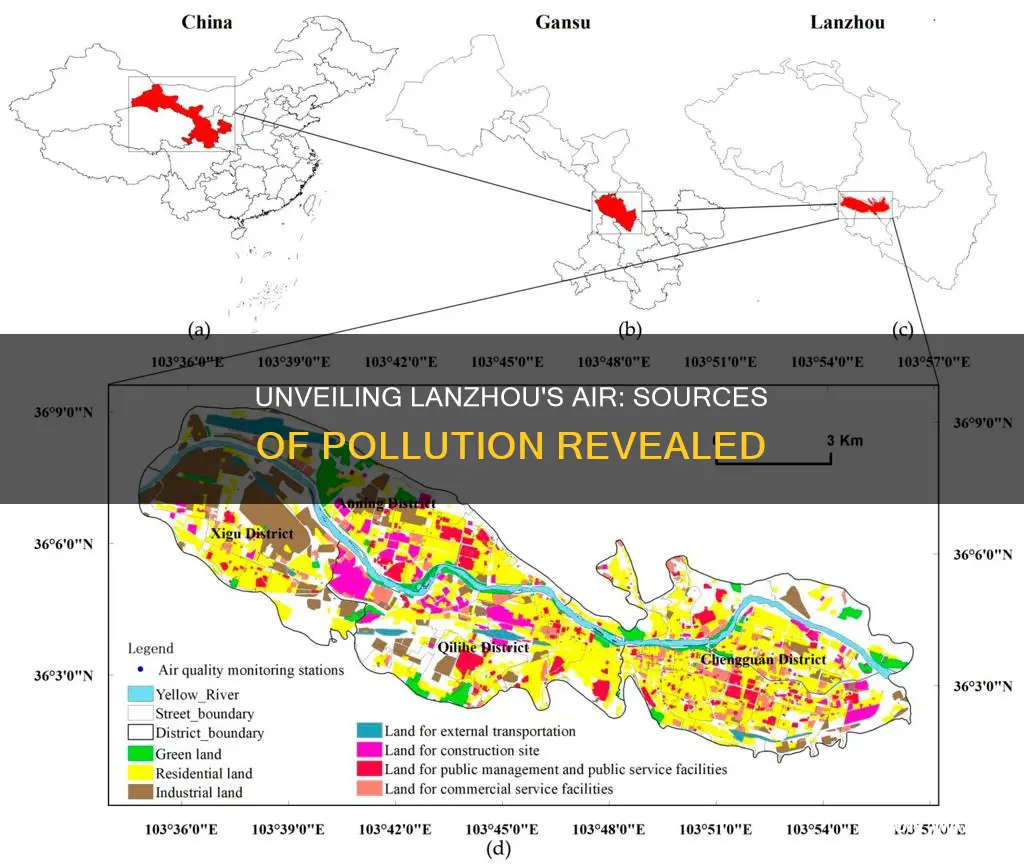
Lanzhou, a city in China, faces significant air pollution challenges, which have detrimental effects on the environment and public health. The primary causes of air pollution in Lanzhou are complex and multifaceted. Industrial emissions from factories and power plants are a major contributor, releasing pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter into the atmosphere. Vehicle emissions from the city's growing number of cars and trucks also play a significant role, emitting pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. Additionally, construction activities and the burning of fossil fuels for heating contribute to the city's air pollution levels. Understanding these causes is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat air pollution and improve the air quality in Lanzhou.
What You'll Learn
- Industrial Emissions: Factories and power plants release pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
- Vehicle Exhaust: Cars, trucks, and buses emit harmful gases, especially in densely populated areas
- Residential Heating: Burning coal and wood for warmth contributes to air pollution in colder regions
- Agricultural Activities: Pesticide use and livestock farming release ammonia and other gases
- Construction Dust: Construction sites generate fine particles from dust, affecting air quality in urban settings

