Environmental pollution, a pervasive global issue, has far-reaching consequences for our planet's health and the well-being of its inhabitants. Among the myriad forms of pollution, it is crucial to understand the specific causes of air pollution, which significantly impacts our environment. Air pollution, a complex and multifaceted problem, arises from various sources, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and natural phenomena. This pollution not only affects the air we breathe but also contributes to climate change, endangers wildlife, and poses risks to human health. By exploring the causes of air pollution, we can gain insights into the intricate relationship between human activities and the environment, and work towards implementing effective solutions to mitigate its detrimental effects.
What You'll Learn
- Air Pollution: Burning fossil fuels releases pollutants like CO2 and NOx, which contribute to climate change and acid rain
- Water Pollution: Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and oil spills contaminate water bodies, harming aquatic life and human health
- Soil Contamination: Chemical pollutants from industrial activities and improper waste disposal can render soil unsuitable for agriculture and habitation
- Noise Pollution: Excessive noise from transportation, construction, and industrial activities can lead to hearing loss and stress
- Light Pollution: Artificial lighting at night disrupts ecosystems, affects wildlife behavior, and can impact human health and sleep patterns

Air Pollution: Burning fossil fuels releases pollutants like CO2 and NOx, which contribute to climate change and acid rain
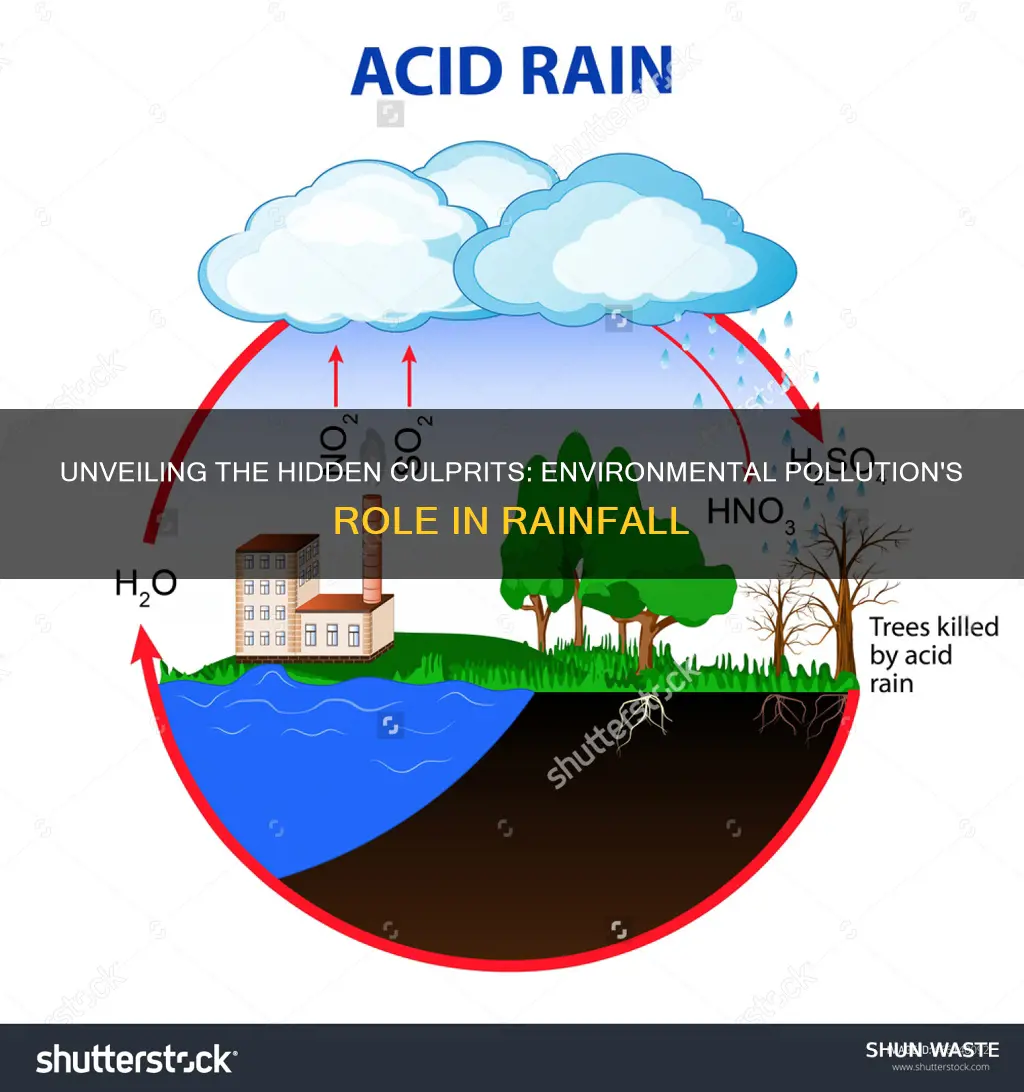
The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is a significant contributor to air pollution and has far-reaching environmental consequences. When these fuels are burned, they release a multitude of pollutants into the atmosphere, with carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) being among the most prominent. These emissions are major drivers of climate change and have a direct impact on the formation of acid rain.
Carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, is released in vast quantities during the combustion of fossil fuels. It is a primary contributor to global warming and climate change. As CO2 accumulates in the atmosphere, it traps heat, leading to a gradual increase in the Earth's temperature. This phenomenon, known as the greenhouse effect, has severe implications for ecosystems and weather patterns worldwide. The rising global temperatures contribute to the melting of polar ice caps, rising sea levels, and disruptions to natural habitats, affecting both wildlife and human populations.
Nitrogen oxides, including nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO), are also released during the burning of fossil fuels. These gases play a crucial role in the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. Ozone pollution is harmful to human health, causing respiratory issues and aggravating existing lung conditions. Moreover, NOx emissions contribute to the formation of acid rain. When nitrogen oxides react with water vapor and other atmospheric components, they produce nitric acid, which can be transported over long distances by wind.
Acid rain, a result of the interaction between nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, has detrimental effects on the environment. It can damage forests, soils, and aquatic ecosystems, making the soil more acidic and harmful to plant life. Acid rain also poses risks to human infrastructure, corroding buildings, bridges, and monuments, especially those made of iron and steel. The impact of air pollution from fossil fuel combustion is thus far-reaching, affecting not only the atmosphere but also ecosystems, human health, and infrastructure.
Addressing air pollution caused by fossil fuel burning requires a multi-faceted approach. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, can significantly reduce CO2 and NOx emissions. Implementing stricter emission standards and regulations for industries and vehicles can also help mitigate pollution. Additionally, promoting energy efficiency and adopting sustainable practices in various sectors can contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment. By recognizing the impact of air pollution on climate change and acid rain, we can take collective action to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and foster a more sustainable future.
Human Impact: How Our Actions Cause Environmental Pollution
You may want to see also

Water Pollution: Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and oil spills contaminate water bodies, harming aquatic life and human health
Water pollution is a critical environmental issue that poses significant threats to aquatic ecosystems and human well-being. Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and oil spills are among the primary culprits behind this detrimental phenomenon. These activities release a myriad of contaminants into water bodies, leading to severe consequences.
Industrial waste, often a byproduct of manufacturing and production processes, contains a cocktail of chemicals, heavy metals, and toxic substances. When discharged into rivers, lakes, or oceans, these pollutants can have devastating effects. For instance, heavy metals like lead and mercury can accumulate in the tissues of aquatic organisms, leading to bioaccumulation. This process results in the concentration of toxins as they move up the food chain, ultimately affecting higher-level predators and even humans who consume contaminated seafood. Industrial waste also contributes to the degradation of water quality, making it unsuitable for drinking, irrigation, and recreational activities.
Agricultural runoff is another significant contributor to water pollution. When fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals are applied to fields, heavy rainfall can carry these substances into nearby water sources. Nitrates and phosphates from fertilizers can cause eutrophication, a process where excessive nutrient levels stimulate algae blooms. This, in turn, depletes oxygen levels in the water, leading to the death of fish and other aquatic life. Pesticides, being toxic, can also directly harm aquatic organisms, disrupting their reproductive cycles and causing population declines.
Oil spills, whether from maritime accidents or industrial activities, have catastrophic impacts on marine environments. Oil is highly toxic and persistent in water, meaning it breaks down very slowly. When spilled, it coats the feathers of birds and the fur of mammals, impairing their ability to maintain body temperature and causing them to lose their natural insulation. The toxic chemicals in oil can also be ingested by marine life, leading to internal organ damage and reproductive issues. Moreover, the long-term effects of oil pollution include the degradation of coastal ecosystems, making it challenging for various species to survive and thrive.
