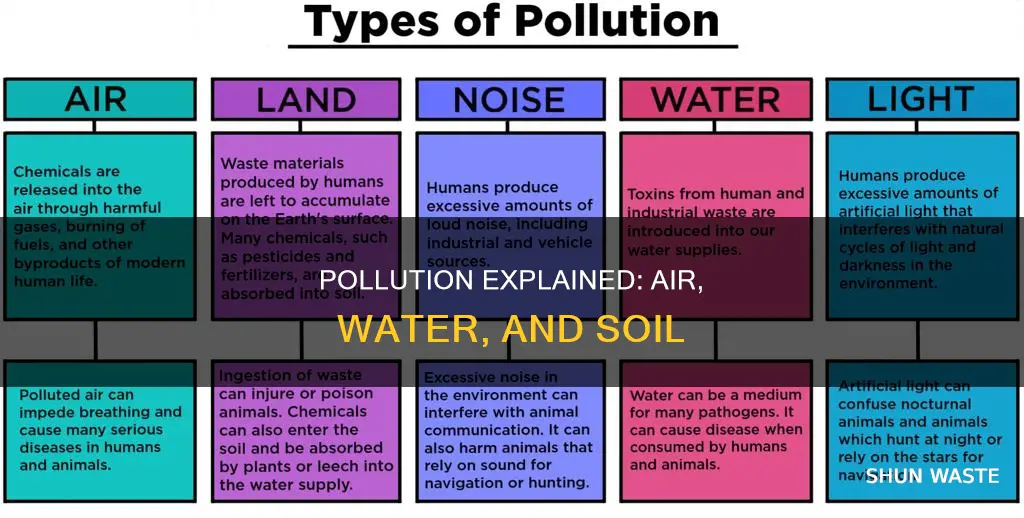
Pollution refers to the presence of extremely high concentrations of harmful substances in the environment, which can be harmful to the health of living organisms. The three main types of pollution are air, water, and soil pollution. Air pollution is caused by the presence of harmful toxic compounds in the air, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide. Water pollution is caused by agricultural runoff, urban waste, waste treatment, and acid rain, which can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic ecosystems and human health. Soil pollution, on the other hand, is the contamination of soil due to harmful substances such as heavy metals, pesticides, and sewage, which can render it unfit for growing crops and impact water sources. These types of pollution are caused primarily by human activities and pose significant risks to both the environment and human health.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | The presence of extremely high concentrations of harmful substances in the environment |
| Types | Air, water, and soil pollution |
| Causes | Human activities, such as industrial discharge, chemical use, littering, and agricultural practices |
| Health Hazards | Respiratory problems, lung diseases, allergies, cardiovascular disease, neurological disorders, and even death |
| Environmental Impact | Climate change, harm to ecosystems and biodiversity, and reduced agricultural productivity |
| Initiatives | EU's Zero Pollution Action Plan (2021), Priority Substances Directive (2013), Marine Strategy Framework Directive (2008) |
What You'll Learn
- Air pollution is the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical, or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere
- Water pollution is caused by toxic substances from farms, towns, and factories dissolving into and mixing with water
- Soil pollution is caused by the presence of toxic chemicals (pollutants or contaminants) in the soil, which can be caused by natural processes or human activities
- Oil pollution in the ocean is caused by tankers, shipping operations, and land-based sources such as factories, farms, and cities
- Radioactive waste is a type of pollution that emits radiation beyond what is naturally released by the environment and is generated by uranium mining, nuclear power plants, and military weapons

Air pollution is the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical, or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere
Air pollution involves the addition of harmful substances to the air, such as gaseous substances or particulates, which can cause a range of health issues and environmental problems. These substances can include carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide, which, when present in high concentrations, become pollutants. The health impacts of air pollution include respiratory problems, such as breathing difficulties, irritation, and lung diseases, as well as other issues like allergies and even death.
One of the significant ways air pollution affects the environment is by contributing to climate change. It often exacerbates natural calamities such as droughts and floods. Additionally, air pollution can have indirect effects on water and soil quality. Pollutants in the air can mix with precipitation, leading to acid rain and particulate deposition, which then contaminate water bodies and soils. This, in turn, affects plant growth and water quality, as well as the health of aquatic ecosystems and other organisms that depend on these ecosystems.
To address air pollution, various measures can be implemented, including the adoption of air quality plans by member states to adhere to ambient air quality standards. Additionally, national emission reduction targets and emissions standards for key sources of pollution, such as vehicles, ships, energy production, and industry, are crucial for mitigating air pollution.
It is important to recognize that air pollution is closely interconnected with water and soil pollution. Water pollution, often a result of human activities, involves the contamination of bodies of water such as lakes, rivers, oceans, and groundwater. Soil pollution, on the other hand, refers to the contamination of soils by the addition of chemicals or physical disruption, which can have detrimental effects on agricultural productivity. These three forms of pollution—air, water, and soil—are interconnected and have far-reaching consequences for human health, biodiversity, and the planet's ecosystems.
Fertilizer Runoff: A Water Pollutant?
You may want to see also

