Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a gaseous air pollutant that is harmful to human health and the environment. It is primarily produced by burning fossil fuels containing sulfur, such as coal, oil, and diesel. Power plants, industrial facilities, and vehicles are significant sources of SO2 emissions. High concentrations of SO2 in the atmosphere can lead to the formation of other sulfur oxides (SOx) and contribute to secondary pollutants, including particulate matter, acid rain, and haze. These pollutants can have detrimental effects on air quality, visibility, ecosystems, and human health, making sulfur dioxide a pressing environmental concern.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Formation | Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is formed when sulfur-containing fuels like coal, oil, or diesel are burned. |
| Sources | Power plants, industrial facilities, metal processing, smelting facilities, vehicles, natural gas extraction, petroleum extraction, oil refining, etc. |
| Effects | Contributes to particulate matter (PM) pollution, acid rain, haze, smog, and respiratory illnesses. Can damage trees, plants, and sensitive ecosystems. |
| Health Impact | Can penetrate deeply into the lungs and contribute to health problems, especially for children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions. |
| Regulations | EPA has set national ambient air quality standards for SO2 and rules to reduce emissions. Policies promoting cleaner fuels and pollution controls on power plants have improved SO2 levels. |
What You'll Learn
- Sulfur dioxide is a gaseous air pollutant composed of sulfur and oxygen
- It is formed when sulfur-containing fuels like coal, oil, or diesel are burned
- The largest sources of sulfur dioxide emissions are power plants, industrial facilities, and vehicles
- Sulfur dioxide contributes to the formation of smog, haze, and acid rain
- It can cause respiratory issues and aggravate heart and lung conditions

Sulfur dioxide is a gaseous air pollutant composed of sulfur and oxygen
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a gaseous air pollutant composed of sulfur and oxygen. It is formed when sulfur-containing fuels such as coal, oil, or diesel are burned. Power plants, industrial boilers, internal combustion engines, and vehicles are significant sources of SO2 emissions. As a pollutant, SO2 has several adverse effects on the environment and human health.
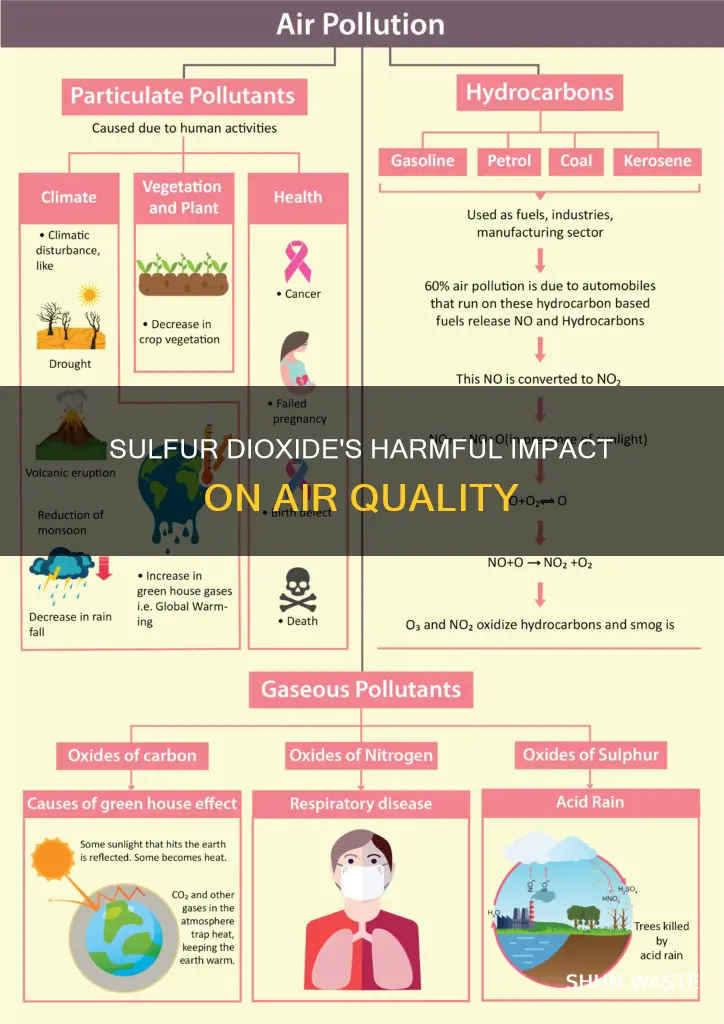
SO2 emissions contribute to the formation of secondary pollutants, including sulfate aerosols, particulate matter, and acid rain. Acid rain, in particular, can have detrimental effects on ecosystems, damaging trees and plants, inhibiting their growth, and causing localized extinctions of aquatic species. Additionally, acid rain can stain and damage stone and other materials, including culturally significant objects like statues and monuments.
The deposition of SO2 and other sulfur oxides (SOx) leads to soil and surface water acidification, further impacting susceptible ecosystems. It also promotes chemical reactions that increase mercury accumulation in water and soil, which can have adverse health consequences for human populations through mercury ingestion.
Furthermore, SO2 contributes to respiratory issues by making breathing more difficult, especially for vulnerable individuals such as children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions. Prolonged exposure to SO2 can aggravate existing heart and lung conditions.
To address the issue of SO2 pollution, governments and regulatory bodies have implemented measures to reduce emissions. For example, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established national ambient air quality standards for SO2 to protect against exposure to sulfur oxides. These standards guide state and local governments in developing plans to reduce SO2 levels in areas that do not meet the EPA's standards.
Deforestation's Impact: Understanding the Pollution Caused by Cutting Trees
You may want to see also