Addressing water pollution requires a multi-faceted approach. Industries must adopt cleaner production methods and proper waste management systems to minimize their environmental footprint. Farmers can benefit from precision agriculture techniques, using targeted fertilizers and pesticides to reduce runoff. Governments play a crucial role in implementing and enforcing environmental regulations, ensuring that industries and agricultural practices adhere to sustainable standards. Additionally, public awareness and education can encourage responsible behavior, such as proper waste disposal and the use of eco-friendly products, contributing to the overall reduction of water pollution.
In conclusion, the contamination of water bodies by industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and oil spills is a pressing environmental concern. It endangers aquatic ecosystems, disrupts the balance of nature, and poses risks to human health. By understanding the sources and impacts of water pollution, societies can take collective action to mitigate these issues, ensuring a healthier and more sustainable future for both the environment and its inhabitants.
Unveiling the Sky's Impact: Plane Pollution's Surprising Extent
You may want to see also

Soil Contamination: Chemical pollutants from industrial activities and improper waste disposal can render soil unsuitable for agriculture and habitation
Soil contamination is a critical environmental issue that arises from various human activities, particularly industrial processes and improper waste management. When chemical pollutants infiltrate the soil, they can have detrimental effects on both the environment and human health. Industrial activities often release toxic substances, including heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals, which can seep into the ground and contaminate the soil. These pollutants can persist for extended periods, making the soil unsuitable for agricultural purposes and potentially hazardous for human habitation.
The consequences of soil contamination are far-reaching. Firstly, it directly impacts agricultural productivity. Contaminated soil may contain high levels of toxic elements, making it difficult for plants to grow and thrive. This can lead to reduced crop yields, affecting food production and potentially causing economic losses for farmers. Moreover, the presence of harmful chemicals in the soil can result in the accumulation of toxins in crops, posing risks to human health when consumed.
Improper waste disposal is another significant contributor to soil contamination. Hazardous waste, such as batteries, electronic waste, and industrial by-products, often contains toxic substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium. When this waste is not managed or disposed of correctly, it can leach into the soil, causing severe pollution. For instance, landfills that are not properly lined can allow pollutants to seep into the ground, affecting nearby soil and water sources.
Addressing soil contamination requires a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, industries must adopt cleaner production methods and technologies to minimize the release of chemical pollutants. Implementing strict regulations and monitoring systems can help ensure that industrial activities do not lead to soil degradation. Secondly, waste management practices should be improved, emphasizing proper disposal and recycling of hazardous materials. Educating communities about the importance of responsible waste handling can also contribute to reducing soil contamination.
In conclusion, soil contamination, primarily caused by chemical pollutants from industrial activities and improper waste disposal, poses a significant threat to the environment and human well-being. It disrupts agricultural productivity, endangers food safety, and can have long-lasting effects on ecosystems. By implementing stricter regulations, promoting sustainable industrial practices, and raising awareness about responsible waste management, we can work towards mitigating soil contamination and preserving the health of our soil resources.
Unraveling the Autism-Pollution Link: A Complex Environmental Mystery
You may want to see also

Noise Pollution: Excessive noise from transportation, construction, and industrial activities can lead to hearing loss and stress
Noise pollution, often overlooked, is a significant environmental issue with far-reaching consequences. It primarily arises from various human activities, including transportation, construction, and industrial operations. These activities generate excessive noise levels that can have detrimental effects on both human health and the environment.
One of the most immediate and well-documented impacts of noise pollution is hearing loss. Prolonged exposure to high-intensity sound can damage the delicate structures of the ear, leading to permanent hearing impairment. Individuals living or working in areas with high noise levels from traffic, such as busy roads or airports, are particularly susceptible to this risk. Over time, the constant exposure to loud noises can result in a condition known as noise-induced hearing loss, which may not be reversible. This issue is not limited to adults; children exposed to excessive noise during their formative years may face long-term hearing consequences.
Beyond hearing loss, noise pollution also contributes to increased stress levels and other health-related issues. Research has shown that chronic exposure to high noise levels can lead to elevated stress hormones, affecting overall well-being. This is particularly relevant in urban areas where construction sites, busy roads, and industrial zones are prevalent. Residents in such areas often experience higher stress levels due to the constant, disruptive noise. The impact of noise pollution on mental health can be significant, leading to anxiety, sleep disturbances, and even cardiovascular problems.