Industrial Emissions: Factories and power plants release pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
The air quality in Lanzhou, a city in China's Gansu Province, has been a growing concern due to the significant industrial activities in the region. One of the primary contributors to this issue is the emissions from factories and power plants, which release a range of pollutants into the atmosphere. These industrial sources are a major concern as they directly impact the health and well-being of the local population and the environment.
Factories in Lanzhou, particularly those in the heavy industries, emit large amounts of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). These gases are released during the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, in industrial processes. Sulfur dioxide is a highly reactive gas that can react with other substances in the atmosphere, forming acidic compounds. When these compounds return to the earth's surface as rain or fog, they can cause acid rain, which has detrimental effects on ecosystems, agriculture, and even buildings. Nitrogen oxides, on the other hand, are a group of highly reactive gases that contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. This smog not only reduces visibility but also poses health risks, especially for individuals with respiratory conditions.
Power plants, both coal-fired and those using other energy sources, play a significant role in air pollution. Coal combustion in power plants releases a substantial amount of SO2 and NOx. These emissions are further exacerbated by the lack of proper emission control technologies in some facilities. As a result, the air in Lanzhou often reaches levels of pollution that exceed national and international standards, making it one of the most polluted cities in China.
The impact of these industrial emissions is far-reaching. It contributes to the formation of fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which is a major concern for public health. Inhaling PM2.5 can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, and it is especially harmful to vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions. Moreover, the pollutants released by factories and power plants can have long-term environmental consequences, including the degradation of air quality, water pollution, and the destruction of local ecosystems.
Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach. Implementing stricter emission standards and regulations for industries is essential. Additionally, encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies, such as those that reduce the use of fossil fuels and capture pollutants, can significantly improve air quality. Regular monitoring and public awareness campaigns can also help in tracking and mitigating the impact of industrial emissions on Lanzhou's air pollution levels.
Unveiling Water's Dark Secret: Diseases Uncovered by Pollution
You may want to see also

Vehicle Exhaust: Cars, trucks, and buses emit harmful gases, especially in densely populated areas
The air quality in Lanzhou, a city in northwestern China, has been a growing concern due to various factors, with vehicle exhaust being a significant contributor to the city's air pollution. Lanzhou's heavy reliance on transportation and dense population make it particularly susceptible to the harmful effects of vehicle emissions.
Cars, trucks, and buses are the primary sources of vehicle exhaust in the city. These vehicles emit a range of pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM). The combustion of fossil fuels in vehicle engines releases these gases, which can have detrimental effects on both the environment and human health.
In densely populated areas, the concentration of vehicle exhaust is particularly high. As traffic flows through the city, the pollutants from vehicle emissions accumulate in the air, leading to poor air quality. This is especially true during rush hours when traffic congestion is at its peak, causing a higher volume of vehicles to emit pollutants in a confined space. The dense population of Lanzhou means that these emissions have a direct impact on the health and well-being of its residents.
The harmful gases emitted by vehicles can have severe consequences. Nitrogen oxides, for instance, contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog, which can cause respiratory issues and aggravate existing health conditions. Carbon monoxide, another harmful gas, is toxic and can lead to headaches, dizziness, and even death in severe cases. VOCs, when combined with sunlight, form ground-level ozone and can also contribute to the formation of smog, reducing visibility and causing respiratory problems.
To address this issue, implementing stricter vehicle emission standards and promoting the use of cleaner technologies is essential. Encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles, hybrid engines, and regular vehicle maintenance can significantly reduce the emission of harmful gases. Additionally, improving public transportation systems and encouraging the use of bicycles or walking in urban areas can help decrease the number of vehicles on the road, thereby improving air quality in Lanzhou.
Ocean's Deadly Embrace: Pollution's Role in Species Extinction
You may want to see also

Residential Heating: Burning coal and wood for warmth contributes to air pollution in colder regions
In colder regions, residential heating is a significant contributor to air pollution, particularly in areas where coal and wood are commonly used as fuel sources. The burning of these solid fuels releases a myriad of pollutants into the atmosphere, posing serious health risks to both the environment and local populations.
Coal, a traditional and widely available energy source, is often burned in inefficient stoves and fireplaces, especially in rural areas. When coal is burned, it emits a range of harmful substances, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These pollutants can have detrimental effects on human health, leading to respiratory issues, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature death. Moreover, the incomplete combustion of coal can result in the release of carbon monoxide, a toxic gas that can cause asphyxiation.
Wood-burning stoves and fireplaces, while often considered more environmentally friendly, are not without their drawbacks. While wood is a renewable resource, the burning process can still release fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air. These pollutants can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, causing irritation, inflammation, and reduced lung function. Additionally, the collection and burning of wood often involve deforestation, which can have long-term ecological consequences.
The impact of residential heating on air quality is particularly pronounced in colder seasons when the demand for warmth increases. As temperatures drop, people tend to use more fuel for heating, leading to a higher concentration of pollutants in the air. This is especially critical in densely populated urban areas where the collective impact of numerous heating sources can significantly degrade air quality.
Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach. Encouraging the adoption of cleaner heating technologies, such as electric or solar-powered heating systems, can significantly reduce the reliance on coal and wood. Additionally, improving the efficiency of existing stoves and fireplaces through proper ventilation and combustion control can help minimize the release of pollutants. Public awareness campaigns can also educate residents about the environmental and health impacts of their heating choices, promoting more sustainable practices.
Unveiling the Chemical Culprits: Understanding Air Pollution's Complex Composition
You may want to see also

