Diesel fuel has been the subject of much debate in recent times, with some arguing that it is a more environmentally friendly option than gasoline, while others claim that it produces more harmful emissions. The science suggests that diesel vehicles produce over four times the amount of certain toxic emissions than petrol cars. However, diesel engines are more fuel-efficient and emit less carbon dioxide. With millions of older diesel engines still in use, diesel fuel continues to contribute to air pollution, particularly in the United States, where it accounts for a significant portion of the transportation sector's CO2 emissions. The environmental impact of diesel fuel is a complex issue, with various factors to consider, including engine type, fuel composition, and regulatory standards.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| CO2 emissions | Diesel fuel contains more carbon per litre than petrol, but diesel engines are "lean-burn", so overall CO2 emissions from diesel cars tend to be lower. |
| Toxic emissions | Diesel vehicles produce more toxic emissions, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and particulate matter (PM). These emissions can have acute respiratory effects and cause cancer. |
| Fuel efficiency | Diesel engines use less fuel to achieve the same performance as petrol engines and have better mileage, resulting in lower fuel costs and reduced emissions. |
| Maintenance | Petrol cars require less maintenance to maintain low pollution levels compared to diesel cars, which need regular maintenance for technologies like particulate filters. |
| Environmental impact | Diesel fuel is heavier and oilier, leading to issues with soot and negative environmental perceptions. However, researchers have made diesel fuel cleaner and more environmentally friendly over time. |
| Health impact | Exposure to diesel exhaust is linked to adverse health effects, including respiratory illnesses, heart problems, and an increased risk of cancer. |
| Regulatory response | The U.S. EPA has established standards for sulfur content in diesel fuel and emissions from new diesel engines, promoting the use of Ultra-Low-Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) fuel. |
What You'll Learn

Diesel engines produce more harmful emissions
Diesel engines have long been associated with harmful emissions, and for good reason. When diesel fuel was first used in cars during the 1970s oil crisis, people noticed their vehicles covered in soot. This, combined with the high levels of nitrogen compounds and particulate matter emitted during diesel fuel combustion, gave diesel a bad environmental reputation.
Diesel vehicles have since been subject to negative publicity due to the amount of toxic emissions they produce. These toxic emissions include nitrogen oxides (NOx), which encompass the toxic nitrogen dioxide (NO2), the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N2O), and nitric oxide (NO), which reacts with oxygen to form NO2. Long-term exposure to nitric oxide is associated with a significantly increased risk of respiratory problems. The fine particulate matter (PM) emitted from diesel engines is also concerning, as it causes cancer and has acute respiratory and cardiovascular effects. Research has linked increases in background concentrations of particulate matter to more hospital admissions and deaths from heart attacks.
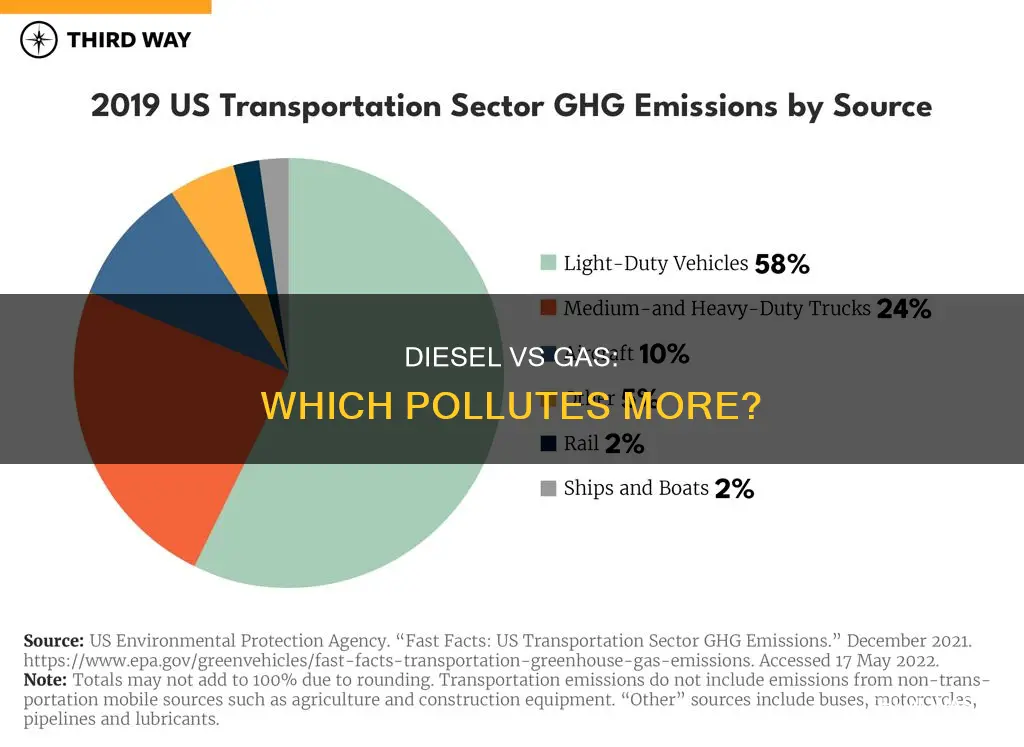
While diesel engines emit lower amounts of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and carbon dioxide than gasoline engines, the impact of diesel emissions on human health and the environment remains significant. Older diesel engines, which can operate for 30 years or more, are particularly problematic, and millions of these dirtier engines are still in use. In 2022, diesel fuel consumption accounted for about 25% of total US transportation sector CO2 emissions and about 10% of total US energy-related CO2 emissions.
To address the issue of harmful diesel emissions, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established standards for the sulfur content of diesel fuel and emissions from new diesel engines. These standards have led to the development of Ultra-Low-Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) fuel, which has a maximum sulfur concentration of 15 parts per million. Most diesel fuel sold in the US for vehicles is now ULSD. The EPA also provides funding for projects that aim to reduce diesel emissions from existing engines.
While diesel engines have been found to produce more harmful emissions than gasoline engines, it's important to note that the latest well-maintained diesel cars, built to current standards, have similar emissions levels to new petrol vehicles.
Understanding Pollution: Toxicity and Its Shades
You may want to see also

