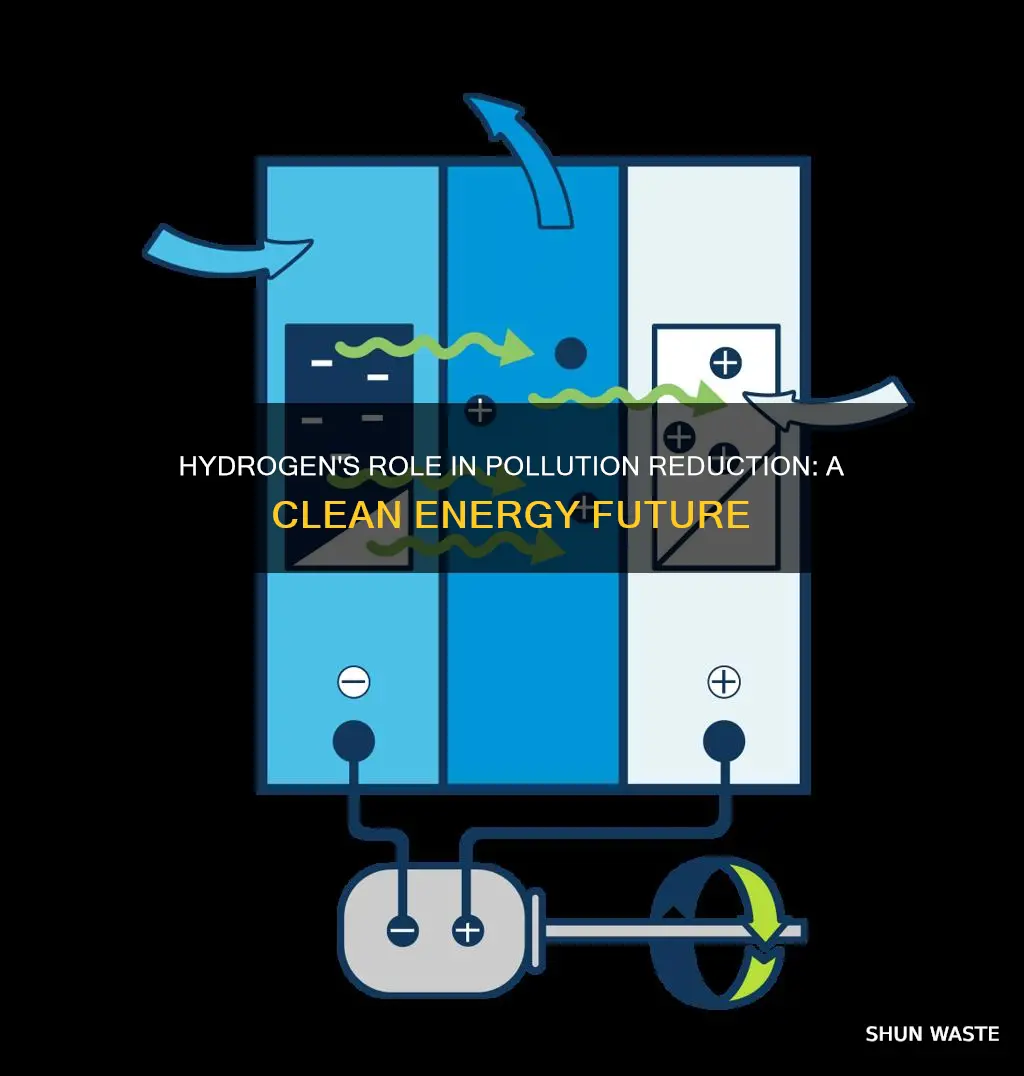
Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe and the lightest chemical element. Hydrogen gas can be stored, transported, and burned to provide power. Unlike most fuels, hydrogen does not produce carbon dioxide (CO2) when burned, instead yielding water. This means that burning hydrogen does not contribute to climate change. Hydrogen can be produced from diverse domestic resources with the potential for near-zero greenhouse gas emissions. However, hydrogen is a leak-prone gas with a potent warming effect of its own. Hydrogen combustion can also create harmful pollutants called nitrogen oxides, which are linked to smog, acid rain, and damaging health impacts such as asthma and respiratory infections.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen production emissions | Hydrogen can be produced with near-zero emissions using renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and nuclear power. |
| Hydrogen combustion emissions | Hydrogen combustion in engines and turbines can emit nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are harmful pollutants linked to smog, acid rain, and respiratory health issues. |
| Greenhouse gas emissions | Hydrogen does not produce carbon dioxide (CO2) when burned, unlike fossil fuels, which contributes to its potential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Air pollution reduction | Hydrogen fuel cells emit only water vapor and warm air, offering a zero-emissions alternative to fossil fuels in heavy-duty vehicles, trains, ships, and power generation. |
| Energy sector applications | Hydrogen has potential in both the stationary and transportation energy sectors, including fuel cell electric vehicles and power generation. |
| Industrial applications | Hydrogen can provide high-temperature heat for industrial processes, such as steel and cement production, without emitting greenhouse gases. |
What You'll Learn

