Cars are a major contributor to air pollution, which is a significant risk to human health and the environment. In the US, 17,000 to 20,000 people die each year from vehicle pollution, with people of colour disproportionately affected. A typical passenger vehicle emits about 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide per year, though this varies depending on the vehicle's fuel, fuel economy, and annual mileage. The production and distribution of gasoline also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. While electric vehicles are generally cleaner, the power plants that fuel them can still produce harmful gases.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Average annual carbon dioxide emissions of a typical passenger vehicle | 4.6 metric tons |
| Average carbon dioxide emissions per gallon of gasoline | 8,887 grams or 19.4 lb |
| Average carbon dioxide emissions per mile | 400 grams |
| Percentage of air pollution caused by cars in urban areas | 50% |
| Number of deaths caused by vehicle pollution in the US each year | 17,000-20,000 |
| Percentage of cars causing 90% of air pollution in Toronto | 25% |
| Percentage of total EU CO2 emissions caused by road transportation | 71.7% |
| Percentage of total EU CO2 emissions caused by passenger cars | 61% |
What You'll Learn

Cars emit 4.6 metric tons of CO2 per year
The production, distribution, and use of gasoline all contribute to the overall carbon dioxide emissions produced by cars. Firstly, the production of gasoline involves extracting oil from the ground, transporting it to a refinery, refining the oil, and then transporting the gasoline to service stations, with each step generating greenhouse gas emissions. Secondly, the distribution of gasoline to consumers also contributes to emissions. Finally, the use of gasoline in vehicles results in tailpipe emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, such as methane and nitrous oxide.
While electric vehicles (EVs) have zero tailpipe emissions, it is important to consider the emissions created during the production and distribution of the electricity used to fuel these cars. The environmental impact of electric cars depends on the energy mix used to generate the electricity, and as the share of electricity from renewable sources increases, electric cars will become even more environmentally friendly.
The impact of car emissions on the environment and human health is significant. High levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere contribute to global warming, leading to rising land and ocean temperatures and more severe weather events. Additionally, air pollution from vehicles, including carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and nitrogen oxides, poses serious health risks, with thousands of people dying annually from vehicle pollution in the US alone.
To address these issues, various measures are being implemented. The EU, for instance, has set targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from transport, aiming for a 90% reduction by 2050 compared to 1990 levels. This includes intermediate targets for cars, such as a 55% emissions reduction by 2030, and a ban on the sale of new petrol and diesel cars by 2035.
Rising Temperatures: Water Pollution's Unseen Catalyst
You may want to see also

Vehicle pollution kills 17,000-20,000 people in the US annually
Vehicle pollution kills 17,000–20,000 people in the US annually, with one in three exposed to unhealthy air. A study by MIT researchers found that air pollution causes about 200,000 premature deaths in the US each year, with vehicle emissions being the biggest contributor. The study tracked emissions from sources such as industrial smokestacks, vehicle tailpipes, marine and rail operations, and commercial and residential heating. Vehicle emissions were found to be the most significant contributor, causing 53,000 premature deaths per year. This is due to the toxic pollutants emitted from the burning of gasoline and diesel, including carbon monoxide, smog-causing volatile organic compounds, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxides, formaldehyde, and benzene.
The impact of vehicle pollution is not evenly distributed across the population. People of color are disproportionately affected, breathing 66% more air pollution from cars and trucks than white residents in some regions. Additionally, nine out of ten Californians live in areas with unhealthy air, largely due to ozone and particle pollution from vehicle emissions. The production and distribution of gasoline also contribute to vehicle pollution, as each step of the process, from extracting oil to transporting it to service stations, produces greenhouse gas emissions.
While modern vehicles are becoming more fuel-efficient, the increasing popularity of gas-guzzling SUVs and pickup trucks offsets much of this progress. Additionally, Americans are driving more miles than ever, resulting in near-record-high gasoline consumption. The surge in vehicle miles traveled and gasoline consumption underscores the urgent need for cleaner transportation solutions. Electric vehicles (EVs) have zero tailpipe emissions, but emissions are still created during the production and distribution of the electricity used to fuel them.
The harmful effects of vehicle pollution are not limited to the US. Worldwide, air pollution kills more than 5.5 million people each year, with China and India bearing the brunt of these deaths. The aging population in China, for example, is increasingly susceptible to the health problems associated with pollution. To combat this issue, Chinese cities have implemented warning systems to get cars off the streets and halt industrial pollution during periods of intense smog.
Airplane Noise Pollution: Understanding the Disturbance
You may want to see also

