Pollution is a pressing issue that affects all parts of the planet and has widespread consequences on human and environmental health. It is caused by a range of factors, including industrial waste, agricultural practices, and the use of fossil fuels, and can lead to contaminated water, poor air quality, and the loss of biodiversity. With approximately 19 million premature deaths estimated to occur annually due to pollution, it is essential to understand its causes to implement effective solutions. This project aims to explore the diverse sources and types of pollution, assess their impacts, and investigate potential strategies for combating this global challenge.
Characteristics and Values of Causes of Pollution
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Air pollution | Burning of fossil fuels, industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, household garbage burning, agricultural emissions, oil spills, and more |
| Water pollution | Industrial waste, agricultural chemicals and pesticides, oil spills, human and animal waste, rising temperatures, and more |
| Land pollution | Mining, extraction, construction, littering, waste disposal, urbanization, agriculture, and more |
| Marine pollution | Not enough information |
What You'll Learn

Industrial emissions and fossil fuels
The combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and petroleum, releases harmful gases like nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides, and carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to the formation of smog, a secondary pollutant that occurs when emissions from fossil fuel combustion react with sunlight. Fossil fuels are also responsible for the release of chlorofluorocarbons, halons, and hydrochlorofluorocarbons, which deplete the ozone layer, allowing harmful ultraviolet rays to reach the Earth's surface.
In the United States, burning fossil fuels for electricity, heat, and transportation accounts for about 74% of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions. The transportation sector, which relies heavily on petroleum-based fuels, is the largest contributor to direct greenhouse gas emissions. The industrial sector, which includes energy-intensive industries such as manufacturing and construction, is the third-largest source of direct emissions. However, when indirect emissions from electricity use are considered, industrial activities account for a much larger share of greenhouse gas emissions.
To mitigate the impact of industrial emissions and fossil fuels on air pollution, several measures can be implemented. These include improving energy efficiency, transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal, and adopting fuel substitution, such as replacing petrol and diesel with Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles. Additionally, regulatory frameworks and infrastructure improvements are crucial for ensuring environmentally acceptable solutions for waste management and industrial waste disposal.
It is important to address the issue of industrial emissions and fossil fuels to reduce their harmful effects on human health and the environment. By implementing the above measures and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources, we can improve air quality and mitigate the impact of climate change.
Corporations' Responsibility in Global Pollution: 71% and Counting
You may want to see also

Agriculture and pesticides
Pesticides can contaminate the air, water, and soil, leading to pollution and adverse effects on human health. They can enter the body through inhalation, oral consumption of contaminated food or water, and skin exposure. The impact of pesticides on human health depends on their toxicity and the length and magnitude of exposure. Farm workers and their families are at the highest risk of exposure to agricultural pesticides through direct contact. Additionally, children are more susceptible to the harmful effects of pesticides due to their developing immune systems.
Pesticides can persist in the environment for extended periods, especially older, cheaper ones that have been banned in developed countries but are still used in developing nations. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are compounds that resist degradation and remain in the environment beyond their intended lifespan. Some pesticides, such as aldrin, chlordane, DDT, and dieldrin, are classified as POPs. These chemicals can travel long distances through the atmosphere, deposit in remote regions, and bioaccumulate in organisms, increasing in concentration up to 70,000 times their original levels.
The use of pesticides in agriculture can also have unintended consequences on other species. Over time, pests can develop resistance to pesticides, and their effects on non-target organisms can facilitate the resurgence of certain pests. Additionally, the repeated application of pesticides can have detrimental effects on biodiversity and ecosystems, with over 60% of global agricultural land at risk of pesticide pollution, and a third of this land located in high-biodiversity regions.
To mitigate the harmful effects of pesticides, alternative methods such as integrated pest management and sustainable agriculture techniques like polyculture are recommended. These approaches aim to reduce the heavy reliance on pesticides and promote more ecologically sound practices. Additionally, advanced oxidation processes have been successful in removing pesticide residues from fruits and vegetables, and wastewater treatment technologies are also being employed to address the issue of pesticide pollution.
Paper Pollution: Understanding Its Environmental Impact
You may want to see also

