Lake Okeechobee, the liquid heart of Florida, has been facing pollution issues for decades. The lake's water is polluted with nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, mainly from agricultural runoff and urban development. This has caused harmful algal blooms, known as eutrophication, which threaten the delicate Florida ecosystems, wildlife, and human health. The Army Corps of Engineers has attempted to manage the lake's water levels and reduce the impact of polluted water releases, but the underlying pollution issues remain a concern for conservationists and residents alike. With the lake's pollution affecting downstream waterways and even reaching the oceans, comprehensive solutions are needed to restore Lake Okeechobee's health and mitigate its environmental impacts.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Phosphorus pollution | High |
| Nitrogen pollution | High |
| Agricultural pollution | High |
| Urbanization pollution | High |
| Algal blooms | Blue-green, red tide, electric green |
| Affected areas | St. Lucie River, Indian River Lagoon, San Carlos Bay, Gulf of Mexico, Atlantic Ocean |
| Impact | Harmful to wildlife, pets, and people |
| Solutions | Wastewater treatment, water storage, improved phosphorus flow control |
What You'll Learn

Sources of pollution
Lake Okeechobee, the "liquid heart" of Florida, has been facing pollution issues for several decades. The primary sources of pollution in the lake are:
Agricultural Runoff:
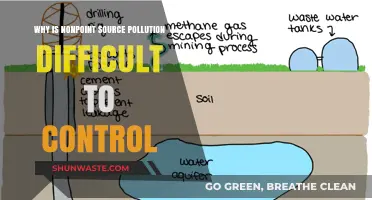
The lake has been heavily polluted by agricultural runoff, particularly from large agricultural operations near the lake, such as Big Sugar and other farmers. Excess nutrients from agriculture, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, are major contributors to harmful algal blooms. Phosphorus, specifically, has been identified as a critical factor in the lake's pollution, with poorly enforced rules to control its flow from agricultural lands.
Urban Development and Wastewater:
Urban development and industrialization have also played a role in the lake's pollution. Inorganic nitrogen levels, influenced by expanding urbanization in Orlando, have been detected in the Kissimmee River, which flows into Lake Okeechobee. Additionally, there is a need for improved wastewater treatment north of the lake, indicating that human waste is another contributing factor to the pollution.
Climate Change and Rainfall:
Climate change and extreme rainfall events have been identified as contributing factors to the prevalence of algal blooms. The management of lake levels, especially during the wet season, is crucial in mitigating the impact of pollution on the lake and its surrounding ecosystems.
Eutrophication and Red Tide:
The pollution in Lake Okeechobee has led to eutrophication, causing blooms of blue-green algae (Microcystis) and red tide (Karenia brevis). These toxic algae blooms threaten the delicate balance of the Everglades ecosystem and have harmful impacts on wildlife, humans, and the economy.
The pollution of Lake Okeechobee has far-reaching consequences, affecting not only the lake itself but also the surrounding rivers, estuaries, and even the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Efforts are currently underway to address the pollution and restore the natural flow of water in the region.
When an Hour and a Half Flies By
You may want to see also

Impact on the environment
Lake Okeechobee, the "liquid heart" of Florida, has been facing pollution issues for decades. The lake's pollution has had significant impacts on the surrounding environment, including the Caloosahatchee River, the St. Lucie River, and the Gulf of Mexico. One of the most pressing concerns is the presence of toxic blue-green algae blooms (Microcystis), which are caused by high levels of phosphorus and nitrogen in the water. These nutrients come from agricultural runoff, urban development, and human waste. When the lake overflows or is drained, the polluted water is released into nearby rivers and estuaries, leading to several environmental issues.
The discharge of polluted water from Lake Okeechobee has resulted in the growth of harmful algal blooms in downstream waterways. These blooms can be toxic to wildlife, pets, and humans. In 2018, for instance, toxic outflows from the lake ravaged native seagrass, which provides habitat for fish and food for manatees. The blooms also have economic impacts, such as losses in the real estate market. Additionally, the release of nutrient-rich water into rivers can lead to an outbreak of blue-green algae, which has been known to kill pets and livestock and cause illness in humans.
The pollution in Lake Okeechobee has also contributed to the decline of the Everglades ecosystem. Historically, water from the lake flowed southward into the Everglades, providing essential nourishment. However, due to changes in the water management system, the lake's water is now redirected through the Lake Okeechobee Waterway, which channels it eastward and westward. This redirection has deprived the Everglades of the freshwater it needs to thrive and has contributed to the struggles of an already fragile ecosystem facing urbanization and pollution.