Diesel engines are more efficient
- Produce more smoke and "smell funny"
- Are harder to start in cold weather
- Are much noisier and tend to vibrate
- Are less readily available than gasoline
- Are more expensive
- Are heavier
However, diesel engines do have some advantages. They have better fuel economy and longer engine life, saving money in the long term. They are also more powerful, especially when towing or hauling, and have a longer lifespan. This is due to the longer strokes of the engine, which give the piston more time to move away from the heat, reducing wear and building up power. The high compression ratio and cylinder pressure also contribute to the engine's durability, resulting in better lubrication and less wear and tear.
The greater efficiency of diesel engines is also reflected in their different chemical makeups. Gasoline is an aromatic hydrocarbon, which is harsher and more corrosive to the engine over time. On the other hand, diesel fuel is made from crude oil and has a smaller air-to-fuel ratio, allowing the engine to burn the fuel more slowly.
Despite the efficiency of newer diesel engines, diesel fuel still contributes to air pollution. This is because it will take a long time for newer, cleaner diesel engine vehicles to replace older diesel engine vehicles. In 2022, diesel fuel consumption accounted for about 25% of total US transportation sector CO2 emissions and about 10% of total US energy-related CO2 emissions. However, it is important to note that the standards for diesel fuel composition and emissions from diesel engines have become stricter, with the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establishing regulations to reduce the sulfur content of diesel fuels and emissions from new diesel engines. As a result, most diesel fuel sold in the US is now Ultra-Low-Sulphur Diesel (ULSD) fuel, which contains a maximum sulfur concentration of 15 parts per million.
Rocket Launches: Polluters or Green Energy?
You may want to see also

Diesel engines last longer
Diesel engines are generally believed to last longer than gasoline engines. This is due to a combination of factors, including design, fuel type, and usage patterns. Firstly, diesel engines are built with stronger and more durable materials to withstand higher compression ratios and cylinder pressures. They have larger crankshafts and camshafts, thicker walls, and larger pistons, which contribute to their longevity. Additionally, diesel engines generate ignition through compression rather than spark plugs, eliminating a potential point of failure.
The fuel used in diesel engines also plays a role in their longevity. Diesel fuel, derived from crude oil, has lubrication properties that reduce cylinder wear compared to gasoline, which contains harsh and corrosive aromatic hydrocarbons. Diesel engines also exhibit slower cylinder wear, further extending their lifespan. Moreover, diesel engines operate at lower temperatures, reducing friction from heat expansion and minimizing thermal stress on engine components.
Usage patterns also contribute to the longer lifespan of diesel engines. Diesel engines are typically used for longer durations without frequent starts and stops, reducing the abrasive effects of engine startup. They are commonly found in semi-trucks and heavy-duty vehicles, where they are designed to run at constant speeds for extended periods with rigorous maintenance routines. Diesel engines also benefit from enhanced cooling systems, featuring multiple sensors, thermostats, and piston cooling nozzles, which prevent overheating and ensure a constant stream of coolant throughout the engine.
While diesel engines have a reputation for longevity, it is important to consider the environmental impact of diesel fuel. Diesel-fueled vehicles have been associated with harmful emissions, including ground-level ozone, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which can have adverse effects on human health and the environment. However, it is worth noting that modern diesel engines built to the latest standards have similar emissions levels to new petrol vehicles when properly maintained.
In summary, diesel engines are designed and built with heavier-duty components, operate at lower temperatures, and benefit from the lubricating properties of diesel fuel, all of which contribute to their longer lifespan compared to gasoline engines. However, the environmental implications of diesel fuel pollution should be addressed through regulations, fuel standard improvements, and the adoption of newer, cleaner diesel engine technologies.
Sugarcane States: Polluting Our Environment?
You may want to see also

