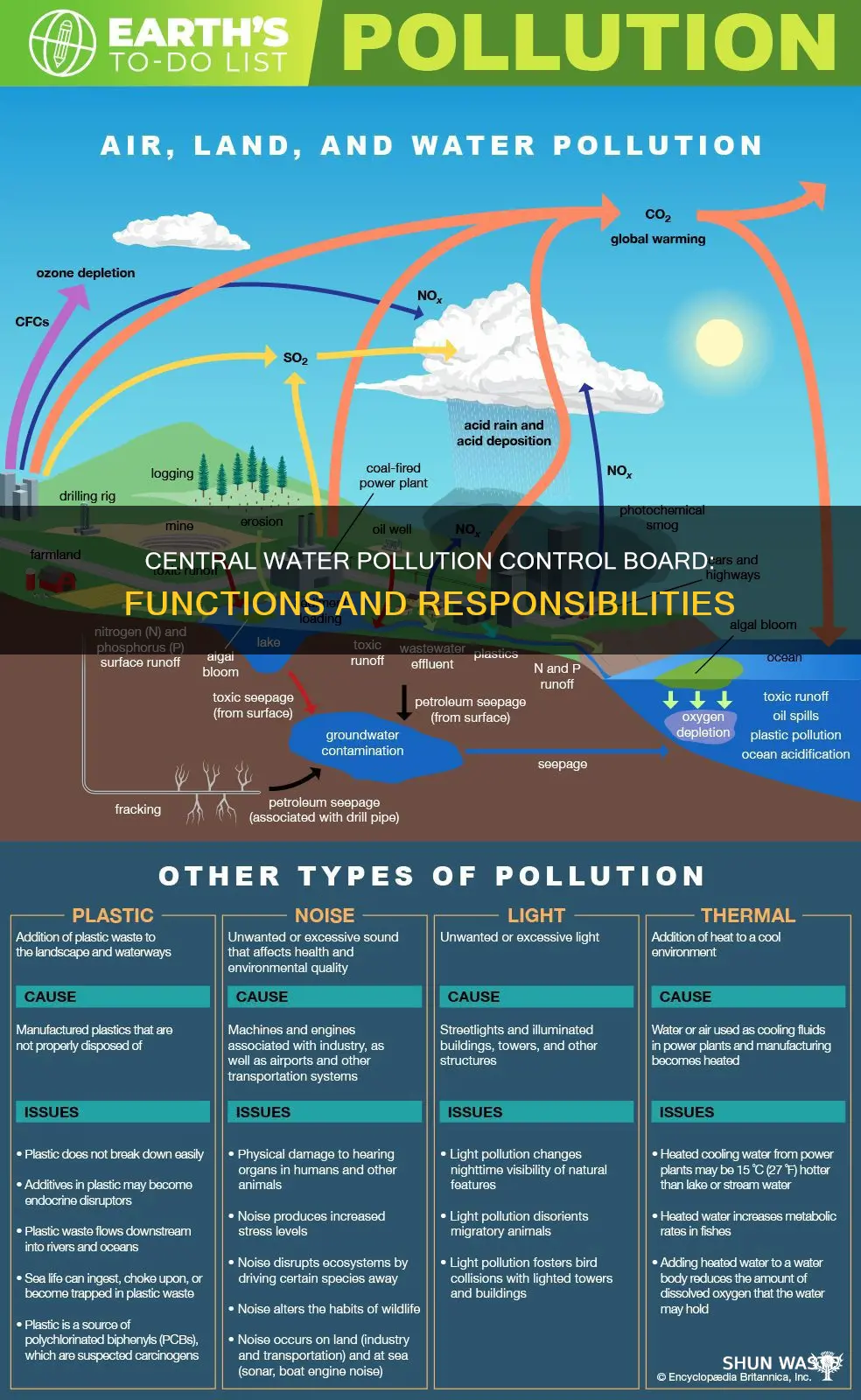
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is a statutory organisation that was established in September 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. The CPCB is responsible for promoting the cleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the states by preventing, controlling, and abating water pollution. It also works to improve air quality and prevent, control, or abate air pollution in the country. The CPCB collects and maintains data on water and air quality, and identifies areas for improvement. It also works with industries and governments at all levels to implement pollution prevention programs and energy conservation efforts. The CPCB has approximately 500 full-time employees, including engineers, scientists, and environmental protection specialists, and is led by a chairperson appointed by the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet of the Government of India.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Year of establishment | 1974 |
| Parent Act | The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 |
| Governing Body | Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (Mo.E.F.C.C.) |
| Functions | To promote cleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the States by prevention, control and abatement of water pollution |
| To improve the quality of air and to prevent, control or abate air pollution in the country | |
| To collect, collate and disseminate technical and statistical data relating to water pollution | |
| To advise the Central Government on matters related to control and abatement of air and water pollution | |
| To coordinate the activities of the State Pollution Control Boards by providing technical assistance and guidance and also resolves disputes among them | |
| To formulate Minimal National Standards (MINAS) for various industries with regards to effluent discharge, emissions, noise levels, and solid waste | |
| To develop a thorough media campaign to manage and stop water contamination | |
| To work with industries and all levels of government in a wide variety of voluntary pollution prevention programs and energy conservation efforts | |
| To evaluate or modify the precision of the air quality stations | |
| To establish the objective requirements for water and air quality | |
| To manage environmental data statistics in which air quality data and water quality data comes through |
What You'll Learn

