Water is a necessity for all life forms, and human development and survival are dependent on it. Water politics, or hydropolitics, is the study of conflict and cooperation between states over water resources that transcend international borders. Water scarcity is a global issue, with a quarter of the world's population facing extreme water stress every year. This scarcity is driven by factors such as overpopulation, overconsumption, urbanisation, agricultural practices, mining, industry, and climate change. The unequal distribution of water resources often shapes geopolitical patterns, with downstream riparian states being affected by the actions of upstream states. Water-related conflicts have occurred throughout history and continue to be a concern, with access to water becoming one of the main geopolitical issues of our century. Water diplomacy aims to foster cooperation and resolve disagreements over shared water resources to ensure water security. Additionally, water pollution is a significant issue, with human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and urbanisation contributing to the degradation of water quality. Legal acts and movements, such as the Water Justice movement, have emerged to protect water resources and prevent increased pollution.
What You'll Learn

Water scarcity and conflict
Water scarcity is a global issue, with a quarter of the world's population facing extreme water stress annually. This stress is caused by a combination of factors, including overpopulation, overconsumption, and climate change. As demand for water increases, freshwater resources are diminishing, exacerbating tensions and contributing to social and political instability.
Water is essential for human survival, playing a critical role in food security, human health, and regional stability. It is also necessary for industries such as agriculture and technology development. The unequal distribution of water resources often shapes geopolitical patterns, with downstream riparian states being highly impacted by the actions of upstream states. This dynamic has led to conflicts, such as those between Iraq, Syria, and Turkey, and among Egypt, Sudan, and Ethiopia over the Nile River.
The concept of "water wars" acknowledges that water resources are often casualties of violent confrontations, either intentionally or accidentally. Water infrastructure may be targeted to achieve political, economic, or military interests, as seen with the Islamic State's use of water as a weapon. However, water scarcity can also be a catalyst for conflict, as evident in the ancient dispute between the Mesopotamian city-states of Lagash and Umma.
To address water scarcity and conflict, cooperation through water diplomacy and multilateral governance is crucial. Water diplomacy aims to foster collaboration and peace by solving, mitigating, or preventing disagreements over shared water resources. The EU, for example, has promoted water resource management and provided access to clean water to millions. Additionally, legal acts and policies have been implemented to protect water quality, regulate usage, and ensure the right to water.
As water scarcity intensifies due to factors like population growth, urbanization, and pollution, the importance of effective water governance and diplomacy will become even more critical in preventing conflicts and ensuring equitable access to this vital resource.
Water Pollution: Marine Life Under Threat
You may want to see also

Water as a tool for political gain
Water is a necessity for all life forms and human development, and its availability has a significant impact on food security, human health, regional stability, and international tensions. The increasing global demand for water, coupled with diminishing freshwater resources, has exacerbated tensions and made water a strategic natural resource.
Water scarcity, caused by factors such as overpopulation, overconsumption, and climate change, has led to water stress, which contributes to social and political instability, food insecurity, and industrial, electricity, and transportation disruptions. This has made water a tool that can be leveraged for political gain.
For example, in the Middle East, water politics has played a significant role in conflicts between Iraq, Syria, Turkey, Egypt, and other Nile riparian states, as well as Israel and Palestine. The cutting or reduction of water supply from one nation to another has been used as a tactic to exert control and achieve political objectives. Similarly, the Islamic State (IS) has used water as a weapon to achieve its military and political goals by contaminating water supplies and using large dams to cut off water supplies or flood areas.
Water diplomacy, which aims to solve, mitigate, or prevent disagreements over shared water resources, is a promising approach to fostering multilateral governance and ensuring water security. However, the unequal distribution of water resources can still shape geopolitical patterns, and the competition for water can spark conflicts or create opportunities for development and growth in certain regions.
Water is also at the heart of environmental movements, such as the Standing Rock protests, where indigenous communities and various global organizations advocate for the defence of access to clean water and against the privatization of water resources. The issue of water pollution and its impact on drinking water quality is a significant concern for these movements, and various legal acts have been signed into law to address this issue.
Water Pollution: Understanding the Causes and Impacts
You may want to see also

Water diplomacy and cooperation
However, cooperation is a more sustainable approach than conflict, and water diplomacy offers a promising path towards multilateral governance of shared water resources. Water diplomacy involves using diplomatic tools to address disagreements over water resources, with the involvement of non-state actors like the World Bank, who can provide essential mediation and information. This is particularly crucial in transboundary water contexts, such as international rivers, where the actions of upstream riparian states significantly impact their downstream counterparts.
An example of water diplomacy in action is the EU's promotion of water resource management, having disbursed over EUR 2.5 billion in 62 countries and provided access to clean water for more than 70 million people. The EU has also supported the implementation of the Helsinki Water Convention 1992, recognising the importance of international agreements in water governance.
Water scarcity, driven by factors like overpopulation, overconsumption, and climate change, is a global issue that exacerbates tensions. Freshwater, essential for human consumption and agriculture, is already scarce, with billions experiencing severe shortages annually. This scarcity is further impacted by human activities such as pollution, urbanisation, and deforestation, highlighting the need for effective water diplomacy and cooperation to address these challenges.
To ensure water security, it is crucial to involve all stakeholders, including local and indigenous communities, who possess valuable knowledge about sustainable water management practices. By working together and prioritising cooperation, societies can address water-related challenges and foster stability, peace, and equitable access to this vital resource.
Floating Cow Farms: Water Pollution Solution?
You may want to see also

