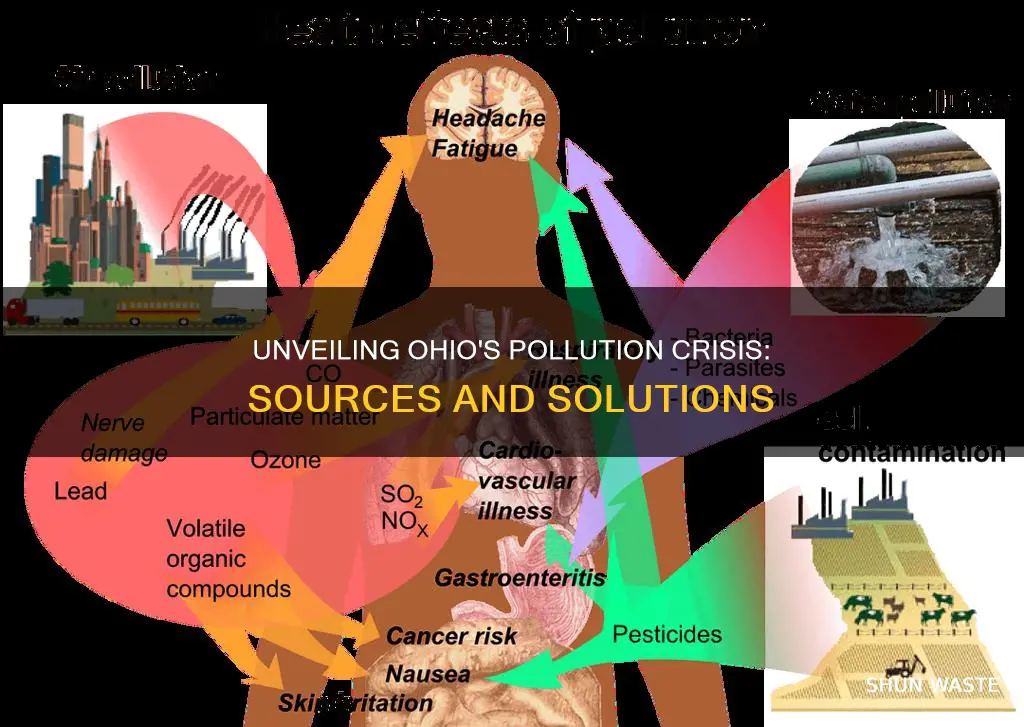
Ohio, a state known for its industrial history and diverse landscapes, is currently grappling with a pressing environmental issue: high pollution rates. The sources of this pollution are multifaceted and often interconnected, ranging from industrial activities to urban challenges. Industrial emissions, particularly from power plants and manufacturing facilities, have long been a significant contributor to air and water pollution. Additionally, urban areas face issues like traffic congestion, which leads to increased vehicle emissions and poor air quality. Agricultural practices, including the use of fertilizers and pesticides, also play a role in water pollution. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat pollution and protect Ohio's environment and public health.
What You'll Learn
- Industrial Emissions: Factories and power plants release pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
- Vehicle Emissions: Cars and trucks emit pollutants, especially in urban areas with heavy traffic
- Agricultural Practices: Intensive farming can lead to soil erosion and nutrient runoff, causing water pollution
- Waste Management: Improper disposal of waste, especially plastics, contributes to air and water pollution
- Construction Activities: Dust, chemicals, and heavy machinery impact air quality and soil health

Industrial Emissions: Factories and power plants release pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
The high pollution rates in Ohio can be attributed to various factors, with industrial emissions playing a significant role. One of the primary contributors is the presence of numerous factories and power plants across the state. These industrial facilities release a range of pollutants into the air, including sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which have detrimental effects on both the environment and public health.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a gas produced during the burning of fossil fuels, particularly coal and oil, in power plants and industrial processes. When released into the atmosphere, it can react with other compounds to form fine particulate matter, which is a major component of air pollution. This particulate matter can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, causing respiratory issues and contributing to the formation of smog.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are another group of gases emitted from industrial activities, especially during the combustion of fossil fuels. These gases play a crucial role in the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. Ozone pollution can cause irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, and it can also exacerbate respiratory conditions, making it particularly harmful to vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health issues.
The impact of these industrial emissions is far-reaching. Power plants, in particular, have been identified as significant sources of air pollution in Ohio. The burning of coal and other fossil fuels releases not only sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides but also carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas. This contributes to climate change, leading to more frequent and severe weather events, which can indirectly affect air quality.
To address these issues, Ohio has implemented various regulations and initiatives to reduce industrial emissions. These include stricter emission standards for power plants and factories, the promotion of cleaner technologies, and incentives for businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. By targeting industrial sources of pollution, the state aims to improve air quality, protect public health, and mitigate the environmental impacts of these emissions.
Paper Production's Environmental Impact: Unveiling the Pollution Truth
You may want to see also

