Water pollution is a pressing issue that affects millions of people worldwide. The contamination of our rivers, reservoirs, lakes, and seas by chemicals, waste, plastics, and other pollutants poses a significant threat to aquatic ecosystems, human health, and the global economy. With rising global temperatures, increased CO2 emissions, and the impact of human activity, it is essential to address the deteriorating water quality and its far-reaching consequences. To limit the effects of water pollution, individuals, communities, and governments must work together to implement solutions and advocate for stronger regulations. This includes reducing the use of pesticides and fertilizers, properly disposing of medications, conserving water, supporting initiatives like the Clean Water Act, and advocating for investments in infrastructure and wastewater treatment. By taking collective action, we can protect our vital water sources and ensure a sustainable future for all.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Understand your local water sources | Learn about the unique qualities of water where you live. Where does your water come from? Is the wastewater from your home treated? Where does stormwater flow to? Is your area in a drought? |
| Support policies and regulations | Speak out in support of the Clean Water Act and advocate for regulations that address modern-day challenges, such as microplastics, PFAS, pharmaceuticals, and other contaminants. |
| Properly dispose of chemicals and waste | Avoid disposing of chemicals, motor oil, automotive fluids, medications, and other hazardous waste into sewers, storm drains, or natural water bodies. Utilize toxic drop-off sites and proper medical waste disposal methods. |
| Reduce pesticide, herbicide, and fertilizer use | Minimize the use of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers to prevent their runoff into water sources. Avoid applying fertilizer before rainfall, and blow or sweep fertilizer back onto the grass if it gets onto paved areas. |
| Conserve water | Keep drinking water in the refrigerator, use water-efficient toilets, run appliances with full loads, wash clothes with cold water, and hang laundry to dry. Water plants efficiently, and use drought-tolerant landscaping. |
| Properly manage livestock and pets | Prevent livestock from directly accessing water bodies, and block pet waste from entering water sources to reduce E. coli levels. |
| Protect soil and vegetation | Replant bare ground, create riparian corridors, and use best management practices to prevent soil erosion and sediment runoff into water bodies. |
What You'll Learn

Reduce toxic agricultural run-off
Agricultural runoff is a significant contributor to water pollution, as it introduces harmful substances into natural water systems. These toxins can have devastating impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health. One of the primary concerns is the leaching of contaminants, such as nitrates from fertilizers, into groundwater and surface water sources.
To reduce toxic agricultural runoff, it is essential to focus on sustainable practices that maintain or enhance soil health, water quality, and biodiversity. Here are some specific strategies:
- Crop Rotation and Cover Cropping: Planting different crops in sequence helps break pest and disease cycles and improves soil fertility, reducing the need for chemical inputs. Cover cropping involves planting non-cash crops during off-seasons to prevent soil erosion, retain nutrients, and enhance soil structure.
- Minimize Chemical Use: Reduce the use of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. These chemicals can be toxic to aquatic life and contribute to soil degradation. Explore alternative pest management methods and promote beneficial microorganisms in the soil.
- Proper Manure Management: Store manure in facilities that prevent it from running off into nearby waterways or impacting groundwater. Ensure that manure application fields do not directly contribute to runoff.
- Erosion Control: Leave crop residue on fields over the winter to reduce erosion. Adopt direct seed and no-till practices, which help prevent soil disturbance and runoff.
- Appropriate Fertilizer Application: Apply fertilizer, including manure, in appropriate volumes and at times when plants can fully utilize the nutrients. Avoid over-application, as excess fertilizer can wash into storm drains and waterways, leading to water pollution.
- Stream Bank Management: Avoid modifications that can impact stream bank channels, such as ditching, dredging, or unrestricted animal access. Maintain streamside vegetation to help stabilize the stream banks and filter runoff.
By implementing these practices, agricultural landowners can play a crucial role in ensuring clean and safe water for drinking, recreation, and supporting aquatic life. It is also essential to advocate for regulations and policies that address modern-day challenges, such as microplastics, pharmaceuticals, and other emerging contaminants, to comprehensively tackle the issue of water pollution.
Human Impact: Polluting Land, Water, and Air
You may want to see also