Diesel engines are more cost-effective
Diesel engines have been a subject of debate for their higher pollution levels compared to gasoline engines. However, they have certain advantages that make them more cost-effective in specific contexts.
Firstly, diesel engines are known for their better fuel economy, which means they use less fuel to achieve the same performance as a petrol engine. This "lean-burn" characteristic results in lower overall fuel costs over the life of the engine. This is particularly advantageous for vehicles with high mileage or those used for long-distance travel, as the fuel savings can offset the typically higher cost of diesel fuel.
Secondly, diesel engines have a longer engine life compared to their gasoline counterparts. While diesel engines may have a higher initial cost, their longevity can lead to cost savings in the long run by reducing the need for frequent engine replacements. This makes them a more economical choice for vehicles intended for long-term use or those subjected to heavy-duty operations.
Additionally, advancements in technology have helped address some of the historical disadvantages of diesel engines. New diesel engine designs, utilizing advanced computer control, have significantly reduced issues related to smoke, noise, vibration, and cost. These improvements enhance the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of diesel engines, making them more appealing to consumers.
It is worth noting that, in certain scenarios, the advantages of diesel engines may be negated. For example, in government fleets with limited daily travel distances, the higher cost per gallon of diesel fuel can offset its slight advantage in miles per gallon. Moreover, diesel engines typically require more frequent and costly maintenance due to routine maintenance needs and the higher cost of replacement parts.
In conclusion, while diesel engines have faced scrutiny for their environmental impact, they offer improved fuel economy and longer engine life. These factors contribute to their cost-effectiveness, particularly for specific use cases such as high-mileage or long-distance vehicles. However, it is essential to consider the specific context of usage, as factors like travel distance and maintenance requirements can influence the overall cost-effectiveness of diesel engines.
Caddisfly Pollution Sensitivity: A Natural Warning System
You may want to see also

Diesel engines are subject to stricter regulations
Diesel engines have been subject to stricter regulations in recent years due to the harmful pollutants they emit. Burning diesel fuel produces ground-level ozone and particulate matter, which has adverse effects on human health and the environment. The fine particulate matter emitted from diesel engines is associated with poor heart health and can cause cancer and acute respiratory issues.
To address these issues, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established standards for the sulfur content of diesel fuel and emissions from new diesel engines. The EPA's Diesel Emissions Reduction Act Program, created under the Energy Policy Act of 2005, provides grants and loans to promote diesel emission reductions. As a result of these regulations, modern diesel engines are cleaner than ever before. However, the longevity of diesel engines, which can operate for 30 years or more, means that millions of older, more polluting engines are still in use.
The EPA has also introduced cleaner-burning diesel fuel known as Ultra-Low-Sulfur Diesel (ULSD), which has a maximum sulfur concentration of 15 parts per million. Most diesel fuel sold in the United States for vehicles is now ULSD. Additionally, new technologies such as direct injection devices, CRT particulate filters, and catalytic converters have been developed to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency in diesel engines.
While diesel engines have been scrutinized for their emissions, it is important to note that gasoline engines also contribute to air pollution. Gasoline engines emit higher amounts of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and carbon dioxide compared to diesel engines. However, gasoline engines have the advantage of being self-regulating, requiring less maintenance and less driver input to maintain their performance.
In conclusion, diesel engines have been subject to stricter regulations due to the harmful pollutants they emit. While modern diesel engines are cleaner, the persistence of older engines and the impact of diesel emissions on human health and the environment remain concerns. To address these challenges, regulatory bodies like the EPA have implemented standards and initiatives to reduce diesel emissions and promote cleaner alternatives.
Sunflowers: Soil Pollution Solution?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, diesel vehicles cause more than four times the pollution of petrol cars.
Diesel fuel produces many harmful emissions when burned, including nitrogen oxides, ground-level ozone, and particulate matter.
Exposure to diesel exhaust can lead to asthma, respiratory illnesses, and increased risk of heart problems.
EPA regulations have led to cleaner diesel engines, and the development of ultra-low-sulfur diesel fuel has helped to reduce emissions from diesel vehicles.