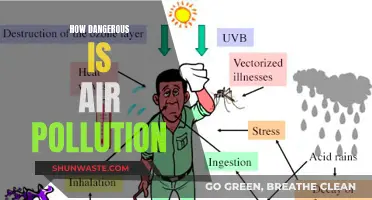
Air pollution is a pressing issue that poses significant risks to human health and the environment. It refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air, including solid and liquid particles, as well as certain gases. These pollutants can be released into the atmosphere through various human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, vehicle emissions, industrial processes, agriculture, and waste management. Natural sources, such as wildfires, volcanic eruptions, and dust storms, also contribute to air pollution. The health impacts of air pollution are wide-ranging, including respiratory infections, asthma, bronchitis, heart disease, and lung cancer. It is a major global health concern, causing approximately 6.5 to 8 million deaths annually. Addressing air pollution requires a combination of policy interventions, technological advancements, and individual actions to reduce emissions and mitigate the harmful effects on people and the planet.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Air pollution is the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere. |
| Sources | Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities, forest fires, waste management, agriculture, nuclear weapons, toxic gases, germ warfare, rocketry, etc. |
| Effects | Air pollution is responsible for more than 6.5 million deaths each year globally, causing respiratory and other diseases and acting as a significant risk factor for stroke, heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and lung cancer. |
| Impact | Air pollution affects human health, the environment, and the climate, leading to rising sea levels, extreme weather, heat-related deaths, and the increased transmission of infectious diseases. |
| Prevention | WHO provides technical support to member states, offering guidance, tools, and advice on health issues related to air pollution. The US EPA also works with governments and stakeholders to reduce air pollution and its damage. |
| Vulnerable Groups | Children, the elderly, low-income communities, communities of color, indigenous peoples, and future generations are among those most vulnerable to the health and climate effects of air pollution. |
| Standards | National Ambient Air Quality Standards were established in 1970, and the US EPA has since revised standards for common pollutants to better protect public health and the environment. |
What You'll Learn

Causes of air pollution
Air pollution is caused by a combination of human-made and natural sources. It is primarily caused by the burning of fossil fuels for industry, construction, transportation, and heating. The major human-made sources of air pollution include vehicle emissions, fuel oils, natural gases, industrial processes, and agricultural emissions.
Vehicle emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution, with road vehicles producing a significant amount of nitrogen dioxide emissions and greenhouse gases. Vehicles with petrol and diesel engines release exhaust gases, as well as non-exhaust emissions from tyre and brake wear and road surface erosion. Diesel trains, ships, and planes also contribute to air pollution.
Industrial processes, particularly coal-fueled power plants, release pollutants such as ozone, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides. The burning of fossil fuels in factories, power plants, and refineries emits harmful gases and contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone, also known as smog.
Agricultural emissions, including methane released from livestock digestion and manure management, contribute substantially to air pollution. Ammonia, a hazardous gas emitted during agricultural activities, along with insecticides, pesticides, and fertilizers, release harmful chemicals into the atmosphere.
Natural sources of air pollution include wildfires, which release smoke, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter into the air. Volcanic eruptions emit ash, gases, and soot, while decomposing organic matter in soils releases methane. Additionally, dust storms and desert dust can cause poor air quality even in distant locations.
Other human activities that contribute to air pollution include deforestation, waste management practices, and the use of nuclear weapons, toxic gases, and rocketry. The burning of polluting fuels, such as firewood, agricultural waste, coal, or charcoal for cooking and heating in low-income countries, also leads to harmful household air pollution.
VOC Air Pollution: Understanding Volatile Organic Compounds
You may want to see also

Health effects of air pollution
Air pollution has a wide range of health effects on people of all ages. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nine out of ten people worldwide breathe air containing high levels of pollutants, and air pollution kills an estimated seven million people every year.
One of the most significant health impacts of air pollution is its contribution to respiratory problems. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the air can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, causing or worsening breathing and lung diseases, including lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma. Short-term exposure to fine particles can trigger asthma attacks, while long-term exposure increases the chances of developing COPD and lung cancer. Children are particularly vulnerable to the respiratory effects of air pollution, with higher pollution levels increasing their risk of developing asthma and bronchitis symptoms in adulthood.
In addition to respiratory issues, air pollution has been linked to various other health problems. It has been associated with an increased risk of heart attacks, abnormal heartbeats, and cardiovascular disease. Air pollution has also been linked to systemic inflammation, type 2 diabetes, obesity, Alzheimer's disease, and dementia. Exposure to air pollution during pregnancy may also have adverse effects on fetal development, including low birth weight and an increased risk of autism.
The health effects of air pollution are not limited to outdoor exposure. Indoor air pollution, such as from cooking with polluting open fires or simple stoves fuelled by biomass or coal, can also have significant health impacts. Pollutants such as radon, smoke, and lead dust, as well as carbon monoxide from faulty furnaces, can contribute to the adverse health effects of indoor air pollution.
Overall, air pollution poses a major threat to human health, leading to hospitalizations, cancer, and premature death. Reducing air pollution through the adoption of renewable energy sources, fuel-efficient vehicles, and electric alternatives can help mitigate these health risks and improve public health outcomes.
Air Pollution Decrease: Quarantine's Surprising Impact
You may want to see also