Hydrogen fuel cells emit water vapour and warm air, not harmful gases
Hydrogen fuel cells are an innovative technology that offers a clean and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. One of the most significant advantages of hydrogen fuel cells is that they emit only water vapour and warm air, with no harmful gases released into the atmosphere.
This is in stark contrast to conventional combustion engines, which produce a range of harmful pollutants, including nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter. These emissions contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on both public health and the environment. By switching to hydrogen fuel cells, we can significantly reduce these harmful emissions and improve air quality, particularly in highly populated areas.
The process by which hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity is fundamentally different from that of combustion engines. Fuel cells operate through an electrochemical reaction, which does not involve the burning of fuel. As a result, there are no harmful direct emissions produced, regardless of the temperature at which the fuel cells operate. This is a crucial advantage, as it ensures that even in high-temperature applications, hydrogen fuel cells remain a clean and safe energy solution.
While hydrogen combustion in turbines or industrial heating applications can produce nitrogen oxides (NOx), this is not an inherent issue with hydrogen fuel cells themselves. NOx formation occurs when air, containing nitrogen and oxygen, is exposed to extremely high temperatures (>1,500°C). However, current research indicates that hydrogen combustion via turbines can achieve comparable NOx emissions to those of natural gas turbines. Additionally, the larger stable combustion temperature range of hydrogen allows for a higher ratio of air to fuel, effectively diluting the hydrogen and reducing the temperature, which in turn lowers NOx emissions.
In conclusion, hydrogen fuel cells offer a promising path towards reducing pollution and mitigating climate change. By emitting only water vapour and warm air, they provide a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. With their potential for near-zero greenhouse gas emissions and the ability to power fuel cell electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cells can help strengthen national energy security, conserve petroleum resources, and diversify our transportation energy options for a greener and more resilient future.
Leaner Air Fuel Ratios: Reducing Pollutants?
You may want to see also

Hydrogen can be produced from renewable energy sources
Renewable electricity can be converted to hydrogen through a process called electrolysis, which involves splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. This process can be powered by electricity from low-carbon sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower. Electrolysis offers a way to couple continuously increasing renewable energy sources with end uses that are more challenging to electrify, such as heavy industry, long-haul transport, and seasonal energy storage.
One of the key advantages of producing hydrogen from renewable energy sources is the potential for near-zero greenhouse gas emissions. When used in a fuel cell, hydrogen emits only water vapor and warm air, making it a much cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. This makes hydrogen-powered fuel cells ideal for use in vehicles, as they emit none of the harmful substances produced by gasoline and diesel engines, such as nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter.
In addition to reducing emissions, hydrogen produced from renewable energy sources can also provide economic benefits. For instance, global energy trade through hydrogen derivatives can improve economic resilience by allowing importing countries to tap into cheaper energy resources and diversifying their energy sources.
However, there are also challenges to producing hydrogen from renewable energy sources. One significant challenge is the cost, as renewable hydrogen is currently two to three times more expensive to produce than hydrogen from fossil fuels. Additionally, there is a lack of infrastructure for transporting and storing hydrogen, and energy losses occur during the conversion process. Nonetheless, with increasing policy attention and financial support for renewable hydrogen, these challenges can be addressed to unlock the full potential of hydrogen as a clean and versatile energy carrier.
Ethanol's Impact: Reducing Air Pollution and Improving Air Quality
You may want to see also