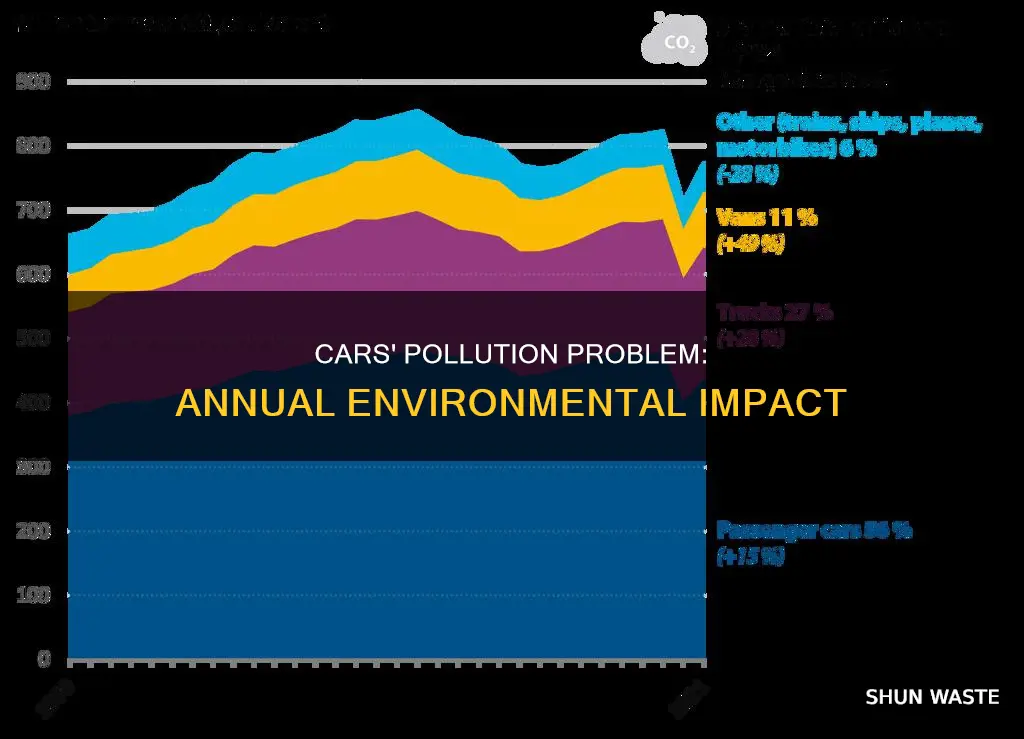
SUVs release 700 megatonnes of greenhouse gases annually
Cars are a major source of pollution, and their emissions have severe environmental and health impacts. A typical passenger vehicle with a fuel economy of about 22 miles per gallon and an annual mileage of 11,500 miles emits around 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide annually. This figure can vary based on factors such as fuel type, fuel economy, and distance travelled. In addition to carbon dioxide, vehicles emit methane, nitrous oxide, and hydrofluorocarbon from air conditioning leaks. These gases have a higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide, exacerbating their environmental impact.
The popularity of gas-guzzling SUVs and pickup trucks significantly contributes to pollution levels. Despite improvements in fuel efficiency, the increasing preference for these larger vehicles offsets much of the progress made. SUVs alone release 700 megatonnes of greenhouse gases annually, which equates to 1,000,000 tonnes per megatonne. This emission figure is alarmingly higher than those from shipping and aviation, which stood at 233 megatonnes for aviation as a reference. The high emissions from SUVs are due in part to their fuel economy and the number of miles driven, but the primary factor is their growing popularity. In 2018, nearly 40% of new car sales worldwide were SUVs, totalling approximately 35 million vehicles. This trend persists in 2023, with SUVs constituting 46% of the global auto market and accounting for nearly half of car sales in Europe and America.
The consequences of these emissions are dire. The excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere leads to rising global temperatures, resulting in more frequent and severe weather events. The year 2024 was the hottest on record, with carbon dioxide levels at 424 parts per million and climbing rapidly. The oceans, which have absorbed 90% of the extra heat, may have reached their limit, as evidenced by the unprecedented rise in ocean temperatures. As a result, we are witnessing more severe storms, droughts, and other climate disasters, causing billions of dollars in damages.
To address these issues, several regions have implemented initiatives to reduce emissions. The EU, for instance, aims for a 90% reduction in transport greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 and has set intermediate targets for 2030 and 2035. Additionally, sales of electric vehicles have surged, and they are gaining popularity as a cleaner alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. However, it is important to consider the emissions associated with electricity production and the environmental impact of battery production and disposal.
While electric vehicles offer a promising solution, it is essential to acknowledge the ongoing challenges. In some regions, such as parts of the US, electric power generation still relies heavily on coal, contributing to harmful gas emissions. Furthermore, hybrid electric vehicles, while emitting fewer gases than gas-powered cars, continue to release significant emissions. Nevertheless, with advancements in renewable energy sources and improvements in battery sustainability, electric vehicles have the potential to become even more environmentally friendly in the future.
Electric Cars: Air Pollution Solution or Problem?
You may want to see also