Water pollution is caused by toxic substances from farms, towns, and factories dissolving into and mixing with water
Water pollution is a pressing issue that poses significant risks to both human health and the environment. It occurs when harmful substances, often in the form of toxic chemicals or microorganisms, contaminate bodies of water such as streams, rivers, lakes, oceans, or aquifers. Water pollution is primarily caused by the dissolution and mixing of toxic substances from farms, towns, and factories.
Farms and agricultural practices contribute significantly to water pollution. The use of pesticides and fertilisers in agriculture can lead to contamination when these chemicals seep into groundwater or run off into surface waters during rainfall. Animal waste from farms and livestock operations also introduce bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens into water sources, degrading water quality. According to the UN, agriculture is the leading cause of water degradation worldwide, particularly in rivers and streams.
Towns and cities are another major source of water pollution. Domestic sewage from urban areas often contains pathogens, which are disease-causing microorganisms. These pathogens can include bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances that pose direct threats to public health. Additionally, putrescible organic matter in sewage can deplete the dissolved oxygen content of water through natural decomposition processes, further compromising water quality.
Factories and industrial sites also play a significant role in water pollution. Improperly disposed of wastewater from industrial plants and chemical process facilities can introduce toxic chemicals such as lead, mercury, and chromium into freshwater systems. These toxic substances not only render water unsafe for human consumption but also disrupt marine ecosystems by changing water temperatures and creating "dead zones" with dangerously low oxygen levels.
The cumulative effect of these toxic substances from farms, towns, and factories dissolving into and mixing with water has severe consequences. Water pollution jeopardises human health, with unsafe water being a leading cause of premature deaths worldwide. It also harms biodiversity, contributing to the ongoing extinction of species. The declining water quality severely impacts both human well-being and the natural ecosystems that depend on clean water.
Addressing water pollution requires a multifaceted approach. Implementing proper waste management systems, reducing the use of toxic chemicals, and improving sewage treatment processes are crucial steps. Additionally, adopting sustainable agricultural practices and regulating industrial waste disposal can help mitigate the dissolution and mixing of toxic substances from farms, towns, and factories into water sources.
Poultry Farms: Water Pollution and Its Prevention
You may want to see also

Soil pollution is caused by the presence of toxic chemicals (pollutants or contaminants) in the soil, which can be caused by natural processes or human activities
Soil pollution refers to anything that causes contamination of the soil and degrades soil quality. It occurs when pollutants are present in the soil in quantities that reduce soil quality and make it uninhabitable for microorganisms and macroorganisms. Soil pollution is primarily caused by human activities, although natural processes can also play a role.
Human activities that cause soil pollution include the use of pesticides and herbicides, industrial waste, and the dumping of technological waste. Pesticides and herbicides contain harmful chemicals that can accumulate in the soil over time. In addition, the overuse of pesticides can lead to a loss of fertility in the soil. Industrial activities such as manufacturing and mining can also release toxic substances into the soil, including heavy metals like lead and mercury. Other sources of soil pollution include construction sites, where various chemicals can be released into the air and spread through the wind, and the storage of waste in landfills, which can leak into the soil and contaminate groundwater.
Natural processes that contribute to soil pollution include the rare cases of natural accumulation of chemicals and certain phenomena such as erosion, increased salt content, and acidification. However, human activities are the primary cause of soil pollution, and they can work in conjunction with natural processes to increase the levels of toxic contamination in the soil.
Soil pollution has severe consequences for human health, biodiversity, and food security. Pollutants in the soil can enter our bodies through the food chain, causing various illnesses. It also affects the quality of air and water, as contaminated water can seep into the soil and further spread to water bodies. Soil degradation can lead to a decline in biodiversity, as it destroys habitats and endangers species. According to the Global Land Outlook report by the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification, soil pollution is the biggest environmental cause of disease and death worldwide.
Water Pollutants: Understanding Two Common Contaminants
You may want to see also

