Hybrid cars are often touted as the green saviour of the automobile industry, with their combination of a smaller gasoline engine and an electric motor for fuel economy. However, it is important to consider the environmental impact of their production and use. While hybrid cars produce fewer emissions than conventional cars, they still cause pollution, especially when using the gasoline engine. The production of hybrid cars may also offset some of the benefits of reduced emissions during use, as they require more energy and emit more greenhouse gases during manufacturing. The electricity used to charge hybrid cars may also come from power grids that burn coal or natural gas, contributing to carbon pollution. Despite these concerns, hybrid cars remain a significant step towards reducing pollution and can be a good choice for those seeking to minimise their environmental impact.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Hybrid cars still cause pollution because they | Use a combustion engine that releases the same wastes as a conventional vehicle |
| The manufacturing process of hybrid cars | Requires more energy and emits more greenhouse gases than the manufacturing process of conventional cars |
| Hybrid cars are | More energy-intensive to produce than conventional cars |
| Hybrid cars | Burn the same kind of fuel used in conventional, gas-powered cars |
| Hybrid cars | Produce fewer emissions than conventional cars |
| Hybrid cars | Are more fuel-efficient than traditional vehicles |
| Hybrid cars | Are smaller and quieter than traditional vehicles |
What You'll Learn
- Hybrid cars still use gasoline engines, which create emissions
- The manufacturing process for hybrid cars may be more harmful to the environment
- Hybrid cars still use less fuel and emit fewer greenhouse gases than conventional cars
- The electricity used to charge hybrid cars may be generated by burning coal or natural gas
- Hybrid cars use copper in their motors and wiring, which must be mined, degrading the environment

Hybrid cars still use gasoline engines, which create emissions
Hybrid cars are often touted as the green saviour of the automobile industry. They are marketed as a solution to the environmental destruction caused by transportation, as they release fewer and cleaner wastes, resulting in lower pollution levels. However, it is important to remember that hybrid cars still use gasoline engines, which create emissions.
While hybrid cars do have an electric motor that reduces pollution, they also have a combustion engine that releases the same wastes as conventional vehicles. This means that when using the gasoline engine, hybrid cars will create emissions like any other vehicle. The gas engine typically kicks in at higher speeds, so while hybrid cars produce fewer emissions overall, they still contribute to pollution levels.
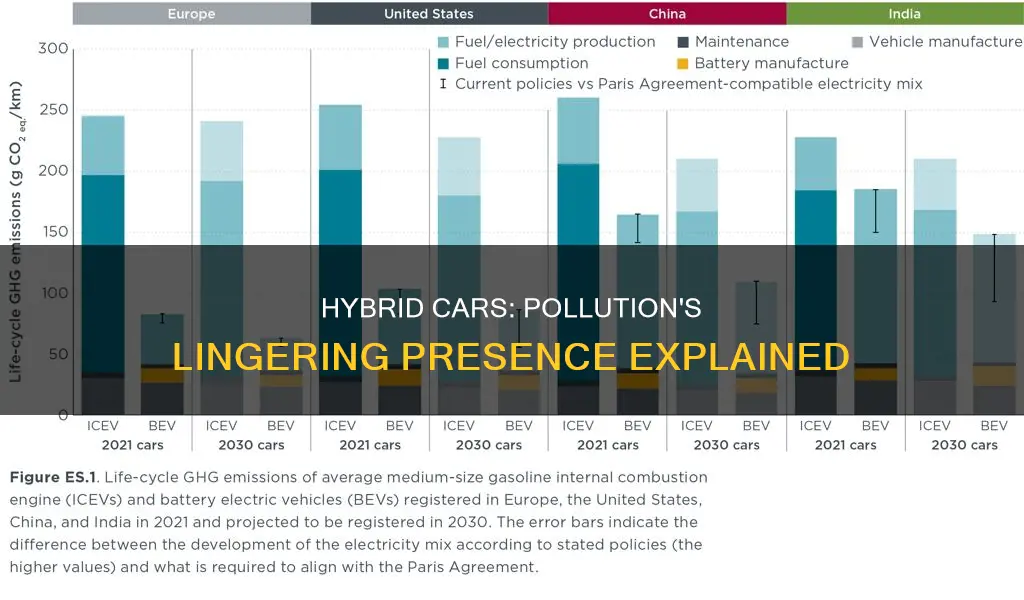
The impact of hybrid cars on the environment is a complex issue. On the one hand, they offer a significant advantage over traditional gasoline-powered cars in terms of reduced emissions and fuel consumption. This has led to an increase in sales, with many eco-conscious consumers seeing hybrids as an investment in the environment. However, it is important to consider the entire life cycle of a hybrid car, from production to decommissioning, when evaluating its environmental impact.
The production of hybrid cars requires a significant amount of energy and can result in higher emissions. The manufacturing process for hybrid car batteries, in particular, can create more carbon pollution than the production of a gasoline car. Additionally, the mining of rare earth metals like lithium, which are used in hybrid car batteries, can have a detrimental effect on the environment. While hybrid cars may produce fewer emissions during their use, the pollution created during their production cannot be ignored.
Overall, while hybrid cars with gasoline engines do create emissions, they still offer a greener choice than conventional vehicles. They produce lower levels of greenhouse gases during operation and have a smaller carbon footprint over their lifetime. However, it is important to consider the trade-offs involved in the production and use of hybrid cars to fully understand their impact on the environment.
Cars' Impact on Utah's Pollution: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