It is formed when sulfur-containing fuels like coal, oil, or diesel are burned
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a gaseous air pollutant that is formed when sulfur-containing fuels like coal, oil, or diesel are burned. SO2 is a major air pollutant and is harmful to both human health and the environment.
Coal-fired power plants are one of the biggest sources of SO2 emissions. Other large sources include industrial facilities, commercial and institutional boilers, internal combustion engines, and manufacturing processes. The burning of fossil fuels by power plants and industrial facilities is the largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere.
Vehicles, locomotives, and ships that use diesel or fuel with high sulfur content are also significant contributors to SO2 emissions. Federal regulations to reduce the sulfur content in diesel fuels have helped to lower emissions. However, old buses, trucks, and off-road equipment that use diesel engines continue to be major sources of SO2.
When SO2 is released into the atmosphere, it can lead to the formation of other sulfur oxides (SOx). These compounds can react with other atmospheric components to form small particles that contribute to particulate matter (PM) pollution. These particles can penetrate deeply into the lungs and cause respiratory issues, especially for vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
Additionally, SO2 and SOx contribute to the formation of acid rain, which can harm ecosystems, damage trees and plants, and inhibit their growth. They also react with other compounds to form fine particles that reduce visibility, creating thick haze and smog.
Industrial Facilities: Major Sources of Air Pollution
You may want to see also

The largest sources of sulfur dioxide emissions are power plants, industrial facilities, and vehicles
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a gaseous air pollutant composed of sulfur and oxygen. It is formed when sulfur-containing fuels such as coal, oil, or diesel are burned. The largest sources of sulfur dioxide emissions are power plants, industrial facilities, and vehicles.
Power plants that burn fossil fuels, particularly coal, are a major source of SO2 emissions. In North America, 71 out of 92 major "hot spots" of sulfur dioxide are power plants. The burning of fossil fuels by power plants and other industrial facilities is the largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere. Industrial processes such as metal processing and petroleum refining can also be significant contributors to SO2 emissions.
Vehicles, particularly those with internal combustion engines, also contribute to SO2 emissions. Diesel vehicles and equipment were once a major source of SO2, but federal regulations to reduce the sulfur content in diesel fuels have significantly lowered emissions from this source. Older diesel engines in buses, trucks, locomotives, ships, and off-road equipment can still be a concern.
In addition to power plants and vehicles, ports and smelters are also significant sources of SO2 emissions. People living or working near these sources are at the highest risk of exposure to high levels of SO2. While policies and technologies promoting cleaner fuels and pollution controls have helped reduce SO2 levels, it remains a health concern. High levels of SO2 can still occur due to equipment malfunction or during the startup or shutdown of polluting sources.
The Dark Side of Household Waste: Land Pollution
You may want to see also