Furthermore, the pollution in Lake Okeechobee has had indirect effects on Florida Bay and the Atlantic Ocean. The diversion of polluted freshwater has reduced the natural flow of freshwater to Florida Bay, located at the southern tip of peninsular Florida. This has disrupted one of the world's most unique ecosystems. Additionally, the polluted water from the lake eventually makes its way into the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean, where it contributes to red tide blooms. Red tide is a type of algae that occurs naturally but has become more harmful due to pollution. It poses risks to both human health and marine life.
Efforts are being made to address the pollution in Lake Okeechobee and mitigate its environmental impacts. The Lake Okeechobee Watershed Restoration Project and the Lake Okeechobee Component A Reservoir project aim to improve wastewater treatment and water storage north of the lake. Additionally, the Army Corps of Engineers has temporarily halted the release of polluted water from the lake into the Caloosahatchee River to allow the environment to recover. While these initiatives are a step in the right direction, it will take years to undo the damage that has been done to this crucial ecosystem.
Protecting Soil: Preventing Pollution for a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Impact on human health
Lake Okeechobee is the largest lake in Florida and the second-largest in the southeastern United States. The lake has been facing pollution issues for decades, with the primary sources of pollution being agricultural runoff and urban development. High levels of phosphorus and nitrogen from these sources have led to frequent and harmful algal blooms, known as eutrophication, which have impacted not only the lake but also the surrounding environment and human health.
The toxic algae blooms in Lake Okeechobee have resulted in noxious fumes and waterborne poisons that pose significant risks to human health. Inhaling the fumes or coming into contact with contaminated water can lead to illness and, in some cases, have been fatal to both humans and animals. The Florida Department of Health has issued warnings about the potential dangers of blue-green algae in certain areas, urging residents to be vigilant as winds and tides can spread these harmful blooms.
The discharge of polluted water from Lake Okeechobee into nearby rivers and estuaries, such as the Caloosahatchee River and the St. Lucie Estuary, has further exacerbated the impact on human health. These releases of nutrient-rich water have contributed to the growth of harmful algal blooms downstream, affecting the quality of water that comes into contact with humans. The mixing of freshwater with saltwater in these estuaries can also lead to red tide blooms, another type of algae that can cause respiratory issues and illness in humans.
The pollution in Lake Okeechobee has also had indirect effects on human health. For example, the discharge of polluted water into the Everglades, an already struggling ecosystem, has led to the death of wildlife and has impacted the habitat of numerous endangered species. The loss of wildlife and disruption of ecosystems can have long-lasting consequences on human health, including the potential for increased disease transmission and reduced access to essential resources.
Additionally, the economic impacts of Lake Okeechobee's pollution cannot be overlooked. The real estate industry, for instance, has taken a hit, with potential sales being lost due to the unsightly and harmful algal blooms. Tourism and recreational activities in and around the lake may also be affected, potentially impacting the livelihoods of those who depend on these industries.
Efforts are being made to address the pollution in Lake Okeechobee and mitigate its impact on human health. The Lake Okeechobee Watershed Restoration Project and the Lake Okeechobee Component A Reservoir project aim to improve wastewater treatment and water storage north of the lake. While these initiatives are a step in the right direction, it will take time and sustained efforts to restore the lake and fully protect human health in the surrounding areas.
Wetlands: Natural Nitrogen Pollution Filters
You may want to see also

Efforts to combat pollution
Lake Okeechobee, the "liquid heart" of Florida, has been facing pollution issues for several years. The lake's water is routinely discharged into nearby rivers and estuaries, leading to environmental and public health concerns. Efforts to combat this pollution and restore the lake's ecosystem are currently underway.
One key initiative is the Lake Okeechobee System Operating Manual (LOSOM), which aims to manage the lake's water levels and reduce the frequency and impact of discharges. By controlling the water levels, the hope is that the amount of polluted water released into surrounding waterways will be minimized. This is particularly important for the Caloosahatchee River, which often receives large volumes of nutrient-rich water from the lake, leading to harmful algal blooms.
The Army Corps of Engineers, responsible for managing the lake's levels, has taken steps to hold back polluted water from being released. In one instance, they stopped the release of millions of gallons of water daily into the Caloosahatchee River for a period to allow the environment to recover. While these short-term holds provide some relief, long-term solutions are still needed to address the underlying pollution issues.
