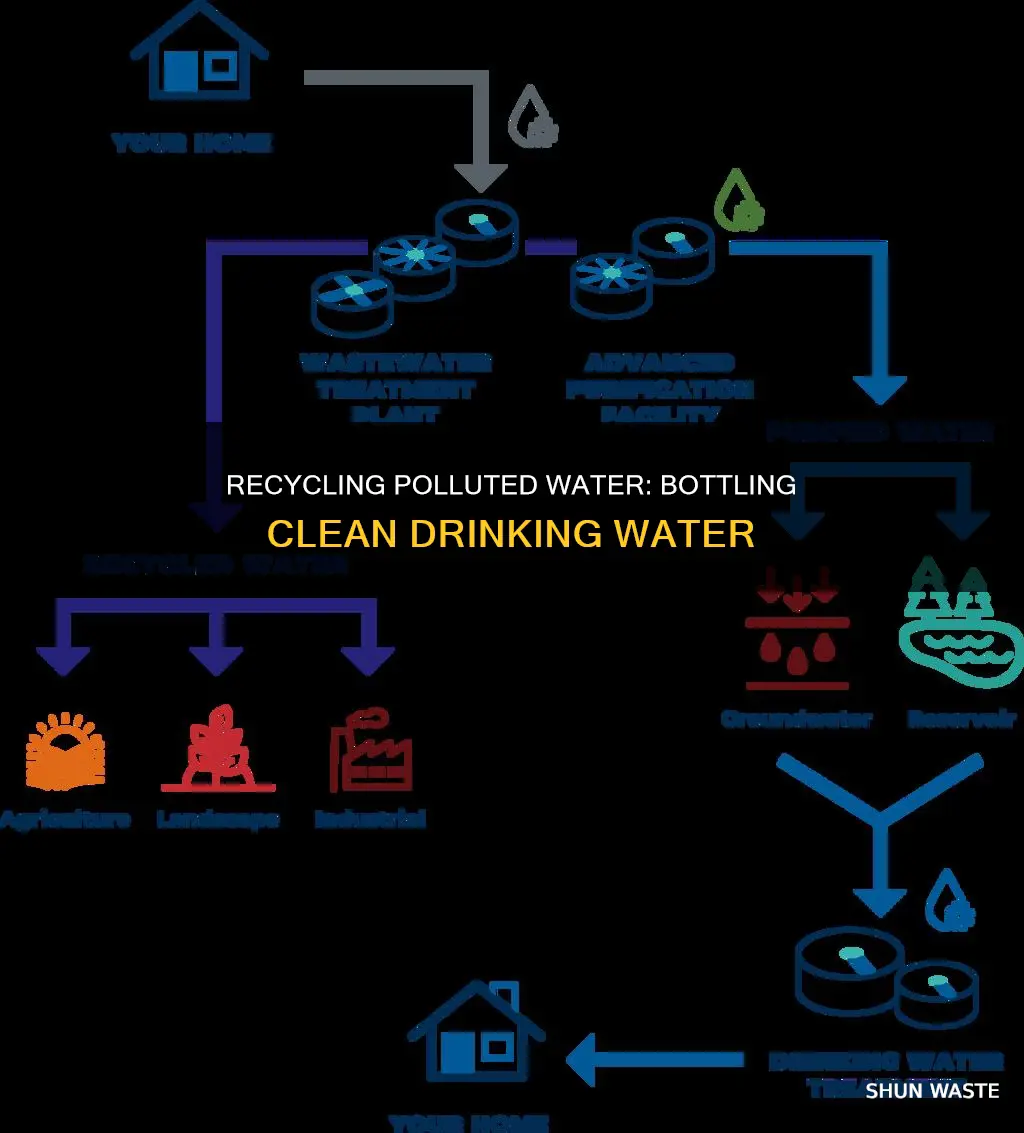
Plastic pollution is a growing concern, with global plastic waste expected to triple by 2060. As consumers, we can play our part in reducing plastic waste by cutting down on single-use plastics and recycling plastic bottles. One way to do this is by using bottleless water coolers, which filter water on-site, reducing the need for plastic water bottles. While water delivery services may offer to refill plastic bottles, these can only be reused a limited number of times before they are discarded, contributing to plastic pollution. Recycling plastic bottles not only reduces pollution but also fosters a culture of sustainability and responsible consumption. Additionally, recycling reduces the demand for plastic production, conserves natural resources, and minimizes energy consumption. When it comes to dealing with polluted water bottles, various methods can be employed, such as using bottle emptiers, sieves, or evaporation techniques, to ensure proper disposal and prevent environmental harm.
What You'll Learn