Advising the central government on water pollution prevention and control
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is a statutory organisation constituted under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. It was established to advise and assist the central government on matters relating to the prevention and control of water and air pollution.
The CPCB plays a crucial role in generating relevant data, providing scientific information, and offering technical inputs for the formation of effective national policies and programs aimed at tackling water pollution. It collects, collates, and disseminates technical and statistical data related to water pollution, including water quality monitoring. This data is essential for informed decision-making and policy formulation by the central government.
The CPCB also works closely with the State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) to coordinate their activities and provide guidance. They assist the SPCBs in conducting investigations and studies, offering technical assistance, and resolving disputes. The CPCB ensures that the SPCBs are equipped with the necessary resources and expertise to enforce environmental laws and regulations within their respective states.
Additionally, the CPCB plays a vital role in organising awareness programmes and training initiatives. They collaborate with various agencies and stakeholders to educate the public about pollution prevention, control, and the importance of environmental protection. By fostering a culture of environmental awareness and responsibility, the CPCB empowers individuals to actively contribute to pollution reduction efforts.
The CPCB's role in advising the central government is not limited to providing data and technical insights but also extends to policy formulation and implementation. They work closely with the government to develop and implement comprehensive plans for the prevention, control, and abatement of water pollution. This includes setting standards for wastewater treatment, effluent discharge, and commercial pollutants, ensuring that industries adhere to environmental regulations, and promoting sustainable practices.
In summary, the CPCB serves as a critical advisor to the central government, providing expertise, data, and technical guidance to inform policy formulation and implementation. Their efforts are focused on preventing and controlling water pollution, protecting water resources, and ensuring sustainable environmental practices. By working closely with the government and coordinating with the SPCBs, the CPCB plays a pivotal role in safeguarding India's water security and ecological balance.
Ocean Pollution: Water Crisis and Solutions
You may want to see also

Monitoring and maintaining water quality data
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is a statutory organisation constituted in September 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. The CPCB is tasked with monitoring and maintaining water quality data to promote the cleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the states by preventing, controlling, and abating water pollution.
The CPCB collects, collates, and disseminates technical and statistical data relating to water pollution. It measures and maintains water quality data, with the quality level of rivers and ponds being major fields that come under the water quality data criteria. The CPCB also runs nationwide programmes of ambient air quality monitoring, such as the National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP), which help inform its water quality monitoring efforts.
The CPCB plays a crucial role in generating relevant data, providing scientific information, and rendering technical inputs for the formation of national policies and programmes aimed at improving water quality. It works with industries and all levels of government in various pollution prevention programmes and energy conservation efforts. The CPCB advises the central government on preventing and reducing water contamination and provides technical assistance and guidance to the State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs), helping to resolve disputes among them.
The CPCB also has the power to carry out the duties of a State Pollution Control Board if one of its directives is not followed. It can make instructions for the SPCBs to carry out and establish, alter, or repeal stream regulations after consulting with the relevant state government. The CPCB is responsible for planning and carrying out national programmes to prevent, control, or reduce water pollution, and it plays a key role in developing media campaigns to raise awareness about water pollution and promote environmental awareness.
Sewage's Sinister Impact: Polluting Our Precious Waterways
You may want to see also

Promoting the cleanliness of streams and wells
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is a statutory organisation constituted in September 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. The CPCB has been tasked with promoting the cleanliness of streams and wells in different areas of the states by preventing, controlling, and abating water pollution.
To achieve this, the CPCB collects, collates, and disseminates technical and statistical data relating to water pollution. It measures and maintains water quality data, with river and pond quality being the major fields that come under the water quality data criteria. The CPCB also runs nationwide programmes of ambient air quality monitoring, such as the National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP). This helps to determine the present air quality status and trends, and to control and regulate pollution from industries and other sources to meet air quality standards.
The CPCB also works with industries and all levels of government in a wide variety of voluntary pollution prevention programmes and energy conservation efforts. It advises the central government on matters related to the prevention and control of water and air pollution, and it coordinates the activities of the State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) by providing technical assistance and guidance, as well as resolving disputes among them.
The CPCB has the authority to make instructions to carry out all the State Board's duties, and each State Board is bound by these instructions. The CPCB also has the task of developing a thorough media campaign to manage and stop water contamination. It plays a role in generating relevant data, providing scientific information, and rendering technical inputs for the formation of national policies and programs to promote awareness at different levels of the government and public.
The CPCB also formulates the Minimal National Standards (MINAS) for various industry categories regarding their effluent discharge (water pollutants), emissions (air pollutants), noise levels, and solid waste. These standards are required to be adopted by State Governments as minimal standards.
Water Pollution: Strategies for Effective Control and Sustainability
You may want to see also