Treat wastewater
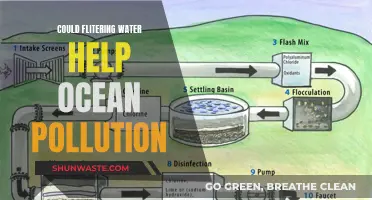
Wastewater treatment is a critical aspect of water pollution control, aiming to remove impurities from wastewater before it reaches natural bodies of water. This process involves removing suspended solids and pollutants, including physical, chemical, and biological contaminants. Here are some detailed steps and measures to treat wastewater effectively:
Understanding Wastewater
Wastewater, or sewage, is used water that contains a range of contaminants. It includes human waste, food scraps, oils, soaps, and chemicals, and wastewater from various sources like sinks, showers, and toilets in residential homes. Businesses and industries also contribute their share of wastewater that requires treatment.
Treatment Plants and Processes
Wastewater treatment plants employ physical, chemical, and biological processes to purify water. These processes can be categorized into preliminary, primary, secondary, and tertiary treatments. Primary treatment involves removing about 60% of suspended solids from wastewater, making it essential to reduce the impact of solid materials decaying and using up oxygen needed by aquatic life.
Managing Septic Systems
Approximately 20% of homes in the United States rely on septic systems for local wastewater treatment. Proper maintenance of these systems is crucial to prevent them from becoming a source of nutrient pollution. Homeowners should have their septic systems inspected regularly, pump their tanks as needed, and address common failure causes like aging infrastructure, poor design, or overloading.
Reducing Pollutants
To limit water pollution, it is essential to minimize the use of certain products that contribute to wastewater pollution. This includes reducing the use of pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, and automotive fluids like motor oil. Additionally, proper disposal practices are crucial, such as not flushing medications, drugs, or certain paper products down the toilet and avoiding the use of garbage disposals.
Supporting Regulations and Infrastructure
Supporting regulations and investing in infrastructure improvements are vital to enhancing wastewater treatment. Speaking out in favor of acts like the Clean Water Act helps hold polluters accountable. Additionally, advocating for investments in wastewater treatment plants, lead-pipe removal programs, and stormwater-abating green infrastructure can help address modern-day challenges, including microplastics, pharmaceuticals, and other emerging contaminants.
By following these steps and recognizing the importance of treating wastewater effectively, we can significantly limit the effects of water pollution and protect our environment and health.
Strategies to Reduce Air, Water, and Noise Pollution
You may want to see also

Reduce air pollution
While water pollution is a pressing issue, air pollution is a significant contributor to it. Here are some ways to reduce air pollution and, in turn, limit its effects on water sources:
Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Transitioning to cleaner and renewable energy sources is crucial. This includes adopting wind and solar power, improving fuel efficiency in vehicles, and shifting to electric cars and trucks. These measures not only reduce air pollution but also curb global warming, which exacerbates the impacts of pollutants.
Limit Nitrogen and Phosphorus Emissions:
Nitrogen and phosphorus are significant contributors to nutrient pollution in water bodies. By reducing emissions of these chemicals, we can help prevent algal blooms and maintain water quality.
Improve Waste Management:
Properly disposing of chemical cleaners, oils, and non-biodegradable items ensures that they do not end up in water bodies. Additionally, recycling and responsible waste management practices can reduce the amount of plastic and other pollutants that find their way into our water sources.
Enhance Soil Management:
Soil erosion due to air pollution leads to a loss of water quality. Implementing erosion control measures, such as terracing or planting cover crops, can help reduce the amount of sediment and pollutants that enter water bodies.
Promote Public Transportation and Reduce Vehicle Emissions:
Encouraging the use of public transportation, electric or hybrid buses, carpooling, and active commuting (walking or cycling) can significantly reduce vehicle emissions. This not only improves air quality but also directly impacts water pollution, as stormwater runoff carries pollutants from roads into waterways.
Support Policy Interventions:
Advocate for policies that address the root causes of pollution, such as legal restrictions on toxic substances and community-level initiatives to reduce motor vehicle usage. These interventions can have a more sustainable impact on reducing air pollution and, consequently, mitigating its effects on water sources.
Phosphate Detergents: Water Pollution's Unseen Culprits
You may want to see also