Vehicle Emissions: Cars and trucks emit pollutants, especially in urban areas with heavy traffic
Vehicle emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution in Ohio, particularly in urban areas with heavy traffic. Cars and trucks release a variety of pollutants, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM), which can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. These emissions are a major concern, especially in densely populated cities where traffic congestion is common.
The primary source of these emissions is the combustion of fossil fuels in vehicle engines. When gasoline or diesel is burned, it produces a range of pollutants. Nitrogen oxides, for instance, are formed when fuel is burned at high temperatures, and they contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. VOCs, on the other hand, are released during the evaporation of gasoline and the operation of vehicle engines, and they react with NOx in the presence of sunlight to form ozone. Particulate matter, which includes tiny particles and liquid droplets, is emitted as a result of incomplete combustion and can be harmful when inhaled.
Urban areas with heavy traffic experience higher vehicle emissions due to the concentration of vehicles in a limited space. When cars and trucks are idling or moving at slow speeds, they emit more pollutants per mile compared to when they are traveling at higher speeds. This is because the engine operates less efficiently at lower speeds, leading to increased fuel consumption and higher emissions. Additionally, stop-and-go traffic, which is common in urban settings, causes frequent starts and stops, further contributing to emissions.
To address this issue, various measures can be implemented. One approach is to encourage the use of electric vehicles (EVs) and promote the adoption of cleaner technologies. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution. Governments can offer incentives for purchasing EVs and invest in charging infrastructure to support their widespread use. Another strategy is to improve public transportation systems, making them more efficient and accessible. This can reduce the number of private vehicles on the road, thereby decreasing overall emissions.
Furthermore, implementing stricter vehicle emission standards can play a crucial role in mitigating pollution. These standards set limits on the amount of pollutants that vehicles can emit, encouraging manufacturers to design and produce cleaner cars and trucks. Regular vehicle inspections and maintenance programs can also ensure that vehicles meet these standards and help identify and fix emission-related issues. By combining these approaches, Ohio can effectively reduce vehicle emissions and improve air quality, especially in urban areas, contributing to a healthier environment for its residents.
Dairy's Dirty Secret: How Milk Production Pollutes Our Waterways
You may want to see also

Agricultural Practices: Intensive farming can lead to soil erosion and nutrient runoff, causing water pollution
Intensive farming practices in Ohio have become a significant contributor to the state's environmental challenges, particularly in the context of water pollution. The state's agricultural sector, known for its vast farmlands and livestock operations, has experienced a rapid shift towards intensive methods in recent decades. While these practices aim to maximize productivity and efficiency, they often come at a cost to the environment.
One of the primary concerns is soil erosion. Intensive farming involves the cultivation of large areas of land with heavy machinery and frequent tillage. This can lead to the removal of natural soil cover, making the earth more susceptible to erosion by wind and water. In Ohio, the state's diverse topography, including rolling hills and valleys, exacerbates this issue. When heavy rainfall occurs, as it often does in the region, the exposed soil can be easily washed away, leading to sedimentation in nearby water bodies. This sediment runoff not only degrades water quality but also can smother aquatic habitats, negatively impacting fish and other aquatic organisms.
Nutrient runoff is another critical consequence of intensive agricultural practices. Farmers often use large amounts of fertilizers and manure to enhance crop yields and livestock production. While these inputs are essential for plant growth, excessive use can result in over-fertilization. When it rains, the excess nutrients, including nitrogen and phosphorus, can be washed off the fields and carried into nearby streams, rivers, and eventually, the Ohio River. This nutrient pollution causes algal blooms, which deplete oxygen levels in the water, leading to the death of fish and other aquatic life. The impact is particularly severe in the state's larger water bodies, such as Lake Erie, where nutrient runoff has contributed to significant ecological imbalances.
To mitigate these issues, sustainable farming practices should be adopted. Conservation tillage, which minimizes soil disturbance, can help prevent erosion. Implementing buffer zones along water bodies can act as a natural filter, trapping sediment and nutrients before they enter the waterways. Additionally, precision agriculture technologies can optimize fertilizer use, ensuring that only the necessary amounts are applied, reducing the risk of runoff. By embracing these strategies, Ohio's agricultural sector can work towards minimizing its environmental footprint and preserving the state's precious water resources.
Unveiling India's River Pollution: Causes and Solutions
You may want to see also