To address this problem, it is crucial to implement measures that reduce noise levels. This can be achieved through various means, such as using noise barriers along roads, adopting quieter construction techniques, and enforcing noise regulations for industrial operations. Additionally, raising awareness about the dangers of noise pollution and promoting the use of noise-canceling headphones or ear protection can help individuals protect themselves.
In conclusion, noise pollution, stemming from transportation, construction, and industrial activities, poses a serious threat to human health and the environment. Its effects, including hearing loss and increased stress, highlight the need for proactive measures to mitigate this often-overlooked form of pollution. By taking steps to reduce noise levels and educate the public, we can create healthier and more peaceful living environments.
Unveiling the Hidden Causes of Land Pollution: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Light Pollution: Artificial lighting at night disrupts ecosystems, affects wildlife behavior, and can impact human health and sleep patterns
Light pollution, a growing environmental concern, refers to excessive and inappropriate artificial light at night, which has far-reaching consequences for both natural and human environments. This phenomenon, often overlooked, significantly disrupts ecosystems and wildlife behavior, while also impacting human health and sleep patterns. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing sustainable practices and preserving the delicate balance of our natural world.
In the natural world, artificial lighting at night can have detrimental effects on various species. Many animals rely on the natural light-dark cycle for navigation, foraging, and reproductive behaviors. For instance, nocturnal animals like owls and bats use the moon's light to hunt and navigate. When artificial lights interfere with this natural cycle, it can lead to disorientation and disrupted feeding patterns. Birds, too, are affected; migratory birds use celestial cues for navigation, and artificial lighting can alter their flight paths, potentially leading them to dangerous areas.
The impact of light pollution on wildlife is not limited to behavior and navigation. It can also affect the breeding and feeding habits of many species. For example, some fish species rely on moonlight to trigger spawning, and artificial lighting can disrupt this process. Similarly, the presence of artificial light can cause some plants to flower prematurely, affecting their reproductive cycles. These disruptions can have cascading effects on the entire food chain, leading to imbalances in ecosystems.
Human health and well-being are also significantly impacted by light pollution. The human body has evolved to respond to the natural light-dark cycle, known as the circadian rhythm. Artificial lighting at night can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. This disruption can lead to sleep disorders, increased risk of depression, and even cardiovascular issues. Moreover, light pollution can interfere with the natural healing processes of the body, affecting overall health and productivity.
Addressing light pollution requires a multi-faceted approach. On an individual level, people can contribute by using motion-sensor lights, installing shielded fixtures to direct light downward, and adopting energy-efficient lighting. Communities can also play a vital role by implementing dark-sky-friendly regulations and promoting awareness about the issue. Additionally, urban planners and architects can design buildings and public spaces with careful consideration of lighting needs, ensuring that artificial light is used efficiently and without causing unnecessary ecological disruption.
In conclusion, light pollution is a critical environmental issue that demands attention. By understanding its causes and impacts, we can take steps to mitigate its effects. From preserving the natural behavior of wildlife to protecting human health, the consequences of artificial lighting at night are far-reaching. It is through collective awareness and action that we can ensure a healthier, more sustainable environment for both current and future generations.
Unveiling the Hidden Water Pollutants: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Air pollution, particularly from fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), is a significant contributor to respiratory problems. These pollutants can come from vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and the burning of fossil fuels. When inhaled, they can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing inflammation, irritation, and reduced lung function.
Water pollution, often resulting from industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and improper disposal of chemicals, has detrimental effects on aquatic environments. It can lead to the contamination of water bodies with toxic substances, including heavy metals, pesticides, and fertilizers. This pollution can harm or kill fish and other aquatic organisms, disrupt the food chain, and even render water unsafe for drinking and recreational use.
Environmental degradation, such as deforestation and the destruction of natural habitats, can indirectly contribute to the emergence and spread of diseases. When natural buffers between humans and wildlife are removed, pathogens can more easily transmit between animal populations and humans. For example, the loss of forest cover can increase the risk of zoonotic diseases, like certain types of influenza, as animals and humans come into closer contact.
Yes, environmental pollution has been linked to various mental health issues. Exposure to air pollution, especially in urban areas with high traffic density, has been associated with increased anxiety and depression. Additionally, living in areas with high levels of noise pollution can lead to sleep disturbances, stress, and even cognitive impairments, particularly in children and the elderly.