Mining and extraction
One of the major environmental concerns associated with mining is water pollution. Mining requires a significant amount of water for processing ore, and it also generates large quantities of waste rock and tailings, which can contaminate water sources. Tailings are the materials left behind after the valuable fraction of material has been extracted, and they often contain toxic substances such as cyanide, mercury, arsenic, and heavy metals. These tailings are usually stored in large dams to prevent environmental damage, but leakages can occur, leading to water pollution.
The impact of mining on water sources is a growing concern, especially in regions like Canada, where the mineral industry generates significant amounts of waste rock and tailings annually. In British Columbia, waste rock and exposed bedrock walls are the primary sources of metal pollution in waterways. Similarly, in North America, tailings represent a significant source of heavy metal contamination in rivers and lakes.
Another issue with mining is the high water usage associated with it. While mining may only account for a small percentage of total national water use in some countries, the quality of the water used is often poor, and the discharge of contaminated mine effluent further exacerbates water pollution. Additionally, mining activities can disturb water bodies during exploration and construction, leading to sedimentation and other long-term impacts that may need to be managed for decades or even centuries.
To address these environmental challenges, modern mining programs aim to remove and reuse harmful chemicals, and more sustainable mining techniques are being explored. These include underground mining, phytomining, and asteroid mining, which have the potential to be less invasive and generate less waste.
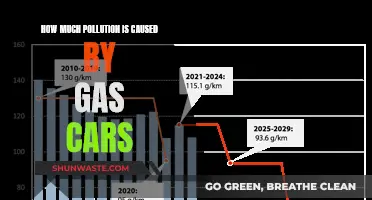
Gas Cars: Major Polluters on Our Roads?
You may want to see also

Poor waste management
Improper waste disposal methods, such as open-air incineration, uncontrolled dumping, and non-engineered landfills, lead to air pollution. The burning of waste releases harmful gases, including methane, which contribute to global climate change. Open and unsanitary landfills further contribute to the contamination of drinking water sources, causing infections and transmitting diseases.
The disposal of hazardous waste, such as electronic waste and industrial garbage, poses a significant risk to ecosystems and the health of urban residents. Electronic waste, or e-waste, is the fastest-growing waste stream, containing complex and hazardous substances. The improper handling of such waste can lead to the release of dangerous chemicals and pollutants into the environment, impacting both human and animal life.
In addition, the breakdown of waste in landfills can result in the release of methane and other greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming and climate change. Improper waste management practices can also lead to resource depletion, as recyclable materials are lost, and environmental pollution, as waste seeps into the soil and water sources.
To address these issues, it is essential to prioritize waste reduction and proper waste management practices. This includes minimizing waste generation, recycling, and recovering materials and energy from waste. Implementing sustainable waste management practices can help mitigate adverse health and environmental impacts, conserve resources, and improve overall sustainability.
Power Sources: Pollution's Main Culprits Revealed
You may want to see also

Climate change
Air pollution and climate change are primarily caused by burning fossil fuels, and they share many of the same solutions. The causes of climate change are often the same as the causes of air pollution: transport, the power sector, industrial emissions, agriculture, crop burning, and residential heating. The same pollutants that degrade air quality also exacerbate the climate crisis and damage the environment. These super pollutants or Short-Lived Climate Pollutants (SLCPs) include methane, black carbon (soot), and tropospheric ozone. They contribute to global warming, cause local environmental degradation, and harm ecosystems, biodiversity, and human health.
Tropospheric ozone and methane are also greenhouse gases, which trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere and cause global warming. The recent increase in greenhouse gas pollution is trapping excess heat and causing the climate to warm. Greenhouse gases remain in the atmosphere for years, and their warming effect is larger than the cooling effect of aerosols. Carbon dioxide comes from combusting fossil fuels, and methane comes from natural and industrial sources, including large amounts released during oil and gas drilling.
The effects of climate change on air quality will continue to vary by region. In many areas of the United States, climate change is expected to worsen harmful ground-level ozone, increase people's exposure to allergens like pollen, and contribute to worsening air quality. Climate change can also decrease visibility and make it harder to see into the distance. Changes in the amount of outdoor air pollutants can also affect indoor air quality. Increases in outside air pollutants, such as ozone and particulate matter, could lead to higher indoor exposures. Mold, dust mites, bacteria, and other indoor pollutants may increase as climate change-related precipitation and storms become more frequent and intense.
Regulatory initiatives, partnership programs, and individual actions can all help reduce air pollutants that harm human health, as well as greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. Cleaning our air is one of the most immediate ways to protect the planet and improve health.
Livestock Pollution: How Does it Harm the Environment?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The combustion of fossil fuels, industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural activities are some of the major causes of air pollution.
Water pollution is caused by industrial waste, agricultural waste, oil spills and leaks, and rising temperatures due to global warming.
Land pollution is caused by litter, waste, urbanization, construction, mining, extraction, and agriculture.