Environmental impact of air pollution
Air pollution is a pressing issue that poses significant risks to both human health and the environment. It refers to the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by chemicals, physical or biological agents that alter the natural composition of the atmosphere. While air pollution has declined globally over the last two decades, it remains a critical concern, with 99% of the global population still breathing air that exceeds WHO guideline limits.
The environmental impacts of air pollution are extensive and far-reaching. Firstly, air pollution directly affects the quality of the air we breathe, leading to respiratory issues and other health problems in humans. According to the WHO, air pollution is associated with approximately seven million premature deaths annually worldwide. Fine particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide levels above WHO recommendations are linked to asthma, heart disease, and stroke.
Secondly, air pollution has detrimental effects on ecosystems, vegetation, water bodies, and soil quality. It can contaminate the surfaces of lakes, rivers, and oceans, damaging aquatic ecosystems and reducing water quality. Air pollution can also impact soil fertility and crop yields, threatening food security. Additionally, it harms plant life, including young trees, and contributes to the degradation of local ecosystems.
Furthermore, air pollution is a significant contributor to global warming and climate change. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat energy in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures worldwide. This, in turn, affects weather patterns, ecosystems, and the distribution of plant and animal species.
The impact of air pollution extends beyond the natural environment to built environments as well. Certain pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, can break down stone and damage buildings and other structures. Air pollution also affects visibility, with smog and haze obscuring shapes and colours in the environment.
Addressing air pollution requires a multifaceted approach. Transitioning to cleaner fuels and industrial processes, adopting renewable energy sources, improving fuel efficiency, and promoting electrification are crucial steps. Additionally, implementing policies that support sustainable land use, cleaner household energy, energy-efficient housing, and better waste management can effectively reduce ambient air pollution.
Chengdu's Air Quality: A Pollution Problem?
You may want to see also

Sources of air pollution data
Air pollution is a pressing issue that poses a major threat to health worldwide. It is a leading risk factor for death, with one in ten deaths globally attributed to air pollution. The World Health Organization (WHO) monitors air pollution exposure levels and their health impacts, such as deaths and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). WHO's air quality database compiles ground measurements of annual mean concentrations of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), representing data for cities and towns. As of 2022, the database includes over 4300 human settlements across 108 countries and is regularly updated.
The Community Emissions Data System (CEDS) is another valuable resource for long-term global and national data on air pollution, dating back to the 18th century and frequently updated with the latest estimates. This system provides insights into trends in emissions of air pollutants over time.
At a national level, organizations like the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (MPCA) research the sources and distribution of toxic air pollution within their state. They found that air pollution contributed to a significant number of deaths, hospitalizations, and emergency room visits for heart and lung problems in Minnesota's largest cities.
Additionally, interactive maps and tools are available to access air quality data and standards for different countries and pollutants. For instance, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides an interactive map of air quality monitors and various reports on outdoor air quality data across the US. The EPA also offers tools like the Fire and Smoke map for real-time air quality information during fire events.
Protecting Yourself from Air Pollution: Masks and Air Purifiers
You may want to see also

Reducing air pollution
Air pollution is a major environmental health problem affecting people in low-, middle-, and high-income countries. It is caused by the emission of pollutants into the atmosphere, which can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. Outdoor air pollution is responsible for an estimated 4.2 million premature deaths worldwide annually, caused by exposure to fine particulate matter, which in turn causes cardiovascular and respiratory diseases and cancers.
To reduce air pollution, individuals can make changes to their daily habits and behaviours. For example, driving less and opting for more environmentally friendly modes of transportation, such as carpooling, biking, bussing, or telecommuting, can significantly reduce vehicle emissions. Keeping your car well-maintained and ensuring proper tyre inflation can also help improve fuel efficiency and reduce pollution. Additionally, limiting idling time and turning off your engine when not in motion can further decrease emissions and improve air quality.
Another way to reduce air pollution is by transitioning to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. This includes adopting renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, and maximising fuel efficiency in vehicles. Replacing gasoline-powered cars and trucks with electric vehicles can also help limit air pollution at its source. At home, individuals can reduce energy consumption by using energy-efficient appliances, turning off electrical devices when not in use, and opting for energy-saving light bulbs.
On a community level, local businesses, city offices, and schools can be directed towards programs that promote sustainability and reduce air pollution. Implementing initiatives such as the Small Business Environmental Assistance Program can help businesses comply with environmental regulations, reduce waste, and lower emissions. Additionally, supporting policies and investments that promote cleaner transportation, energy-efficient housing, improved waste management, and sustainable land use can effectively reduce key sources of ambient air pollution.
Lastly, planting and caring for trees in urban areas can help filter pollutants, absorb carbon dioxide, and release oxygen into the atmosphere. This not only improves air quality but also helps cool the surrounding environment. Addressing air pollution requires a collective effort involving individuals, communities, and policymakers working together to implement sustainable practices and policies that protect public health and the environment.
Air Pollution: A Global Crisis and Concern
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Air pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the air. These substances can be gases like ozone or nitrogen oxides, small particles like soot, or other chemicals like lead.
Air pollution is primarily caused by burning fossil fuels for industry, construction, transportation, and heating. Vehicle emissions, fuel oils, natural gas, and industrial processes are the primary sources of human-made air pollution. Natural sources of air pollution include wildfires, dust storms, and volcanic eruptions.
Air pollution has severe impacts on human health and the environment. It is associated with respiratory disorders, heart diseases, lung cancer, asthma, and other health problems. It also contributes to climate change by trapping heat in the atmosphere, leading to rising sea levels, extreme weather, and increased transmission of infectious diseases.