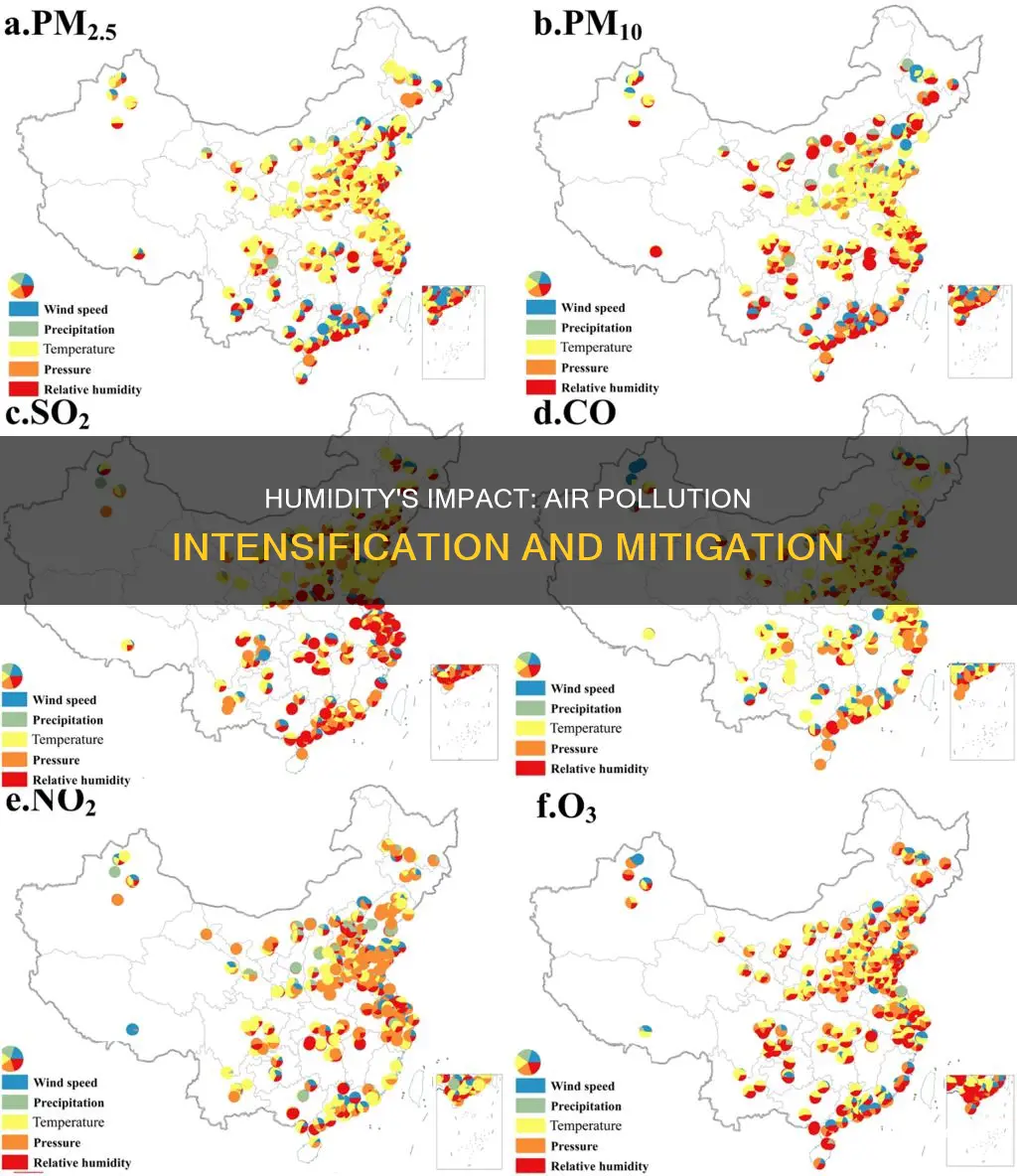
Humidity is the gaseous water in the air and it affects the quality of the air we breathe. It is a combination of dry air and water vapour, and the degree of this combination determines the temperature. Relative humidity, which is the amount of water vapour in the air at certain temperatures, is essential for human health and comfort. It helps regulate our internal body temperature through perspiration. However, low or high humidity can cause poor breathing due to heat stress and airborne germs. High humidity increases the rate of harmful chemicals in the air and contributes to bacterial and viral organisms that cause respiratory infections. On the other hand, low humidity can also cause respiratory issues and increase airborne germs.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Humidity definition | gaseous water in the air; the amount of water vapour in the atmosphere |
| Ideal humidity level | between 20% and 60% |
| Humidity level in an enclosed area | between 30% and 50% |
| High humidity | can cause damage to homes, health problems, and mould growth |
| Low humidity | can cause dry skin, eye irritation, and respiratory issues |
| Effect on air quality | high humidity increases the rate of harmful chemicals, dust mites, and bacterial growth in the air; low humidity increases airborne germs |
| Effect on particulate matter | high humidity increases the size of particulate matter, causing it to fall out of the air |
| Effect on climate | humidity affects weather conditions such as fog, storms, and rainfall, which in turn influence the climate |
What You'll Learn