The manufacturing process for hybrid cars may be more harmful to the environment
Hybrid cars are often touted as the green saviour of the automobile industry, and they are increasingly popular. However, the manufacturing process for hybrid cars may be more harmful to the environment.
Firstly, the production of hybrid cars requires a significant amount of energy. An in-depth study by the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory found that hybrid cars require more energy to produce than conventional cars, emitting more greenhouse gases and burning more fossil fuels during the manufacturing process. This is due to the energy-intensive nature of manufacturing hybrid car batteries. The process of mining the rare earth metals used in hybrid car batteries, such as lithium, can be particularly harmful to the environment. In the Bayan Obo region of China, for example, miners have been found to use acids to extract gold-flecked metals, which has contaminated groundwater and destroyed nearby agricultural land.
Secondly, the assembly line production of hybrid cars also requires a lot of energy. The process involves forging materials like steel, aluminium, glass, and plastic, which demands a significant amount of energy.
Thirdly, the transportation of hybrid car parts can also contribute to pollution. The nickel used in hybrid car batteries, for example, may travel a significant distance before reaching the factory, burning more fuel in the process.
While hybrid cars offer improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions during operation, the manufacturing process may generate more pollution than the production of conventional cars. This hidden environmental impact of hybrid cars raises important questions about the overall sustainability of these vehicles.
Vehicle Fuel's Water Pollution: Understanding the Harmful Impact
You may want to see also

Hybrid cars still use less fuel and emit fewer greenhouse gases than conventional cars
Hybrid cars have been touted as the green saviour of the automobile industry. They are more fuel-efficient than conventional cars and emit fewer greenhouse gases. This is because they have a second electric motor, which means they burn less fuel and emit lower levels of greenhouse gases during operation. The electric motor also cuts down on pollution.
However, it is important to consider the energy expended to produce hybrid cars. A significant amount of energy goes into producing hybrid cars, and this has been a point of criticism. The manufacturing process for hybrid cars is more energy-intensive and results in higher production emissions. This is especially true when considering the energy required to manufacture the battery.
While hybrid cars do emit fewer greenhouse gases than conventional cars, it is worth noting that they still produce emissions. Hybrid cars, when using the gas engine, create pollution similar to conventional vehicles. The electric engine is typically used at low speeds or when stopped, so when driving at high speeds, the combustion engine takes over and releases the same wastes as a conventional vehicle.
Despite the emissions associated with the production and operation of hybrid cars, they still offer a significant advantage over traditional gasoline-powered cars in terms of reduced emissions and fuel consumption. This is especially true when considering the entire lifetime of the vehicle. Over time, the emissions associated with manufacturing and charging an electric vehicle are typically offset by the lower emissions during operation.
In conclusion, while hybrid cars may not be completely free of emissions, they still use less fuel and emit fewer greenhouse gases than conventional cars. This makes them an attractive option for eco-conscious consumers who are looking to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Beijing's Air Pollution: Causes and Concerns
You may want to see also

