The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a system used to warn the public about dangerous levels of air pollution. It measures six major air pollutants: ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), particle pollution (PM2.5 and PM10), and two others. The AQI is calculated using a formula that takes into account the measured ambient concentrations, corresponding standards, and likely health impacts of each pollutant. The higher the AQI value, the greater the level of air pollution and the more serious the potential health concerns. AQI values at or below 100 are generally considered safe, while values above 100 indicate unhealthy air quality that may be harmful to certain sensitive groups of people. Real-time AQI data is available for over 10,000 stations worldwide, providing valuable information for individuals to protect themselves from the harmful effects of air pollution.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To communicate about outdoor air quality and health |
| Focus | Health effects experienced within a few hours or days after breathing polluted air |
| Pollutants measured | Ground-level ozone, particle pollution, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide |
| Scale | 0 (perfect air) to 500 (immediate danger) |
| Categories | 6 (Good, Satisfactory, Moderate, Poor, Severe, Hazardous) |
| Reporting | Daily |
| Sources | EPA maps, local radio, TV, newspaper, weather apps |

Ground-level ozone
Ozone (O3) is a highly reactive gas composed of three oxygen atoms. While
Air Pollution: A Public Health Crisis
You may want to see also

Particle pollution
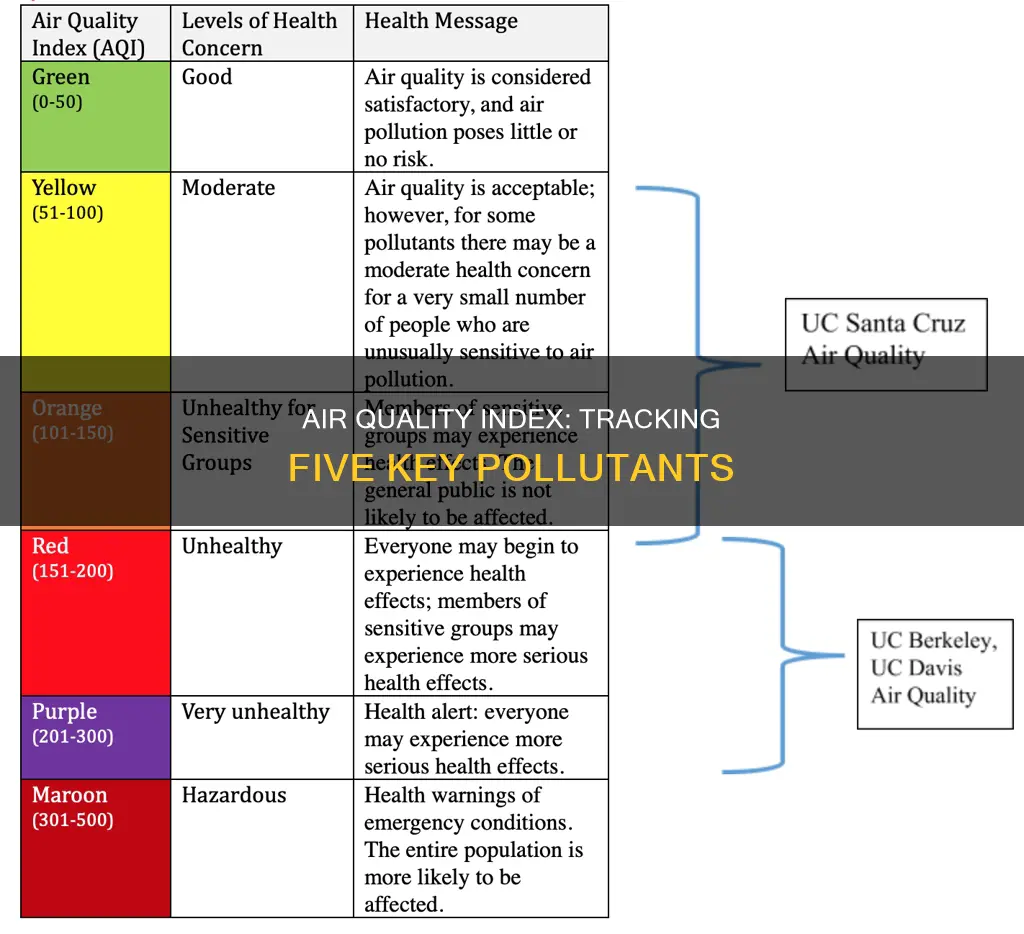
Ground-level ozone and particle pollution are considered two of the most critical criteria pollutants that threaten air quality and public health. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establishes an Air Quality Index (AQI) for these pollutants, which is a tool for communicating about outdoor air quality and its potential health impacts. The AQI is divided into six color-coded categories, with each category representing a range of index values indicating the level of air pollution and associated health concerns. For instance, an AQI value of 50 or below signifies good air quality, while a value over 300 indicates hazardous air quality.
The GAIA air quality monitor is a device that uses laser particle sensors to measure PM2.5 and PM10 particle pollution levels in real time. It provides instant access to air pollution levels for over 80 countries and offers specific historical data for particular cities. This monitor is easy to set up and comes with mounting equipment, power cables, and an optional solar panel.
Air Pollution: Calculating the True Cost of Poor Air Quality
You may want to see also