Developing national standards for industries' effluent discharge
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is a statutory organisation that was constituted in September 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act 1974. The CPCB has been tasked with developing national standards for industries' effluent discharge. Effluents refer to the wastewater or liquid waste that is discharged from industrial processes, which can contain a variety of pollutants. Developing national standards for effluent discharge is crucial to protect water resources and ensure environmental health.
The CPCB plays a vital role in the abatement and control of pollution in India. It generates relevant data, provides scientific information, and offers technical inputs for the formation of national policies and programs related to pollution control. The CPCB also works closely with industries and governments at all levels to implement various pollution prevention programs and energy conservation initiatives.
One of the key functions of the CPCB is to advise the central government on matters related to the prevention, control, and abatement of water and air pollution. The CPCB provides technical services to the Ministry of Environment and Forests, assisting in the implementation of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. It also coordinates with and guides the State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs), helping to resolve disputes and ensure consistent application of standards across the country.
The CPCB has the authority to establish requirements and guidelines for effluent discharge from industries. These guidelines are known as Minimal National Standards (MINAS) and are specific to different categories of industries. The MINAS set the minimum acceptable levels of effluent discharge, covering water pollutants, emissions (air pollutants), noise levels, and solid waste. State governments are required to adopt these standards as their minimum standards, ensuring a consistent level of environmental protection across the country.
The development of national standards for effluent discharge involves several key steps. Firstly, the CPCB conducts research and assessments to identify the sources and types of pollutants present in industrial effluents. This includes monitoring pollution levels and maintaining records of environmental data. The CPCB also collaborates with SPCBs, industries, and other stakeholders to gather information and ensure a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
The CPCB then uses this data to formulate specific guidelines for each category of industry. These guidelines may include standards for treatment processes, discharge limits, and allowable concentrations of pollutants in effluents. The CPCB may also provide manuals, codes, and guidance documents to assist industries in achieving compliance with the national standards.
Dispose of Polluted Water in Oxygen: A Guide
You may want to see also

Coordinating the activities of the State Pollution Control Boards
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is a statutory organisation constituted in September 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. The CPCB is tasked with coordinating the activities of the State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) and providing them with technical assistance and guidance. It also helps resolve disputes among the SPCBs.
The CPCB plays a crucial role in ensuring the effective implementation of legislation relating to the prevention and control of environmental pollution. It advises the central government on matters related to the control and abatement of water and air pollution and works closely with the SPCBs to address these issues.
The SPCBs, established by state governments, are responsible for enforcing environmental laws and regulations within their respective states. They play a pivotal role in India's environmental governance framework by acting as regulatory and advisory bodies. Their primary objective is to prevent, control, and abate environmental pollution, with a focus on air and water pollution.
The SPCBs monitor air and water quality, set environmental standards, and ensure compliance through regular inspections and monitoring of industrial and other activities. They also provide technical assistance, conduct research, and engage in public education and awareness campaigns. By collaborating with the CPCB and other local bodies, the SPCBs help maintain ecological balance and safeguard public health and the environment.
The CPCB supports the SPCBs by providing technical expertise and guidance. It assists the SPCBs in conducting investigations and studies into water contamination and provides direction to address conflicts between active boards. The CPCB also helps the SPCBs in planning and implementing comprehensive programs for the prevention, control, or abatement of pollution.
Water Pollution: A Deadly Threat to Animals
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Central Water Pollution Control Board's primary function is to promote the cleanliness of streams and wells by preventing, controlling, and abating water pollution.
The Central Water Pollution Control Board also advises the central government on matters related to the prevention and control of water and air pollution. It also coordinates the activities of the State Pollution Control Boards, assists them, and helps resolve disputes. It also plays a role in generating relevant data, providing scientific information, and rendering technical inputs for the formation of national policies and programs.
The Central Water Pollution Control Board's functions regarding air pollution include improving air quality and preventing, controlling, or mitigating air pollution in the country. It also evaluates or modifies the precision of air quality stations and monitors air quality through the National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP).