Oil pollution in the ocean is caused by tankers, shipping operations, and land-based sources such as factories, farms, and cities
Pollution is the presence of extremely high concentrations of harmful substances in the environment. These pollutants are often the result of certain human activities and can be harmful to the health of living organisms. Air, water, and soil pollution are the three main types of pollution causing health hazards today.
Oil pollution in the ocean is a pressing issue, with tankers, shipping operations, and land-based sources such as factories, farms, and cities contributing to the problem. Oil spills are a significant cause of ocean oil pollution. The Deepwater Horizon incident in 2010 is an example of a large-scale oil spill, where an explosion of the drilling platform resulted in approximately 134 million gallons of oil spilling into the Gulf of America, impacting the environment and human health. Oil spills can harm sea creatures, ruin beaches, and make seafood unsafe to eat.
In addition to large-scale incidents like Deepwater Horizon, thousands of smaller oil spills occur each year, some spilling less than a barrel of oil. These spills contribute to the overall oil pollution in the ocean and have cumulative negative effects on the ecosystem. Oil pollution in the ocean can also come from natural seeps, where oil enters the ocean through fractures or faults in the seafloor. While natural seeps are a smaller source compared to oil spills, they still play a role in the overall pollution problem.
Land-based sources, such as factories, farms, and cities, contribute significantly to ocean oil pollution through runoff. Oil from these sources flows into rivers and eventually makes its way to the ocean. This type of pollution is often a result of inadequate management and treatment of industrial and agricultural waste. Factories and industrial facilities may discharge oil-contaminated wastewater into water bodies, which then flows into the ocean. Farms and cities contribute to oil pollution through runoff from vehicles, machinery, and other oil-based products.
The impact of oil pollution in the ocean is far-reaching and long-lasting. It harms marine life, disrupts ecosystems, and contaminates seafood. Cleaning up oil spills and restoring affected areas is a challenging and costly process. The Oil Pollution Act of 1990 established that those responsible for oil spills can be held accountable for the cleanup and restoration process. This includes paying for the assessment of the spill's impacts and funding restoration projects through settlements.
Testing Water Pollution: Methods and Techniques
You may want to see also

Radioactive waste is a type of pollution that emits radiation beyond what is naturally released by the environment and is generated by uranium mining, nuclear power plants, and military weapons
Pollution is the presence of extremely high concentrations of harmful substances in the environment, which can be harmful to the health of living organisms. Air, water, and soil pollution are the three main kinds of pollution causing health hazards today. Radioactive waste is a type of pollution that emits radiation beyond what is naturally released by the environment.
Uranium is a naturally occurring radioactive element that has been mined and used for its chemical properties for over a thousand years. It is now primarily used as fuel for nuclear reactors that generate electricity. The process of extracting uranium from rock leaves behind radioactive waste, which is hazardous to humans and the environment.
Uranium can be recovered in two ways: by conventional mining of the rock (ore), or by using strong chemicals to dissolve uranium from the rock while it is still in the ground and pumping it to the surface. The latter method is known as chemical extraction. When uranium is found near the surface, miners employ open-pit mining to dig the rock out, stripping away the topsoil and rock above the uranium ore. Underground tunnels are used when uranium is found deep underground. The waste rock produced by underground and open-pit mining is often piled up outside the mine, which can cause radioactive dust to be blown into populated areas and contaminate water sources.
Radioactive waste from uranium mining contains hazardous chemicals and can emit radiation that poses risks to human health and the environment. Radium, a decay product of uranium, can further decay to form radon, a radioactive gas. Radon disperses into the atmosphere and does not pose a significant risk to the public or miners. However, underground mines can present a radiation hazard to miners if proper air ventilation is not maintained.
In addition to uranium mining, nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons are also significant sources of radioactive waste. The nuclear fuel cycle and nuclear weapons reprocessing contribute the majority of radioactive waste in countries with nuclear power infrastructure. This waste often contains radium and its decay products, with uranium dioxide concentrate from mining being significantly more radioactive than the granite used in buildings.
The management and disposal of radioactive waste are crucial to mitigate its environmental and health impacts. Various methods have been proposed, such as land-based subductive waste disposal and the Remix & Return approach, which blends high-level waste with uranium mine tailings to dilute its radioactivity. The EU's Zero Pollution Action Plan aims to reduce air, water, and soil pollution, including radioactive waste, to levels no longer considered harmful to health and natural ecosystems by 2050.
Water Pollution: Three Devastating Impacts on Our Oceans
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Pollution is the presence of high concentrations of harmful substances in the environment. These harmful substances are known as pollutants, which can be defined as any unwanted or harmful substance that enters the environment at a faster rate than it can be dispersed, diluted, decomposed, recycled, or stored in some harmless form.
Air pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the air, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide. These substances are often the by-products of human activities, such as vehicle exhaust or industrial processes, and can have negative impacts on both human health and the environment.
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water sources, including rivers, lakes, and oceans, by harmful substances. This can include chemical pollution, such as toxic chemicals like arsenic and fluoride, as well as plastic pollution from improperly disposed-of waste. Water pollution can create health risks as these waterways are often used for drinking water and can also harm aquatic ecosystems.
Soil pollution is the contamination of soil by harmful substances, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and sewage. This pollution can render the soil unfit for growing crops, disturb the soil profile, and spoil soil fertility. Soil pollution often occurs alongside water pollution as polluted water can seep into and contaminate the soil.







