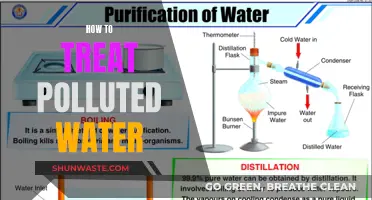
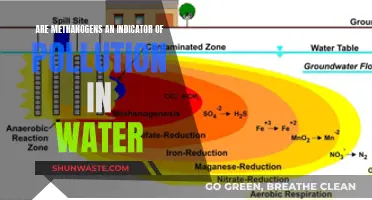
Water pollution is a pressing issue that affects one in three people worldwide. It occurs when water becomes contaminated by microorganisms and chemical substances, rendering it toxic and unfit for human use. This contamination can be caused by various factors, including industrial waste, agricultural runoff, improper waste management, and natural sources. The consequences of water pollution are dire, leading to health issues such as cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and infections, as well as environmental degradation and economic challenges. With industrialization, agricultural production, and urbanization, the problem of water pollution has intensified, and it is now more crucial than ever to address this global crisis.
What You'll Learn
- Water pollution is a health hazard, causing diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and cancer
- Industrial and agricultural activities are major sources of water pollution
- Water pollution is worsened by climate change and population growth
- Water pollution is caused by human and animal waste, toxic chemicals, and plastics
- Water pollution impacts the environment, killing fish and other marine life

Water pollution is a health hazard, causing diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and cancer
Water pollution is a pressing issue that affects one in three people worldwide, according to the United Nations. It is caused by a range of factors, from natural sources like mercury filtering from the Earth's crust to human activities such as agriculture, industrial processes, and the use of chemicals. The consequences of water pollution are dire, as it poses a significant health risk by causing various diseases, including cholera, dysentery, and cancer.
Cholera is a waterborne disease that, along with dysentery, has led to millions of cases and deaths worldwide. It is spread through faecal contamination of food and water, predominantly in areas with poor sanitation and impoverished conditions. Diarrheal diseases, including cholera, are a leading cause of death among children in developing nations, with around 800,000 fatalities each year.
Dysentery, an inflammation of the intestine, is caused by bacterial or amoebic infections transmitted through contaminated food and water. It is characterised by frequent passage of faeces with blood and mucus, abdominal cramps, and rectal pain. Worldwide, approximately 140 million people develop dysentery annually, and about 600,000 people succumb to the disease.
In addition to waterborne diseases, water pollution is linked to an increased risk of cancer. Certain contaminants in drinking water, such as arsenic, disinfection byproducts, nitrate, asbestos, radon, agricultural chemicals, and hazardous waste, are associated with various types of cancer. For example, ingestion of high levels of arsenic is a known cause of bladder cancer. Studies have also found associations between rectal and bladder cancer and long-term exposure to contaminated drinking water.
The impact of water pollution on human health is far-reaching, leading to illnesses and deaths, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children and those in developing countries. Addressing water pollution and improving water quality are crucial to mitigating the health hazards posed by contaminated water.
Food Waste: Water Pollution's Unseen Contributor
You may want to see also

Industrial and agricultural activities are major sources of water pollution
Water pollution is a pressing issue that affects one in every three people on the planet, according to the United Nations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines polluted water as water that has been altered to the extent that it becomes unusable and toxic, unfit for drinking or essential purposes like agriculture.
Industrial and agricultural activities are significant contributors to water pollution, with toxic substances from factories, farms, and livestock operations dissolving into water sources. The industrial sector releases various toxic chemicals, organic and inorganic substances, solvents, and volatile organic compounds during production. Industries such as distilleries, tanneries, pulp and paper, textiles, food, iron and steel, and nuclear energy are major culprits.
Agricultural pollution, on the other hand, includes runoff from farms containing fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste. This waste contains high levels of pathogens, bacteria, and viruses that can contaminate water supplies. The use of pesticides also harms pollinators like bees and butterflies, contributing to their declining populations. Additionally, the excessive use of heavy metals like copper and zinc in livestock feed can accumulate in the soil and eventually contaminate water sources.
The impact of industrial and agricultural water pollution on human health is significant. Contaminated water can cause various diseases, with diarrhea being the most common. Other health issues include skin rashes, pink eye, respiratory infections, hepatitis, and even more severe conditions like cancer, hormone disruption, and altered brain function.
Furthermore, water pollution from these sources has detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems. For example, high levels of nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, from synthetic fertilizers and animal waste, can degrade water quality, leading to the loss of aquatic life and their habitats. Eutrophication, caused by nutrient accumulation, impacts the biodiversity of lakes and coastal waters. Ocean acidification, partly due to carbon pollution, makes it difficult for shellfish and coral to survive and may impact the nervous systems of marine life.
Old Tires: Water Polluters and Environmental Hazards
You may want to see also