Water pollution and environmental damage
Water is essential for all life forms and human development, and access to clean water is a fundamental human right. However, water pollution and environmental damage pose significant threats to this vital resource. Water pollution, primarily caused by human activities, has severe ecological, social, and political implications.
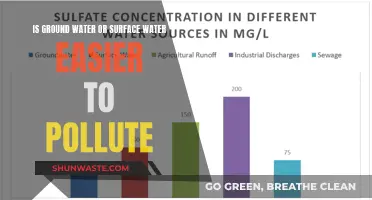
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water sources, such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater, with harmful substances. This pollution can be caused by a range of factors, including industrial and agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, chemical and oil spills, and marine debris. These pollutants can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, killing marine life and disrupting the delicate balance of these environments. Contaminants can include toxic chemicals, heavy metals, nutrients (leading to eutrophication and harmful algal blooms), and pathogens, which can cause various health issues in humans and animals.
Climate change is another critical factor contributing to water pollution and environmental damage. As the planet warms, glaciers and ice caps melt, causing sea levels to rise and altering freshwater resources. Climate change also leads to more frequent and severe droughts and floods, further impacting water availability and quality. Additionally, increased temperatures can exacerbate water scarcity, particularly in regions already facing water stress due to overconsumption, population growth, and inadequate water management practices.
Water-related conflicts, or "water wars," have occurred throughout history, and water scarcity and pollution can act as catalysts for violent confrontations. Water infrastructure is often a casualty of violent conflicts, either intentionally or accidentally. Additionally, water resources may be weaponized to achieve political, economic, or military objectives, as seen with the Islamic State's use of water contamination and dam control to exert power over its enemies.
To address water pollution and environmental damage, various legal acts and policies have been implemented worldwide. These include international agreements, such as the Helsinki Water Convention 1992, and local regulations aimed at reducing pollution, regulating water usage, and improving water quality. Water diplomacy, which emphasizes cooperation and the involvement of non-state actors, is also gaining prominence as a means to foster multilateral governance over shared water resources and ensure water security.
Water Pollution: 5 Startling Facts You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Water security and food production
Water security is essential for food production, and both are inextricably linked to geopolitical stability. Water is a fundamental resource for human survival and development, playing a significant role in food security, human health, and regional stability. The availability of water per capita is inadequate and shrinking worldwide due to increasing global demand, local scarcity, population growth, and climate change.
Water stress, driven by urbanization, agricultural practices, industry, mining, and climate change, is a growing challenge. It contributes to social and political instability, food insecurity, and disruptions in essential sectors like industry, electricity, and transportation. The issue of water scarcity affects different regions unevenly, with 4 billion people experiencing severe water shortages for at least one month annually. This lack of availability has severe consequences for food production and regional stability.
Water is essential for food production, whether vegetable or animal. In the context of food production, water security refers to the availability of sufficient water of suitable quality to meet the needs of agriculture and livestock farming. Water is used in various stages of food production, including irrigation, livestock watering, and processing. The impact of water scarcity on food production is already evident in many regions, with conflicts arising over water rights and access.
For example, the situation along the Nile River is particularly concerning. The construction and filling of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) have led to tensions between Ethiopia, Sudan, and Egypt, as the flow of the river downstream will be reduced, affecting the water supply of these nations. This example illustrates the complex geopolitical dimensions of water security and food production, where negotiations and international cooperation are necessary to balance the needs of all parties involved.
Water diplomacy and cooperative efforts are crucial in mitigating conflicts and promoting sustainable solutions. The EU, for instance, has actively promoted water resource management and provided access to clean water to millions of people. Additionally, legal acts and policies, such as the Helsinki Water Convention 1992, aim to prevent increased pollution and protect drinking water sources. These initiatives recognize the importance of water security for food production and seek to address the challenges posed by water scarcity through collaboration and the involvement of all stakeholders, including local communities and non-state actors.
Mining's Watery Grave: Pollution from Mining Activities
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Water is a necessity for all life forms and human development. Water politics, or hydropolitics, is politics affected by the availability of water and water resources. Water scarcity is a global issue, with a quarter of the world’s population facing extreme water stress every year. Water stress is driven by urbanization, agricultural practices, mining and industry, and climate change. Water stress can contribute to social and political instability, food insecurity, and industrial, electricity, and transportation disruptions. Water is also used as a tool to achieve political, economic, or military interests.
Water scarcity affects different regions globally, with 4 billion people experiencing severe shortages for at least one month of the year. This lack of availability has a serious impact on the world's population, increasing tensions. Water scarcity is caused by overpopulation, overconsumption, and climate change. Water is critical for agriculture, industry, and domestic uses, and its availability is essential for food security, human health, and regional stability.
Water pollution is a significant issue that affects water availability and quality. It is caused by human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, and pollution. Water pollution is addressed through water resource policies and laws that aim to reduce and eliminate pollution, regulate water usage, and improve water quality. Water diplomacy aims to solve, mitigate, or prevent disagreements over shared water resources to ensure water security and foster cooperation.