Humidity increases the rate of harmful chemicals in the air
Humidity is the gaseous water in the air and it affects the quality of the air we breathe. It is a combination of dry air and water vapour, and the degree of this combination determines the temperature. High humidity increases the rate of harmful or toxic chemicals in the air.
High humidity can cause a multitude of issues. For example, it can lead to the growth of mould and bacteria, which can trigger negative respiratory responses. It can also increase the negative effects of harmful air pollutants like smog. Humidity can cause stress to individuals with weakened respiratory systems, especially those with pre-existing conditions like asthma.
High humidity can also cause damage to homes and their contents. Signs of excess humidity include peeling wallpaper, bubbling paint, and warping of wooden floors or furniture. Even electronic equipment can malfunction as a result of moisture.
Humidity can also cause health problems. When humidity levels rise above 50%, a home becomes a breeding ground for dust mites, allergens, and bacterial growth. These particulates can lead to respiratory issues like allergies and asthma, and cause nose, ear, and throat irritation. It can also cause skin rashes when blocked pores cannot release sweat.
High humidity can also lead to an increase in dust mites, which can significantly affect the health of those with asthma or other breathing problems.
In summary, high humidity increases the rate of harmful chemicals in the air, which can have a detrimental effect on human health and property.
Noise Pollution: A Threat to Bat Survival?
You may want to see also

High humidity causes dust mites and mould in homes
High humidity has several negative effects on the home, causing damage to the building and its contents, as well as creating the perfect environment for dust mites and mould to thrive.
Dust mites are tiny, insect-like pests that feed on human skin cells. They are invisible to the human eye and thrive in warm, humid settings. Humidity is the most important factor in determining whether a house has high levels of dust mites. This is because dust mites absorb moisture from the air, rather than drinking water. In areas of low humidity, like deserts, dust mites cannot survive. Dust mites are one of the major indoor triggers for people with asthma and can cause mild to severe allergic symptoms.
Mould is another unwelcome house guest that thrives in humid environments. Mould spores are found everywhere in the environment and are carried into our homes on our clothing and through ventilation. However, it is only when the relative humidity reaches 70% to 80% that mould can spread and grow. The fungi find a suitable breeding ground on almost all organic materials, including many building materials, fibres, hair and skin flakes.
High humidity can also cause damage to the home itself. Signs of excess humidity include peeling wallpaper, bubbling paint, warping of wooden floors or furniture, and even malfunctioning electronic equipment.
To reduce humidity in the home, it is recommended to keep indoor humidity below 50%. This can be achieved through cross-ventilation, using exhaust fans, and regular HVAC maintenance. Dehumidifiers can also be used to remove moisture from the air, improving indoor air quality and reducing the risk of health problems caused by dust mites and mould.
Pollution's Impact: Stunting Development and Growth
You may want to see also