Using a bottle emptier to empty polluted water bottles
Recycling polluted water is an important step towards environmental sustainability. Using a bottle emptier is one way to recycle water from bottles. The Bottle Emptier is a building in the game Oxygen Not Included that is used for emptying bottles of liquid. It is useful for cleaning up spills, and the type of liquid it empties can be chosen by the player using the Element Filter menu.
To use a bottle emptier to empty polluted water bottles, there are a few steps to follow. Firstly, ensure that you have a bottle emptier built near a reservoir or water source. This is where the polluted water bottles will be emptied. Once you have your bottle emptier set up, you need to select the type of liquid you want it to empty. In this case, you would choose "polluted water" from the Element Filter menu.
After selecting the type of liquid, you need to enable the Auto-Bottling option. This allows the Duplicants (game characters) to bottle the liquid at a Pitcher Pump and bring it to the Bottle Emptier. With Auto-Bottling enabled, you can then change the priority on the bottle emptier or sweep the bottles so that the Duplicants will empty them. It is important to note that if the Duplicants are emptying bottles of germ-filled polluted water, both the surface of the bottle emptier and the Duplicants themselves will be covered in germs.
Additionally, it is worth mentioning that the Bottle Emptier can be rotated during construction to direct the flow of liquid to either its left or right side. This can be useful for controlling the flow of polluted water and ensuring it is directed towards the desired location. By following these steps, players can effectively use a bottle emptier to empty polluted water bottles and contribute to sustainability within the game.
Fertilizers' Water Pollution: Understanding the Devastating Impact
You may want to see also

Sieve the water to clean it
Sieving is a method of water filtration that can be used to recycle polluted water. Here are some detailed steps and considerations for sieving water to clean it:
Firstly, it is important to understand the basic mechanism of a water sieve. A water sieve uses a filtration medium, such as a screen or mesh, to separate solids from liquids. The polluted water is passed through the sieve, which traps the solid particles, allowing the liquid water to pass through. This process can effectively remove physical contaminants from the water, improving its cleanliness and potability.
To start sieving the water, set up a water sieve system. This typically involves placing the water sieve at a slight angle to facilitate the flow of water through the filtration medium. Ensure that the sieve is securely positioned over a container to collect the filtered water. You can use a variety of sieving materials, such as a fine mesh screen, a cloth, or even specialised sieving filters designed for water filtration. Choose a material with a pore size that is small enough to capture the contaminants in your water source.
Once the sieve is in place, slowly pour the polluted water onto the filtration medium. The water will gradually pass through the sieve, leaving behind solid particles and contaminants. Depending on the severity of the pollution, you may need to replace or clean the filtration medium periodically to prevent it from becoming clogged. Consider using multiple sieves, especially if you are dealing with heavily polluted water, as this will extend the lifespan of each individual sieve and reduce the frequency of maintenance.
After sieving, the collected water will be significantly cleaner, but it is important to recognise the limitations of this method. Sieving water is effective at removing physical particles but may not eliminate germs, bacteria, or chemical pollutants. For potable water, consider combining sieving with other treatment methods, such as boiling, chemical disinfection, or additional filtration techniques, to ensure the water is safe for drinking.
Finally, remember to properly dispose of the solid waste captured by the sieve. Allow the collected solids to dry, and then dispose of them in a manner that aligns with local waste management guidelines. By sieving polluted water, you can take an important step towards cleaning and recycling water, making a positive impact on the environment and contributing to sustainable practices.
Managing Water and Air Pollution: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also

Recycle plastic water bottles to reduce plastic pollution
Plastic pollution is a pressing global problem that is inflicting a detrimental impact on the environment. Plastic bottles contribute the most to global plastic waste since they are often used once and discarded. The degradation process for plastic bottles can take up to 1000 years. To tackle the plastic pollution problem, we need to reduce and aim to eliminate plastic bottle waste.
One of the best ways to reduce plastic bottle waste is to invest in a reusable water bottle. Single-use water bottles are notorious for generating unnecessary plastic waste, and their impact on the environment can't be ignored. Recycling plastic bottles not only mitigates environmental harm but also fosters a culture of sustainability and responsible consumption. By recycling plastic water bottles, you are eliminating the need for additional plastic to be produced.
Bottleless water coolers differ greatly from traditional water coolers in that the water is filtered on-site rather than pre-filtered and bottled at an off-site manufacturing plant. This minimizes plastic water bottle waste and cuts down on the pollution linked to producing and distributing plastic bottles, which includes emissions like carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide from delivery trucks.
Water jug delivery services encourage customers to return their plastic bottles so that they can be inspected, cleaned, sanitized, and refilled for reuse. However, these bottles can only be refilled an average of 40 times before needing to be discarded. Ideally, these plastic bottles would be recycled, but studies show that less than 30% of plastic beverage bottles purchased in the US are recycled each year, and only about 70% of the plastic material can be recycled.
By opting for a bottleless water cooler in your home or business, you can take a step towards sustainability and help reduce the amount of plastic waste that ends up in our waterways and landfills.
Water Changes: Refreshing Your Aquarium, Removing Pollutants Effectively
You may want to see also