Electric cars don't emit gases, but power plants do
Electric vehicles (EVs) have zero tailpipe emissions, but emissions are created during the production and distribution of the electricity used to power them. The amount of carbon pollution created depends on the energy source used to generate the electricity, such as coal or natural gas, which emit carbon pollution, or renewable resources like wind or solar, which do not.
In the United States, renewables became the second-most prevalent electricity source in 2020. As the share of electricity from renewable sources is expected to increase in the future, electric cars will become even less harmful to the environment. For example, in hydropower-heavy Washington State, an electric vehicle emits 61% less carbon than a hybrid vehicle. However, in coal-heavy West Virginia, an electric vehicle creates more carbon emissions than a hybrid, but still less than a gasoline car.
The production and disposal of an electric car are less environmentally friendly than those of a car with an internal combustion engine. This is because of the additional energy required to manufacture an EV's battery. Nevertheless, over the lifetime of the vehicle, total greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing, charging, and driving an EV are typically lower than those associated with a gasoline car.
According to the US EPA, a typical passenger vehicle emits about 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. This number can vary depending on the vehicle's fuel, fuel economy, and the number of miles driven per year. In addition to carbon dioxide, automobiles using gasoline produce methane and nitrous oxide from the tailpipe, and all vehicles can emit hydrofluorocarbon from leaking air conditioners.
Pollution's Deadly Impact: More Deaths Than You Think
You may want to see also

Cars emit methane, nitrous oxide, and hydrofluorocarbon
Cars are a major source of pollution, contributing significantly to the degradation of air quality and the increase in global temperatures. While carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most well-known greenhouse gas emitted by vehicles, it is important to recognize that cars emit other harmful substances, such as methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and hydrofluorocarbon (HFC).
Methane, nitrous oxide, and hydrofluorocarbon are all greenhouse gases that have a significant impact on global warming. Methane and nitrous oxide are emitted from the tailpipes of automobiles that use gasoline, while hydrofluorocarbon can be released from all vehicles due to leaking air conditioners. Although the emissions of hydrofluorocarbons from gasoline vehicles are relatively small compared to CO2, they have a higher global warming potential due to their ability to absorb more energy per ton emitted. This makes them particularly harmful to the environment.
The emission of these gases is influenced by various factors, including the type of fuel used, the fuel economy of the vehicle, and the number of miles driven per year. For example, older, high-emitting cars tend to emit more nitrous oxide and methane compared to newer, tightly controlled cars. Additionally, the production and distribution of gasoline, as well as the extraction, transportation, and refining processes, contribute to the emission of these gases.
The impact of these emissions on global warming is significant. The higher the level of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the higher the global mean temperature rises. This, in turn, leads to more severe storms, droughts, and other weather-related disasters. Furthermore, the warming of the oceans due to increased carbon dioxide levels has already reached unprecedented levels, and the consequences for the planet are yet to be fully understood.
To address the issue of car pollution, it is crucial to reduce emissions from road transport. This can be achieved through the use of electric vehicles, which have zero tailpipe emissions, improved fuel efficiency, and the implementation of stricter fuel economy standards. Additionally, increasing the average occupancy rate of cars, promoting car-sharing, and encouraging the use of public transport, cycling, and walking can help reduce the number of vehicles on the road and, consequently, lower emissions.
Hydroelectric Power: A Noisy Business?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A typical passenger vehicle emits about 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. This number varies based on the vehicle’s fuel, fuel economy, and the number of miles driven per year. In addition to carbon dioxide, vehicles emit methane, nitrous oxide, and hydrofluorocarbon from air conditioners.
Exposure to harmful air pollutants from vehicles is higher inside vehicles than outside. People who live near busy roads are at a particularly high risk of significant health risks, including respiratory problems, asthma, heart disease, birth defects, and eye irritation. Air pollution from cars has also been linked to cancer.
Car pollution contributes to climate change and global warming. The higher the level of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere, the higher the global mean temperature. This has resulted in more severe storms, droughts, and other weather events.



