Another important effort is the Lake Okeechobee Watershed Restoration Project, which focuses on improving wastewater treatment and water storage north of the lake. This project, spearheaded by the South Florida Water Management District, aims to reduce the amount of pollutants entering the lake and improve water quality.
Additionally, there is a push for better enforcement of existing pollution regulations and standards. This includes increasing water-monitoring efforts to accurately identify sources of pollution and ensuring property owners along the lake follow "best management practices" to reduce pollution. The state's Department of Agriculture and Department of Environmental Protection have roles in inspecting and enforcing compliance, and fines of up to $50,000 can be imposed on polluters.
The Blue-Green Algae Task Force is also addressing agriculture, septic systems, and public health issues related to the lake's pollution. While these efforts are ongoing, it will take time and rigorous implementation to restore Lake Okeechobee's ecosystem and protect the health of Floridians and the state's unique wildlife.
Understanding Particle Size: What is PM?
You may want to see also

The role of the Army Corps of Engineers
Lake Okeechobee, the largest lake in Florida and the second-largest in the southeastern United States, has been facing issues with pollution and toxic algae blooms for decades. The Army Corps of Engineers has played a significant role in addressing these issues and managing the lake's water releases to mitigate their environmental impact.
The Army Corps of Engineers is responsible for deciding how and when to release water from Lake Okeechobee, which has a direct impact on the surrounding ecosystems. In the past, water from the lake naturally flowed southward through the Everglades. However, changes to the water management system resulted in the creation of the Lake Okeechobee Waterway, which redirects lake water eastward into the St. Lucie Estuary and westward into the Caloosahatchee River and Estuary.
The release of nutrient-polluted freshwater from Lake Okeechobee into these waterways has led to toxic algae blooms, particularly blue-green algae (Microcystis), which are harmful to both the environment and public health. Excess nutrients, specifically phosphorus and nitrogen, from agricultural operations, human waste, and urbanization, are the primary causes of these algal blooms.
Recognizing the environmental concerns, the Army Corps of Engineers has implemented measures to reduce the negative impacts of water releases. In 2024, the Army Corps temporarily halted the release of millions of gallons of polluted water from Lake Okeechobee into the Caloosahatchee River to allow the environment to recover. They have also announced a new management plan, the Lake Okeechobee System Operating Manual (LOSOM), which aims to reduce water releases into the St. Lucie Estuary and Caloosahatchee River under normal conditions.
The new plan, developed after running 240,000 model runs, is designed to send more water south into the Everglades and less water east and west during the summer months when the risk of algal blooms is highest. While this plan represents an improvement, some critics argue that it does not go far enough in addressing the water management issues in Florida.
In addition to their short-term measures and new management plans, the Army Corps of Engineers also supports long-term restoration projects, such as the Lake Okeechobee Watershed Restoration Project and the Lake Okeechobee Component A Reservoir project, which aim to improve wastewater treatment and water storage north of the lake. These projects are led by the South Florida Water Management District and supported by various organizations, including NASA's Water Resources Program.
Air Pollution: What's the Primary Source?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, Lake Okeechobee is heavily polluted by runoff from agriculture and development in Central and South Florida. Phosphorus and nitrogen from agricultural waste have been identified as the main contributors to the lake's pollution.
The polluted water from Lake Okeechobee has caused toxic algae blooms, which are harmful to both humans and wildlife. These algae blooms have been linked to outbreaks of red tide, which can make humans very ill, especially those with respiratory issues. The pollution has also impacted the growth of seagrasses and oysters in the estuary.
Efforts are being made to clean the polluted lake water through natural filtration systems. The Army Corps of Engineers has also temporarily halted the release of polluted water from Lake Okeechobee into the Caloosahatchee River to allow the environment to recover. Additionally, there are ongoing projects such as the Lake Okeechobee Watershed Restoration Project and the Lake Okeechobee Component A Reservoir project, which aim to improve wastewater treatment and water storage in the area.
To prevent further pollution, it is crucial to reduce the amount of phosphorus and nitrogen entering the lake. This can be achieved through improved wastewater treatment, stricter enforcement of regulations controlling the flow of phosphorus from agricultural lands, and reducing nitrogen inputs from sources such as the Upper Kissimmee River.