Waste Management: Improper disposal of waste, especially plastics, contributes to air and water pollution
The improper disposal of waste, particularly plastics, is a significant contributor to the high pollution rates in Ohio. Plastic waste, often non-biodegradable, takes up a substantial amount of space in landfills, leading to soil and groundwater contamination. When plastic waste is not managed properly, it can break down into smaller pieces, known as microplastics, which are easily ingested by aquatic organisms and can accumulate in the food chain. This process not only affects the environment but also poses potential health risks to humans and animals.
One of the primary issues is the lack of adequate recycling infrastructure and public awareness. Many residents in Ohio may not be aware of the proper ways to recycle or dispose of plastic waste. As a result, they might opt for the easiest option, which is often to throw plastic items into the trash without considering the environmental impact. This practice contributes to the growing problem of plastic pollution, especially in the state's waterways and coastal areas.
To address this issue, educational campaigns and initiatives should be implemented to inform the public about the importance of proper waste management. These programs can emphasize the environmental and health consequences of improper disposal, encouraging residents to adopt more sustainable practices. For instance, promoting the use of reusable bags, bottles, and containers can significantly reduce plastic waste. Additionally, providing accessible recycling facilities and clear guidelines for waste segregation can make a substantial difference in waste management.
Local governments and waste management companies play a crucial role in this context. They can introduce incentives for recycling, such as rewards or discounts for residents who actively participate in recycling programs. Moreover, investing in advanced recycling technologies and facilities can improve the efficiency of waste processing, ensuring that more plastic waste is recycled rather than ending up in landfills or the environment.
In summary, the improper disposal of waste, especially plastics, is a critical factor in the high pollution rates in Ohio. By raising awareness, implementing educational programs, and improving waste management infrastructure, the state can significantly reduce its environmental impact and move towards a more sustainable future. It is essential to take immediate action to address this issue and ensure the long-term health of Ohio's ecosystems and its residents.
Chlorine Overload: Unveiling the Hidden Dangers in NYC's Tap Water
You may want to see also

Construction Activities: Dust, chemicals, and heavy machinery impact air quality and soil health
Construction activities significantly contribute to the high pollution rates in Ohio, primarily through the release of dust, chemicals, and the operation of heavy machinery. These factors collectively pose a substantial threat to both air quality and soil health, which are essential components of a healthy environment.
Dust Emissions: Construction sites are notorious for generating large amounts of dust, which is a major concern for air quality. The use of heavy machinery, such as bulldozers and excavators, often results in the disturbance of soil, leading to the release of fine particles into the air. These dust particles can be inhaled by nearby residents and workers, posing serious health risks, especially for individuals with respiratory conditions. Moreover, dust can settle on surfaces, including vegetation, and contribute to soil degradation, affecting the overall ecosystem.
Chemical Exposure: Construction projects frequently involve the use of various chemicals, including solvents, paints, and fuels. These chemicals can evaporate into the air, leading to air pollution and potential health hazards for those in the vicinity. For instance, the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from paint and solvent use can contribute to smog formation and have adverse effects on human health. Additionally, chemicals can contaminate soil if not properly managed, leading to long-term environmental damage.
Heavy Machinery and Noise Pollution: The operation of heavy machinery on construction sites generates significant noise pollution, which is often overlooked as a pollutant. Excessive noise can have negative impacts on both human and animal health. For humans, it can lead to hearing damage and increased stress levels. In the case of animals, it can disrupt their natural behaviors and habitats. Furthermore, the vibrations from heavy machinery can contribute to soil compaction, making it harder for plants to grow and affecting the overall soil structure.
To mitigate these pollution concerns, construction companies in Ohio should implement strict dust control measures, such as using water sprays and dust barriers, and ensure proper ventilation in enclosed areas. Regular monitoring of chemical usage and disposal is essential to prevent soil and air contamination. Additionally, employing noise barriers and adopting quieter machinery can help reduce noise pollution. By adopting these practices, construction activities can be made more environmentally friendly, contributing to a healthier Ohio.
Climate Change: A Catalyst for Food Chain Pollution?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Ohio's air quality is influenced by various sources, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and power generation. Industrial activities, particularly those involving the manufacturing and chemical sectors, release significant amounts of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter (PM). Vehicle emissions, especially from older cars and trucks, contribute to air pollution, especially in urban areas. Additionally, power plants, both coal-fired and natural gas, play a role in emitting pollutants, with some facilities being major sources of SO2 and NOx.
Ohio's geographical features, such as its location in the eastern United States and its proximity to the Great Lakes, can influence pollution dispersion. During the winter, temperature inversions can trap pollutants close to the ground, leading to higher pollution levels, especially in the Cincinnati and Cleveland areas. In the summer, the state's position in the eastern corridor can affect the transport of pollutants, with potential contributions from industrial activities in neighboring states. The Great Lakes also play a role, as wind patterns can carry pollutants from the lakes to the land, impacting air quality.
Yes, certain industries and regions have been identified as major contributors to Ohio's pollution. The Greater Cincinnati area, for instance, has historically struggled with air pollution due to its proximity to industrial facilities and heavy traffic. The chemical industry in the state, particularly in the Dayton and Columbus regions, is known for its significant emissions. Additionally, the coal-fired power plants in the eastern part of the state have been major sources of concern for air quality. The Ohio Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regularly monitors and enforces regulations to control emissions from these industries and regions.







