Water pollution is a pressing issue that poses a threat to the health of millions of people worldwide. It is caused by a range of contaminants, including toxic waste, petroleum, fertilisers, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and disease-causing microorganisms, which are released into bodies of water, making it unsafe for human use and disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Inadequate management of wastewater from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources, as well as natural sources like mercury from the Earth's crust, contribute to this global problem. Water pollution has severe consequences, including the spread of diseases such as cholera, hepatitis A, and dysentery, and it affects both wealthy and developing nations. With rising global temperatures, population growth, and unsustainable water consumption, the challenge of ensuring safe and sufficient water sources for all is becoming increasingly complex.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Water pollution is the release of substances (such as chemicals or microorganisms) or energy (in the form of radioactivity or heat) into surface and subsurface waters to the point that the substances interfere with the beneficial use of the water or with the natural functioning of ecosystems. |
| Main Pollutants | Bacteria, viruses, parasites, fertilisers, pesticides, pharmaceutical products, nitrates, phosphates, plastics, faecal waste, and radioactive substances. |
| Sources | Point sources (e.g. pipes, channels) and dispersed sources (e.g. nutrients and pesticides from farming activities, pollutants released by industry into the air). |
| Human Impact | Inadequate management of wastewater, improper disposal of chemical waste, oil leaks from cars and trucks, agricultural practices, and sewage treatment. |
| Health Impact | Exposure to contaminated water can lead to diseases such as cholera, hepatitis A, dysentery, typhoid, and polio. The WHO estimates that about 2 billion people have no option but to drink water contaminated by excrement. |
| Environmental Impact | Water pollution endangers the health of millions of people and disrupts aquatic ecosystems, leading to a loss of biodiversity. |
| Prevention | Reduce CO2 emissions, limit chemical pesticide use, safely treat wastewater, restrict single-use plastics, and improve wastewater management. |
What You'll Learn

Water pollution is caused by human activity and natural processes
Water pollution is a serious issue that affects the health of millions of people worldwide and endangers the environment. It is caused by a combination of human activity and natural processes, both of which introduce pollutants into water bodies.
Human activities that contribute to water pollution include industrial waste disposal, agricultural practices, and improper waste management. Industries often release toxic chemicals and waste products directly into rivers or allow them to leak into groundwater. These chemicals, such as insecticides, heavy metals, and petroleum products, are poisonous or toxic to living organisms. Agricultural practices, such as the use of pesticides and fertilisers, can also lead to water pollution. Excessive use of fertilisers can cause nutrient pollution, leading to an increase in nitrogen and phosphorus levels in water, promoting the growth of harmful algal blooms. Additionally, improper waste management, including the disposal of chemical cleaners, oils, and plastics, can result in these pollutants making their way into water sources.
Natural processes also contribute to water pollution. For example, mercury can filter from the Earth's crust, polluting oceans, rivers, and other water bodies. Eutrophication is a natural process where a water body transitions from a clean, clear condition to a nutrient-rich, algae-filled, and eventually waste-filled state. While eutrophication is a slow and inevitable process, human activities, such as sewage contamination and fertiliser runoff, can accelerate it.
Water pollution has severe consequences for both human health and the environment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 2 billion people are exposed to contaminated water with faecal bacteria, increasing the risk of diseases such as cholera, hepatitis A, and dysentery. Water pollution also affects the economy, with contaminated water reducing the GDP of affected regions by a third.
It is important to address water pollution through various measures. These include reducing CO2 emissions, limiting the use of chemical pesticides, properly treating and reusing wastewater, and reducing plastic consumption, especially single-use plastics. By implementing these measures, we can work towards preserving this precious resource and protecting the health and well-being of people and ecosystems worldwide.
Plastic Pollution: Water Contamination Crisis
You may want to see also

The health implications of water pollution
Water pollution is a serious global issue that poses significant risks to human health and safety. The impact of water pollution on human health is far-reaching, with a range of immediate and long-term effects. The consequences of water pollution are extensive, and the contamination of water sources endangers the health of millions worldwide.
Water, a "universal solvent," readily dissolves and mixes with toxic substances, making it easily polluted. This contamination can lead to the ingestion of harmful substances, causing various health issues. One of the most common diseases caused by water pollution is diarrhoea, which is often transmitted by enteroviruses present in the water. According to estimates, approximately 1 million people die annually from diarrhoea due to unsafe drinking water, poor sanitation, and inadequate hand hygiene. This issue is preventable, and improved water sources and sanitation practices can significantly reduce the risk of diarrhoeal diseases.
In addition to diarrhoea, water pollution can cause other health issues such as cholera, hepatitis A, dysentery, typhoid, and polio. The presence of chemical pollutants, including pesticides, fertilisers, and heavy metals, poses serious health risks if ingested. These pollutants can lead to developmental issues, stunted growth in children, and other health problems. Oil pollution, resulting from spills, industrial activities, and the shipping industry, also poses significant risks to human health.
Furthermore, water pollution can serve as a breeding ground for insects and vectors that transmit diseases such as dengue fever. Household drinking water containers can be breeding grounds for these insects, and simple interventions such as covering water storage containers can help reduce the risk of vector-borne diseases. Additionally, the release of untreated wastewater and the improper disposal of chemicals, oils, and non-biodegradable items contribute to water pollution and endanger human health.
The impact of water pollution on human health is a critical global concern. It is essential to address this issue through improved wastewater treatment, reduction of chemical and plastic usage, and the implementation of sustainable practices to protect the health and well-being of people worldwide.
Brown Pond Water: Polluted or Natural?
You may want to see also