The electricity used to charge hybrid cars may be generated by burning coal or natural gas
Hybrid cars are generally considered to be a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cars that run solely on gasoline. They are powered by a combination of a smaller gasoline engine and an electric motor, which results in better fuel economy and lower emissions. However, it is important to note that hybrid cars still contribute to pollution, particularly during the manufacturing process and when using the gasoline engine.
In some cases, the production and assembly of hybrid cars can result in higher emissions and pollution compared to conventional cars. This is due to the energy-intensive nature of manufacturing hybrid vehicles and the rare earth metals required, such as lithium. The mining and extraction processes for these metals can have significant environmental impacts, including soil removal, groundwater contamination, and agricultural land destruction.
However, it is worth noting that the overall carbon footprint of a hybrid car is generally lower than that of a conventional gasoline car. Hybrid cars emit lower levels of greenhouse gases during operation, and the use of an electric motor reduces pollution. Additionally, advancements in battery technology and the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources for electricity generation can further reduce the environmental impact of hybrid cars over time.
In conclusion, while hybrid cars offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, they are not entirely pollution-free. The electricity used to charge their batteries may be generated by burning fossil fuels, contributing to carbon pollution. However, the impact of this pollution can be mitigated by transitioning to renewable energy sources for electricity generation and by improving the efficiency of hybrid car manufacturing processes.
Cars and Carbon Pollution: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also

Hybrid cars use copper in their motors and wiring, which must be mined, degrading the environment
Hybrid cars are often touted as the green saviour of the automobile industry, with eco-conscious consumers seeing them as an investment in the environment. However, it is important to consider the entire lifecycle of a product, from production to disposal, when assessing its environmental impact.
However, the mining of copper and other rare earth metals for these motors can have detrimental effects on the environment. For example, in the Bayan Obo region of China, miners removed topsoil and extracted gold-flecked metals using acids that entered the groundwater, destroying nearby agricultural land. This is just one example of how the mining of metals for hybrid car components can lead to ecological harm.
Additionally, the production of hybrid cars requires a significant amount of energy and can result in higher emissions during the manufacturing process compared to conventional cars. While hybrid cars do cause pollution, it is important to note that they produce less pollution than conventional cars over their lifetime. The use of an electric motor in hybrids cuts down on pollution, and the majority of hybrids on the road burn the same fuel as conventional cars but with reduced emissions.
Air Pollution: Silent Killer, Long-Term Ailments Revealed
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Hybrid cars, when using the gas engine, create pollution like any other conventional vehicle. The use of an electric motor, however, cuts down on that pollution. The majority of hybrid cars in production and on the road are gas-electric hybrids, and they burn the same kind of fuel used in conventional, gas-powered cars. Hybrid car emissions pollution is real, but the amount of pollutants is significantly reduced compared to conventional cars.
A significant amount of energy goes into producing hybrid cars, but it's no more than what it takes to make conventional cars. Hybrid vehicles are more energy-intensive and result in higher production emissions, but they are still the greener choice overall.
Hybrid vehicles have a positive impact on the environment as they release fewer and cleaner wastes, resulting in smaller pollution levels. They are also more fuel-efficient, boasting mileages that are twenty to thirty percent greater than traditional vehicles.
Hybrid cars are a significant improvement over traditional gasoline-powered cars in terms of reduced emissions and fuel consumption. However, fully electric vehicles are usually the cleanest choice, but it is possible for a hybrid vehicle to create even less climate pollution, depending on how and where they're manufactured and driven.