Use a water cooler to filter water on-site
One way to recycle polluted water and reduce plastic waste is to use a bottleless water cooler to filter water on-site. This type of water cooler differs from traditional water coolers in that the water is filtered on-site rather than being pre-filtered and bottled at an off-site manufacturing plant before delivery. By filtering water on-site, you can minimise plastic water bottle waste and reduce the pollution associated with producing, distributing, and delivering plastic bottles.
Bottleless water coolers, such as those offered by Quench, filter a building's existing water supply directly from the tap, eliminating the need for bottled drinking water delivery services. This not only reduces plastic waste but also decreases fossil fuel depletion and carbon emissions associated with transportation. A standard Quench water cooler can prevent approximately 150 five-gallon plastic water jugs from ending up in landfills and waterways each year, contributing to a more sustainable future.
When choosing a water cooler to filter water on-site, consider the type of filtration system it uses. Basic water filters can handle most small, lightweight particles, but if you are concerned about heavy metals like lead in your water supply, you may need a specialised filter or filtration system. Some water coolers offer additional features, such as heating or cooling the water, so you can select one that best meets your needs.
By investing in a water cooler with an appropriate filtration system, you can effectively recycle polluted water by filtering it on-site. This approach not only reduces plastic waste but also ensures that clean and safe water is readily available for consumption, contributing to both environmental sustainability and personal well-being.
Water Pollution: Understanding the Crisis in Our Oceans
You may want to see also

Heat the water to create steam and then pure oxygen
To recycle polluted water that has been automatically bottled, one method is to heat the water to create steam and then condense it to extract pure water. This process can be achieved through various methods, each involving heat sources and equipment to capture the steam.
One approach is to use a space colony simulation game strategy, where hot regolith (a type of soil) is used to heat the water. By dumping hot regolith into a chamber filled with water, the water will eventually turn into steam. This steam can then be captured using a gas pump and directed wherever needed. This method is simple and effective, making it a popular choice for those looking to recycle polluted water.
Another strategy involves building a steam room in a Space Biome. By constructing a room with specific materials, such as Bunker Tile for the top wall and normal tiles for the sides and bottom, you can create an effective steam-generating environment. Pumping hot water into this room, the heat from the accumulated regolith on the ceiling will boil the water, creating steam. Again, a gas pump can be used to capture and direct the steam as needed.
A third option is to utilise a cooling loop setup with a Thermal Aquatuner and Radiant Pipes. By sending the loop through a large body of liquid, you can reheat the coolant and keep the aquatuner running, generating the heat required to create steam. This method bypasses the need for a Steam Turbine, offering a unique approach to steam generation.
While these methods focus on generating steam, it's important to note that simply boiling polluted water into steam does not purify it. To obtain pure water, the steam must be condensed. This process can be challenging, as directly cooling the steam can damage pipes if a Thermo Regulator is used, and other cooling methods may not be effective. An alternative approach is to cool another gas, such as hydrogen, and use it to cool the steam through bubbling, piping, or a highly conductive tile wall.
Wetlands: Nature's Water Purifiers and Pollution Control
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Recycling water bottles is an important way to reduce pollution and conserve natural resources. To recycle water bottles, you can use a bottleless water cooler, which filters water on-site rather than relying on pre-filtered and delivered water. This reduces plastic waste and the pollution associated with producing and distributing plastic bottles.
One way to dispose of polluted water bottles is to build a bottle emptier that pours into a different pit than your clean water source. You can then place a pump at the bottom of that pit to send the water to a sieve for cleaning.
Recycling plastic water bottles reduces the demand for plastic production, conserves natural resources, and minimizes energy consumption. It also helps prevent plastic pollution in oceans and waterways, protecting marine life and ecosystems.
You can reduce your plastic water bottle waste by opting for a bottleless water cooler in your home or business. This will eliminate the need for bottled drinking water delivery services and reduce fossil fuel depletion, carbon emissions, and plastic waste.







