, further reductions in vehicle emissions are achievable.
China's Fossil Fuel Pollution: A Troubling Reality
You may want to see also

Household products
The major man-made cause of air pollution is the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and oil. This includes emissions from vehicles, airplanes, power plants, and factories. However, household products also significantly contribute to air pollution, and this has often been overlooked.
A wide range of household products, from paints to personal care products, emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air. VOCs are derived from petroleum and are found in many consumer goods. These compounds are released into the air when liquids containing them evaporate, when they are sprayed as aerosols, or when items like candles and incense are burned. While some VOCs are toxic and can cause irritation, headaches, and nausea, even nontoxic VOCs can be harmful. When exposed to other types of air pollution, VOCs can produce ozone, triggering asthma attacks. VOCs exposed to sunlight create particulate matter, which has been linked to heart attacks and premature death.
Common household products that emit VOCs include:
- Paints and printing inks
- Cleaning products
- Air fresheners
- Personal care products such as perfumes, deodorants, soaps, shampoos, and nail polishes
- Disinfectants
- Glues
- Hair sprays
The impact of household products on air pollution has been underestimated, and it is now recognized that these products can contribute as much to ozone and fine particulate matter in the atmosphere as emissions from burning gasoline or diesel fuel. In fact, a study found that household products were responsible for 38% of VOC emissions, compared to 33% for gasoline and diesel emissions.
The problem of VOCs from household products is particularly acute indoors, where VOC concentrations can be up to seven times higher than outdoors. This has implications for indoor air quality and public health, especially as the effects of VOCs can be compounded when exposed to other types of air pollution.
While regulations on VOCs exist, they vary and often focus on ground-level ozone rather than fine particulate matter. More research is needed to understand which VOCs are most problematic and to develop effective strategies to reduce their impact on air pollution.
Birth Defects: Pollution's Annual Toll
You may want to see also

Agriculture
The major man-made causes of air pollution include mobile sources such as cars, buses, planes, trucks, and trains; stationary sources like power plants, oil refineries, industrial facilities, and factories; area sources, including agricultural areas, cities, and wood-burning fireplaces; and natural sources such as wildfires, volcanoes, and wind-blown dust. Fossil fuel combustion, particularly from vehicles, airplanes, power plants, and factories, is a significant contributor.
The chemicals in fertilisers and insecticides can evaporate or be blown off course, contaminating the local atmosphere. Livestock, particularly cows, sheep, and other ruminants, produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Additionally, their manure generates ammonia and hydrogen sulphide. Ammonia can react with other airborne contaminants to form hazardous aerosols, while hydrogen sulphide is a relatively under-reported greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
The concentration of animals in confined spaces, such as factory farms, intensifies the pollution generated. The use of machinery in agriculture, while increasing efficiency, also contributes to air pollution through emissions. Stubble burning, a common practice in Asia, involves burning crop residue after harvest to clear fields for the next season. This practice produces significant air pollution, with strong winds carrying the smoke over long distances, affecting people far from the source.
The impact of air pollution on agriculture itself cannot be understated. Poor air quality can lead to reduced crop yields, damaged crops, and negative effects on plant growth. Ground-level ozone pollution, in particular, is expected to decrease staple crop yields by 26% by 2030, posing a significant threat to global food security. The bidirectional relationship between agriculture and air pollution underscores the urgency of adopting sustainable agricultural practices and reducing air pollution.
Nuclear Accidents: Pollution, Prevention, and Preparedness
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The major man-made cause of air pollution is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and oil. This includes vehicle emissions, airplanes, power plants, and factories.
Other man-made sources of air pollution include cigarette and e-cigarette smoke, household combustion devices, industrial facilities, agricultural emissions, and waste incineration.
Air pollution can cause respiratory and heart illnesses, strokes, lung cancer, and acute and chronic respiratory diseases. It can also irritate the eyes, nose, and throat and increase the chances of skin allergies.
Air pollution can lead to acid rain, which damages plants, degrades water quality, harms crops, and causes buildings and monuments to decay. It also contributes to climate change, ozone depletion, and habitat degradation.



