Agricultural Activities: Pesticide use and livestock farming release ammonia and other gases
Agricultural practices play a significant role in air pollution, particularly in urban areas like Lanzhou, where rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to complex environmental challenges. One of the primary contributors to air pollution in this context is the use of pesticides and the management of livestock farming.
Pesticides, designed to protect crops from pests and diseases, often contain chemicals that can have detrimental effects on the environment. When these chemicals are applied to fields, they can volatilize and transform into gaseous compounds, releasing toxic substances into the air. For instance, organophosphate pesticides, commonly used in agriculture, can release phosphine gas, a highly toxic substance that poses severe health risks to both humans and animals. These gases contribute to the formation of smog and ground-level ozone, which are major components of air pollution.
Livestock farming, a crucial sector in agriculture, also contributes significantly to air pollution. Animal waste, particularly from large-scale intensive farming, releases ammonia and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Ammonia, a colorless gas with a sharp smell, is highly toxic and can cause respiratory issues and eye irritation. Livestock farming also generates large amounts of manure, which, when stored or managed improperly, can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, further exacerbating air pollution.
The impact of these agricultural activities is twofold. Firstly, the release of ammonia and VOCs contributes to the formation of secondary pollutants, such as particulate matter and ground-level ozone, which are harmful to human health and the environment. These pollutants can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, and they also contribute to the formation of acid rain, which damages ecosystems and infrastructure. Secondly, the use of pesticides and the intensive management of livestock farming can lead to soil degradation and water pollution, further exacerbating the environmental impact.
Addressing air pollution in Lanzhou requires a comprehensive approach that includes sustainable agricultural practices. This involves promoting organic farming methods that minimize the use of synthetic pesticides, implementing better waste management systems for livestock farming to reduce ammonia and methane emissions, and adopting precision agriculture techniques to optimize resource use and reduce environmental impact. By focusing on these agricultural aspects, the city can work towards mitigating air pollution and improving the overall environmental quality.
Unveiling Land Pollution's Origins: Causes and Solutions Revealed
You may want to see also

Construction Dust: Construction sites generate fine particles from dust, affecting air quality in urban settings
Construction activities have a significant impact on air quality, particularly in urban areas, due to the generation of fine particles known as construction dust. This type of pollution is a major concern for environmental health and can have detrimental effects on both the environment and human health.
When construction work is carried out, various processes contribute to the creation of dust. One primary source is the breakdown of materials such as concrete, asphalt, and rocks, which generate tiny particles that remain suspended in the air. These particles are often invisible to the naked eye but can be inhaled, leading to respiratory issues. Additionally, the cutting, grinding, and drilling of materials release dust into the atmosphere, further exacerbating air pollution.
The impact of construction dust is twofold. Firstly, it directly affects the surrounding air quality, making it more polluted and potentially hazardous for nearby residents and workers. Fine particles can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, causing irritation, inflammation, and even long-term health complications. Secondly, construction sites often have a higher concentration of other pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals, which, when combined with dust, create a complex mixture that can have severe health implications.
To mitigate the effects of construction dust, several measures can be implemented. Firstly, construction companies should invest in advanced dust control systems, such as water sprays, dust suppressants, and air filtration systems, to capture and reduce the emission of fine particles. Regular cleaning and maintenance of construction equipment and vehicles can also help minimize dust generation. Furthermore, implementing strict safety protocols and providing personal protective equipment (PPE) to workers can significantly reduce the inhalation of dust, protecting both the workforce and the surrounding community.
In urban settings, where space is limited and construction activities are prevalent, it is crucial to prioritize air quality management. Local authorities and construction companies must work together to develop and enforce regulations that ensure construction sites adhere to dust control standards. This includes regular monitoring of air quality, implementing dust management plans, and penalizing non-compliance to maintain a healthier environment for all.
Biomass Energy: A Quiet Power or a Noisy Concern?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The main causes of air pollution in Lanzhou, China, include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and residential heating. Industrial activities, particularly those involving coal combustion and chemical production, release significant amounts of pollutants into the air. Vehicle emissions from the city's dense traffic contribute to air pollution, especially during the colder months when heating demands increase.
Industrial emissions are a major concern in Lanzhou. Coal-fired power plants and steel mills, along with other heavy industries, release sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These pollutants can lead to smog formation and have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
Yes, air pollution levels tend to peak during the winter months. This is primarily due to the combination of colder temperatures and increased energy demands for heating. Residential heating, often relying on coal or biomass, contributes significantly to air pollution during this season.
The local government has implemented various strategies to address air pollution. These include promoting cleaner industrial technologies, encouraging the use of electric vehicles, and improving public transportation systems. Additionally, efforts are being made to enhance energy efficiency and reduce the reliance on coal for heating.