Limit plastic pollution
Plastic pollution is one of the greatest threats to ocean health worldwide. Skyrocketing plastic production, low recycling rates, and poor waste management mean that between 4 and 12 million metric tons of plastic enter the ocean each year. This plastic pollution impacts sea turtles, whales, seabirds, fish, coral reefs, and countless other marine species and habitats.
To limit plastic pollution, individuals can reduce their use of single-use plastics. This includes plastic bags, water bottles, straws, cups, utensils, dry cleaning bags, takeaway containers, and any other plastic items that are used once and then discarded. People can refuse single-use plastics they don't need and purchase reusable alternatives, such as reusable grocery bags, produce bags, bottles, utensils, coffee cups, and dry cleaning garment bags.
Microplastics are also a significant concern, as they can slip through water treatment plants and resemble food to marine animals. Individuals can opt for natural exfoliants like oatmeal or salt in beauty products instead of plastic microbeads. It is also recommended to approach cosmetics with caution, as they may contain microplastics.
In addition to individual actions, regulations and policies are crucial in addressing plastic pollution. People can support the Clean Water Act and advocate for regulations that address modern-day challenges, such as microplastics, PFAS, pharmaceuticals, and other contaminants. This includes supporting investments in infrastructure for wastewater treatment, lead-pipe removal programs, and stormwater-abating green infrastructure.
By combining individual actions with collective efforts to influence policies and regulations, we can effectively limit plastic pollution and protect our oceans and marine life.
Harmonic Mean: Water Pollution's Unseen Culprit
You may want to see also

Penalise untreated waste discharge
Water pollution is a pressing issue that poses a threat to both the environment and human health. One of the major contributors to water pollution is the discharge of untreated wastewater by industries. This has led to an alarming increase in the amount of discharge, causing a destructive impact on aquatic ecosystems. To address this issue, it is crucial to implement measures that penalize the discharge of untreated waste.
One approach to penalizing untreated waste discharge is to enforce strict regulations and permits. In many countries, environmental permits are required for discharging wastewater into surface waters or groundwater. These permits ensure that industries comply with specific standards and treat their wastewater adequately before releasing it into the environment. For example, the US Clean Water Act, derived from the 1948 Water Pollution Control Act, regulates the point-source discharge of effluents into surface waters. Similarly, Europe's Directive 91/1971, later amended by Directive 98/15/EC, enforces appropriate collection and treatment of urban wastewater discharges.
To further deter industries from discharging untreated waste, economic incentives or penalties can be implemented. This follows the "polluter pays" principle, where the cost of polluting is proportional to the degree of pollution caused. For instance, in Spain, there are economic incentives for depuration or emission to less sensitive waters, with the fee modulated based on the level of treatment achieved. While this approach has been criticized for potentially allowing pollution if the polluter can afford the fee, it can still provide a financial disincentive for untreated waste discharge.
In addition to regulations and economic incentives, public awareness and support for water protection initiatives are vital. Individuals can educate themselves about the unique qualities of their local water sources and the potential sources of pollution. By understanding the impact of untreated waste discharge, people are more likely to advocate for stronger regulations and support organizations working to protect water sources. This includes speaking out in favor of acts like the Clean Water Act and pushing for regulations that address modern-day challenges, such as microplastics and pharmaceuticals.
Furthermore, local and federal governments play a crucial role in penalizing untreated waste discharge. They can allocate resources and invest in infrastructure improvements, such as wastewater treatment plants, lead pipe removal programs, and stormwater-abating green infrastructure. By providing the necessary support and enforcement, governments can ensure that industries are held accountable for their waste treatment practices and that those who violate regulations face appropriate consequences.
Overall, addressing the issue of untreated waste discharge requires a multi-faceted approach that includes strict regulations, economic incentives or penalties, public awareness, and government support. By implementing these measures, we can effectively penalize the discharge of untreated waste and mitigate its detrimental effects on our water sources and ecosystems.
Preventing Surface Water Pollution: Strategies for a Cleaner Future
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are several ways to limit water pollution at home. Firstly, avoid flushing pills, liquid or powder medications, drugs, tissues, wrappers, dust cloths, and other paper goods down the toilet. Also, avoid disposing of chemicals, motor oil, or other automotive fluids into water bodies or sewer systems. Minimize the use of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, and do not apply fertilizer before it rains.
Some everyday habits that can help limit water pollution include washing your car less often, using a bucket of soapy water instead of a hose, keeping trash and litter away from creeks, streets, and yards, and picking up after your pets.
You can write to federal governments, local elected officials, and organizations like the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to express your support for water protection and investments in infrastructure. You can also learn about and involve yourself in the policymaking process.
In agriculture, it is important to block livestock from directly accessing water bodies to prevent trampling and the deposit of feces. It is also good practice to create a rotational grazing system that reduces pasture erosion and allows vegetation time to grow.