Carbon monoxide
When carbon monoxide is released into the atmosphere, it contributes to air pollution and has negative effects on human health and the environment. High levels of carbon monoxide in the air can lead to headaches, dizziness, confusion, nausea, and even death in extreme cases. Prolonged exposure to carbon monoxide can also cause cardiovascular problems and harm to the nervous system.
Monitoring carbon monoxide levels is crucial for protecting public health and reducing its harmful effects. The AQI helps individuals take necessary precautions, such as reducing outdoor physical activity or wearing masks, during periods of high carbon monoxide concentrations. Additionally, the data collected through the AQI can inform policies and interventions aimed at reducing carbon monoxide emissions and improving air quality.
The AQI for carbon monoxide is generally based on health-based national ambient air quality standards and scientific information. The EPA has established standards for carbon monoxide concentrations to protect public health, and the AQI values reflect the potential health impact of this pollutant. By providing accessible and timely information about carbon monoxide levels, the AQI plays a vital role in mitigating the harmful effects of this toxic gas on human well-being and the environment.
Air Fresheners: The Hidden Air Polluters in Our Homes
You may want to see also

Sulfur dioxide
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a tool used to communicate about outdoor air quality and health. It is based on the measurement of six pollutants: ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM) of varying diameters, including PM2.5 and PM10. These pollutants are known to have significant impacts on human and environmental health.
The presence of SO2 in the air can lead to a range of health issues. When inhaled, it can irritate the respiratory system, causing coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of SO2 can aggravate respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic bronchitis. Additionally, SO2 contributes to the formation of acid rain, which has detrimental effects on ecosystems, including aquatic life and vegetation.
To protect public health and minimize the impact of SO2 pollution, regulatory bodies like the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have established National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for sulfur dioxide. These standards set limits on the acceptable concentration of SO2 in the air, aiming to reduce the harmful effects of this pollutant on human health and the environment.
The AQI values for SO2 are categorized into different health risk levels. For instance, an AQI value of 50 or below is generally considered safe, while values above 100 are deemed unhealthy, initially for sensitive groups and then for everyone as values increase further. These categories help guide public health actions and recommendations, such as encouraging the use of masks or invoking emergency plans to reduce emissions during periods of high SO2 pollution.
Overall, the inclusion of SO2 in the AQI is crucial for monitoring and managing the levels of this harmful pollutant. By tracking and communicating SO2 concentrations through the AQI, authorities can take appropriate actions to protect public health and mitigate the environmental impacts associated with sulfur dioxide pollution.
Air Pollution: China's Most Polluted City
You may want to see also

Nitrogen dioxide
NO2 emissions contribute to particle pollution and the chemical reactions that produce ozone. Breathing air with high concentrations of NO2 can irritate the airways in the human respiratory system. Short-term exposure can aggravate respiratory diseases, especially asthma, leading to coughing, wheezing, or difficulty breathing. Prolonged exposure to elevated NO2 concentrations may also contribute to the development of asthma and increase susceptibility to respiratory infections. Scientific evidence suggests that exposure to NO2 could cause asthma in children.
Air Pollution: The Silent Killer in Our Midst
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Air Quality Index is a system used to warn the public about dangerous levels of air pollution. The AQI tracks six major air pollutants: ozone (smog), particle pollution (tiny particles from smoke, power plants, factories, etc.), carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10).
The AQI is divided into six color-coded categories, each corresponding to a range of index values. An AQI value of 50 or below represents good air quality, while a value over 300 represents hazardous air quality. AQI values at or below 100 are generally considered safe, while values above 100 indicate unhealthy air quality.
You can find the daily AQI for your area through local radio, TV weather reports, newspapers, or weather apps on your phone. Maps showing real-time AQI data for various locations are also available online.