Low humidity causes airborne germs
Low humidity can cause a host of problems, from skin and eye irritation to respiratory issues. It is also a contributing factor to the spread of airborne illnesses.
When the humidity level in a building is low, viruses and bacteria can more easily disperse and travel throughout, infecting occupants. This is because low humidity dries out our mucous membranes, inhibiting our body's natural defence against airborne germs.
The mucous membranes, or mucous membranes, line several cavities in our body, including the respiratory tract. They produce mucus, which, along with cilia, tiny hairs that line our airways, trap pathogens like viruses and bacteria, preventing them from entering our bodies. However, in low humidity, the membranes dry out, and our body's defence mechanism is weakened.
In addition, low humidity can cause heat stress, which further compromises our respiratory system, making us more susceptible to infections.
To prevent the spread of airborne illnesses, it is recommended to maintain indoor humidity levels between 20% and 60%. If the external temperature is above 20° Fahrenheit, indoor relative humidity should be between 30% and 50%.
To increase humidity, one can open doors and windows to improve cross-ventilation, use a humidifier, or employ exhaust fans, especially when cooking or showering, to remove excess moisture.
How Coal Influences Air Pollution and Quality
You may want to see also

Humidity affects the natural deposition of particulate matter in the air
Particulate matter is made up of miniature particles (approximately 2.5 microns in size) that are suspended in the air. These include pollen, dust, ash, spores, soot, smoke, and aerosol droplets. These particles are so small that they can be breathed deep into the lower respiratory system, posing a threat to human health.
When humidity increases, the size of the particulate matter also increases as the particles absorb the moisture in the air. Eventually, the particles become too heavy to remain suspended in the air and begin to fall—this is known as dry deposition.
The less particulate matter there is in the air, the better it is for living things, as it reduces the risk of respiratory issues. Therefore, humidity helps to naturally cleanse the air of particulate matter, improving air quality and reducing potential health risks.
However, it is important to note that high humidity can also have negative effects on health and air quality. For example, it can cause mould growth, increase the number of dust mites, and lead to respiratory issues, particularly for those with pre-existing conditions like asthma.
Pollution's Impact on Marine Life: Understanding the Devastation
You may want to see also

Humidity can help decrease ozone pollution
While humidity can have a detrimental effect on air quality, it can also help to reduce ozone pollution.
Ozone is a major air pollutant and is formed through a series of complex reactions involving sunlight and other chemicals in the atmosphere. In hot, sunny weather, ozone is produced more efficiently, and during heatwaves, it can reach dangerous levels. However, humidity can help to mitigate this.
Afternoon Thunderstorms
Afternoon thunderstorms are a natural phenomenon that can help to reduce ozone pollution. The clouds associated with these storms block out sunlight, reducing the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. This, in turn, slows down the production of ozone for the duration of the storm.
Destruction of Ozone
The moisture in the air during a thunderstorm can also directly destroy ozone molecules that have already been formed. This process further helps to reduce the amount of ozone pollution in the atmosphere.
Impact of Humidity on Health
While high humidity can cause discomfort and health issues such as respiratory problems, eye irritation, and skin rashes, it is important to maintain a balance. Low humidity can also have negative consequences for human health. When the air is too dry, mucous membranes can dry up, increasing the risk of respiratory infections. Therefore, maintaining the right level of humidity is crucial for both human health and air quality.
Managing Humidity
To improve indoor air quality, it is essential to regulate humidity levels. This can be achieved through cross-ventilation, the use of dehumidifiers, and furnace filters, which help to control the amount of moisture and pollutants in the air. HVAC professionals can also provide guidance and services to ensure optimal humidity and air quality.
Globalization's Impact: Pollution's Reach and Rise
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Humidity is the amount of water vapour in the air. When the air has all the water vapour it can hold, it is at 100% humidity. Relative humidity refers to how much water vapour is in the air at certain temperatures. The recommended level of humidity for comfort is between 20% and 60%, while for indoor spaces, it is between 30% and 50%. If the humidity falls below or exceeds these levels, it can negatively impact air quality and lead to health issues.
High humidity can cause dampness, promoting the growth of mould and dust mites, which can trigger respiratory problems like asthma and bronchitis. It can also lead to eye irritation, a stuffy nose, and wheezing. Additionally, high humidity can damage furniture, walls, and floors.
Low humidity, below 20%, results in dry air, causing static electricity, dry and irritated eyes, and dry skin. It can also lead to mucous membranes drying up, increasing the risk of respiratory infections.
To maintain optimal humidity levels and improve air quality, cross-ventilation can be used by opening windows. Dehumidifiers and furnace filters can also help regulate humidity and reduce dust and other air pollutants.