Sulfur dioxide contributes to the formation of smog, haze, and acid rain
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a gaseous air pollutant composed of sulfur and oxygen. It is formed when sulfur-containing fuels such as coal, oil, or diesel are burned. The largest sources of SO2 emissions are from power plants, commercial and institutional boilers, internal combustion engines, and industrial processes such as petroleum refining and metal processing. Diesel vehicles and equipment were a major source of SO2, but federal regulations to reduce the sulfur in diesel fuels have significantly lowered emissions. Ports, smelters, and other sources of sulfur dioxide can also cause high concentrations of emissions nearby.
SO2 emissions that lead to high concentrations of SO2 in the air generally also lead to the formation of other sulfur oxides (SOx). SOx can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form small particles that contribute to particulate matter (PM) pollution. These particles may penetrate deeply into the lungs and, in sufficient quantities, can contribute to respiratory illness and other health problems, especially in children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions. Longer exposures can aggravate existing heart and lung conditions.
SO2 and other sulfur oxides can contribute to acid rain, which can damage trees and plants, inhibit plant growth, and harm sensitive ecosystems and waterways. Acid rain is caused by the deposition of SO2 and other SOx, which leads to soil and surface water acidification. This acidification can cause slower growth and injury to forests and the localized extinction of fish and other aquatic species. SO2 deposition also promotes chemical reactions that facilitate the accumulation of mercury in water and soil, which can lead to elevated mercury levels in food and, in turn, increase the risk of adverse health effects in human populations.
In addition to contributing to acid rain, SO2 and other sulfur oxides can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form fine particles that reduce visibility, resulting in a thick haze or smog. Ozone, a key component of smog, is a gaseous pollutant that forms in the atmosphere through complex chemical reactions between nitrogen dioxide and various volatile organic compounds, such as gasoline vapors. These fine particles can also stain and damage stone and other materials, including culturally important objects such as statues and monuments.
Human Activities: A Major Cause of Water Pollution
You may want to see also

It can cause respiratory issues and aggravate heart and lung conditions
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a major air pollutant and a serious health concern. It is a gaseous pollutant composed of sulfur and oxygen, which forms when sulfur-containing fuels such as coal, oil, or diesel are burned. The largest sources of SO2 emissions are power plants, commercial and institutional boilers, internal combustion engines, and industrial processes such as petroleum refining and metal processing. Diesel vehicles and equipment were once a major source of SO2, but federal regulations to reduce sulfur in diesel fuels have significantly lowered emissions.
SO2 emissions that lead to high concentrations of the gas in the air can have adverse health effects. It can contribute to respiratory illness by making breathing more difficult, especially for children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions. Longer exposures to SO2 can aggravate existing heart and lung conditions. The small particles formed by the reaction of SO2 with other compounds in the atmosphere can penetrate deeply into the lungs and, in sufficient quantity, can contribute to serious health problems.
People who live and work near large sources of SO2 emissions, such as power plants, ports, and smelters, are at the highest risk of exposure. While SO2 levels have improved over time due to policies promoting cleaner fuels and pollution controls, high levels can still occur due to equipment malfunction or during the starting up or shutting down of operations at polluting sources.
In addition to its direct health impacts, SO2 also contributes to secondary pollutants such as sulfate aerosols, particulate matter, and acid rain. Acid rain can damage trees and plants, inhibit their growth, and harm sensitive ecosystems and waterways. Furthermore, SO2 deposition contributes to soil and surface water acidification, which can have ecological consequences such as localized extinction of aquatic species and increased mercury levels in food, leading to potential adverse health effects in human populations.
Trash Disposal: Understanding Its Impact on Our Environment
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a gaseous air pollutant composed of sulfur and oxygen.
SO2 is released into the atmosphere when sulfur-containing fuels such as coal, oil, or diesel are burned. The largest sources of SO2 emissions are power plants, industrial facilities, and vehicles.
SO2 contributes to the formation of secondary pollutants such as sulfate aerosols, particulate matter, and acid rain. Acid rain can damage trees and plants, inhibit their growth, and harm sensitive ecosystems and waterways. SO2 also contributes to the formation of thick haze and smog, which reduce visibility.
Sulfur dioxide contributes to respiratory illness by making breathing more difficult, especially for children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing conditions. Longer exposures can aggravate existing heart and lung conditions.



