Hydrogen can be used to power vehicles, reducing emissions
Hydrogen has a diverse range of applications and can be used to power vehicles, reducing emissions and pollution. Hydrogen fuel cells emit only water vapour and warm air, in contrast to gasoline and diesel vehicles, which emit harmful nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter. Hydrogen-powered vehicles, therefore, present a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based engines.
The versatility of hydrogen fuel means it can be used in cars, trucks, buses, and even agricultural equipment. Hydrogen fuel cells can generate electricity without harmful emissions, and even high-temperature fuel cells do not create harmful direct emissions. This makes hydrogen ideal for use in heavy trucks, trains, and ships, providing a zero-emissions option and improving local air quality.
However, it is important to note that hydrogen combustion, particularly in turbines used to generate electricity, can emit nitrogen oxides (NOx). This occurs when air, which contains nitrogen and oxygen, is exposed to very high temperatures (›1,500°C). Hydrogen burns at a higher temperature than natural gas, and thus combustion may result in higher NOx emissions. Nevertheless, hydrogen has a larger stable combustion temperature range, allowing for a higher ratio of air to fuel, which dilutes the hydrogen and results in lower-temperature combustion, ultimately reducing the amount of NOx emissions produced.
Recent innovations have further contributed to the reduction of harmful emissions from hydrogen engines. Scientists from the University of California, Riverside, have developed a low-cost method to improve the efficiency of catalytic converters in hydrogen internal combustion engines. By infusing platinum in catalytic converters with a highly porous material called Y zeolites, the conversion of unhealthful nitrogen oxides into harmless nitrogen gas and water vapour is enhanced. This technology not only reduces pollution from hydrogen engines but also from diesel engines equipped with hydrogen injection systems.
Hydrogen, as a fuel, has the potential to reduce pollution and emissions from the transportation sector, which accounts for a significant portion of energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions. By utilising hydrogen to power vehicles, we can work towards strengthening national energy security, conserving petroleum resources, and diversifying our transportation energy options for a more sustainable and resilient future.
How to Reduce Ozone Pollution in Your Home
You may want to see also

Hydrogen can replace fossil fuels in industrial processes
Hydrogen is a versatile energy carrier that can be used in industrial processes, as well as for electricity generation and transportation. It can be produced from diverse domestic resources, such as natural gas, coal, solar energy, wind, and biomass, and has the potential for near-zero greenhouse gas emissions. When burned, hydrogen yields water, not the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2), meaning it does not contribute to climate change.
In addition to reducing emissions, hydrogen can also improve local air quality. Hydrogen-powered fuel cells emit only water vapour and warm air, whereas gasoline and diesel vehicles emit harmful nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter.
However, it is important to note that hydrogen production can have a large environmental impact depending on how it is produced. Currently, most hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, which results in significant CO2 emissions. To reduce the environmental impact of hydrogen production, it can be combined with carbon capture and storage technology, or produced through electrolysis using electricity from low-carbon sources such as renewable or nuclear energy.
Rooftop Gardens: Nature's Solution to Pollution Problems
You may want to see also

Hydrogen can be used for home heating and cooking
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, and unlike fossil fuels, burning it does not release carbon dioxide. This makes it an ideal alternative fuel source for home heating and cooking, which currently rely on fossil fuels like natural gas.
Natural gas accounts for almost 85% of the fuel used for heating and cooking in UK homes and around 40% in US homes. Burning natural gas as a fuel source in homes, workplaces, and industries accounts for 37% of all carbon dioxide emissions in the UK and 48% in the US. Therefore, switching to hydrogen for heating and cooking could significantly reduce carbon emissions.
However, there are some challenges and considerations to using hydrogen for home heating and cooking. Hydrogen is a tricky gas to manage. It diffuses into steel, making it brittle, and it is harder on electronics than natural gas. Hydrogen is also much smaller and slipperier than natural gas, making it harder to control and more prone to leakage. It burns hotter, which means that existing appliances like boilers, cooking appliances, and gas fires may not be able to tolerate the increased heat and would need to be replaced with hydrogen-ready versions.
The cost of hydrogen is also much higher than natural gas. In California, the retail cost of filling up with hydrogen is $15.61 per kilogram, compared to $4 USD per gigajoule of natural gas. This means that heating a home with hydrogen instead of natural gas could cost several thousand dollars more per year.
Despite these challenges, manufacturers have already built hydrogen boilers, and governments in the UK and US have set targets to reduce carbon emissions by 2035, so experts believe the switch to hydrogen heating will start to happen in the next 10 years. Hydrogen blending trials are also underway to determine how much hydrogen can be mixed with natural gas to lower emissions.
Soil Pollution: Preventing the Degradation of Our Earth's Skin
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Hydrogen reduces pollution by providing an alternative source of energy that does not produce the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) when burned. Instead, it yields water.
Hydrogen can be produced from diverse domestic resources such as natural gas, coal, solar energy, wind, and biomass.
Hydrogen holds the promise of strengthening national energy security, conserving petroleum, and providing a zero-emissions option for certain applications, such as heavy trucks, trains, and ships.



