Water pollution is worsened by climate change and population growth
Water pollution is a pressing issue, with one in three people on the planet lacking access to clean water. While water pollution is primarily caused by human activity, it is worsened by climate change and population growth.
Climate Change
Climate change is altering nearly every stage of the water cycle. As global temperatures rise, terrestrial water storage is decreasing, with soil moisture, snow, and ice dropping at a rate of 1 cm per year. This reduction in freshwater resources is further exacerbated by rising sea levels, which increase the salinization of groundwater, making it unfit for human use. Moreover, climate change is causing unpredictable rainfall patterns, leading to more frequent and intense flooding in some areas and prolonged droughts in others.
The impact of climate change on water availability is closely linked to the energy industry. For instance, the burning of fossil fuels contributes to ocean acidification, making it more difficult for shellfish and coral to survive. Additionally, the extraction of natural resources, such as hydropower, can impact renewable energy sources and water availability.
Population Growth
Population growth intensifies water pollution by increasing water consumption and the demand for freshwater. With more people relying on finite freshwater resources, water scarcity becomes a significant concern. This scarcity is further exacerbated by inadequate infrastructure in many regions, leading to a shortage of safe, clean drinking water.
The agricultural sector, which consumes about 70% of the earth's surface water supplies, is a significant contributor to water pollution. As the population grows, so does the demand for food production, requiring more groundwater extraction. This, in turn, leads to increased pollution from pesticides, fertilizers, and animal waste, which seep into water sources.
Combined Impact
The combination of climate change and population growth exacerbates water pollution and scarcity. As the population increases, the pressure on water resources intensifies, particularly in regions with inadequate infrastructure. Climate change-induced droughts and unpredictable rainfall patterns further strain these already limited water resources. Additionally, population growth contributes to increased industrial and community-level waste disposal, adding to the pollution of water sources.
Dupe Slimelung Risk From Polluted Water?
You may want to see also

Water pollution is caused by human and animal waste, toxic chemicals, and plastics
Water pollution is a pressing issue that affects one in three people on the planet. It occurs when harmful substances contaminate a body of water, degrading water quality and rendering it toxic to humans or the environment. One of the main causes of water pollution is human and animal waste. Animal waste, or manure, from agricultural operations can contaminate surface water during floods, carrying pathogens such as E. coli, as well as nutrients and viruses. Human waste, in the form of sewage, also introduces waterborne pathogens like bacteria and viruses, which can cause diseases such as cholera, giardia, and typhoid.
Toxic chemicals are another significant contributor to water pollution. These chemicals can come from industrial and municipal wastewater, as well as agricultural activities. Heavy metals, toxic sludge, and chemicals from factories and farms are released into waterways, posing a threat to aquatic life and human health. Additionally, fertilizers and pesticides used in agriculture can wash into waterways during rain, leading to nutrient pollution and algal blooms that reduce oxygen levels in the water, creating "dead zones" devoid of life.
Plastics are also a major cause for concern in water pollution. The increasing production of disposable plastic products has overwhelmed the world's ability to manage and recycle them effectively. Plastic waste, including single-use plastics and microplastics, has become ubiquitous, polluting rivers, reservoirs, lakes, and seas. Once plastics enter water bodies, they are challenging to retrieve, especially in the ocean. Microplastics have been found in municipal drinking water systems and even in human blood, lungs, and feces, raising concerns about their potential impact on human health.
Water pollution is a critical issue that jeopardizes human health and the environment. It is caused by a combination of human and animal waste, toxic chemicals, and plastics that contaminate our precious water sources, highlighting the urgent need for collective action to address this global problem.
Wetlands: Pollution's Impact on Water Quality
You may want to see also

Water pollution impacts the environment, killing fish and other marine life
Water pollution is a pressing issue that affects one in every three people on the planet, according to the United Nations. It is caused by a range of factors, including human activities such as agriculture, industrial waste, and sewage. The main pollutants include bacteria, viruses, parasites, fertilisers, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and even radioactive substances. These pollutants have a detrimental impact on the environment, particularly on fish and other marine life.
Fish are highly susceptible to the toxic effects of water pollution. Pesticides, for example, can directly kill fish or accumulate in their bodies over time, leading to fatal consequences. Similarly, heavy metals in water, resulting from burning fossil fuels, can stunt fish growth and impair their senses, making them easier prey for predators. Furthermore, the decay of plant life can lower the dissolved oxygen levels in the water, creating "dead zones" where fish cannot survive. Water pollution also affects the food sources of fish. Invertebrates, which fish feed on, can be killed by pesticides and sediment, reducing the availability of food for fish.
Marine mammals, such as whales, are also severely impacted by water pollution. Ingesting plastic is a significant cause of death for these creatures. Discarded fishing nets and large plastic debris can entangle and injure marine mammals, often leading to their demise. Microplastics, which are invisible to the naked eye, are easily consumed by marine life and can adsorb toxins, leading to toxic contamination. This bioaccumulation of toxins in the food chain poses a significant threat to apex predators such as great white sharks and orcas.
Additionally, water pollution disrupts the natural habits of marine life. Light pollution in shallow waters near urban areas interferes with the circadian rhythms of coastal organisms, affecting their feeding, migration, and reproductive behaviours. The increasing acidification of the oceans, caused by the absorption of carbon pollution from burning fossil fuels, makes it more difficult for shellfish and coral to survive. It also potentially impacts the nervous systems of certain fish species.
Water pollution has far-reaching consequences for fish and other marine life, threatening their survival and disrupting the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems. It is essential to address this issue through measures such as reducing pollution, treating wastewater, and protecting natural habitats to ensure the health and diversity of marine environments.
Fabric Industry Discharge: Water Pollution's Hidden Danger
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Water pollution can have a negative impact on the environment as it can cause the temperature in freshwater systems to change, making them dangerous for many water-dwelling organisms. It can also make water toxic to humans, leading to infections and health problems.
Water pollution can cause a range of health issues in humans, from cancer to cardiovascular conditions, hormone disruption, and altered brain function. It can also lead to skin rashes, pink eye, respiratory infections, and hepatitis. According to the United Nations, more deaths are caused by polluted water than all types of violence combined, including war.
Water is essential for social and economic development, as well as energy production and adaptation to climate change. Poor water quality can hinder economic growth and contribute to poverty.
Water pollution disproportionately affects communities in least-developed countries, where sanitation and wastewater treatment facilities are severely lacking. It also affects communities near heavily polluted rivers, such as the River Ganges, where faecal bacteria levels are extremely high.