The impact of water pollution on the economy
Water is a prerequisite for all life on Earth and is essential for social and economic development, energy production, and adaptation to climate change. However, water pollution poses a significant threat to this vital resource, endangering the health and well-being of millions worldwide. The impact of water pollution on the economy is far-reaching and multifaceted.
One of the most immediate economic consequences of water pollution is the increased cost of water treatment. Contaminated water requires advanced and often costly treatment processes to make it safe for human consumption. For example, the presence of nitrates in drinking water sources can significantly increase treatment expenses, as seen in Minnesota, where nitrate-removal systems drove supply costs up from a few cents to over $4 per 1,000 gallons.
Water pollution also has a detrimental effect on the agriculture and fishing industries. Agricultural pollution is the leading cause of water degradation worldwide, and the impact goes both ways. On the one hand, agricultural practices contribute to water pollution through the use of pesticides, fertilisers, and the improper treatment of wastewater. On the other hand, water pollution reduces agricultural yields by decreasing water quality, making it challenging to grow crops and raising the salinity of the water, which spoils food that could feed millions. Similarly, harmful algal blooms caused by nutrient pollution kill fish and contaminate shellfish, resulting in significant losses for the fishing and shellfish industries.
Water pollution also impacts the tourism industry, with losses amounting to nearly $1 billion annually. Water bodies affected by pollution and harmful algal blooms drive away tourists from fishing, boating, and other water-related activities. Waterfront property values can also decline due to the unpleasant appearance and odour of polluted water, particularly when algal blooms are present.
The health consequences of water pollution further contribute to the economic burden. Contaminated water exposes individuals to various diseases, including cholera, hepatitis A, dysentery, and diarrhoeal illnesses. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 2 billion people have no alternative but to consume water contaminated with excrement. This lack of access to clean drinking water leads to increased healthcare spending, which affects both wealthy and developing nations.
Additionally, water pollution hinders economic growth, particularly in middle-income countries. Research has shown that when rivers become moderately polluted, growth downstream is reduced by 1.4%, and heavy pollution results in a 2% decrease in growth. These figures are even higher for middle-income countries, with a 1.8% reduction in growth for moderate pollution and a 2.5% reduction for heavy pollution.
Overall, water pollution has far-reaching implications for the economy, affecting industries such as agriculture, fishing, and tourism, while also driving up healthcare costs and stalling economic growth. Addressing water pollution is crucial not only for preserving public health but also for ensuring sustainable economic development.
Purifying Water: Strategies for Pollution-Free Sources
You may want to see also

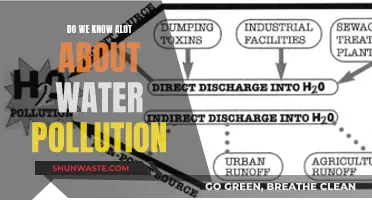
The sources of water pollution
Water pollution is an environmental issue that concerns everyone. It is the contamination of water bodies such as rivers, oceans, lakes, and groundwater by human activities, which can be harmful to organisms and plants that live in these water bodies. The main sources of water pollution include industrial waste, sewage and wastewater, mining activities, marine dumping, accidental oil leakage, and chemical pesticides and fertilizers.
Industrial Waste
The industrial sector is a major contributor to water pollution. Many industries generate large amounts of wastewater containing various chemicals, heavy metals, and other toxic substances that are released into water bodies without proper treatment. For example, the textile industry uses dyes and fixatives that are hard to remove by conventional water treatment methods. Similarly, factories often release untreated wastewater containing dyes, fixatives, oil, grease, and other forms of non-biodegradable waste. These substances can alter the physical properties of water, introduce harmful toxins, and reduce oxygen levels, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and the death of aquatic species.
Sewage and Wastewater
Sewage and wastewater are significant sources of water pollution, especially when not properly managed. Sewage consists of blackwater (excrement, urine, and flush water from toilets) and greywater (from showers, sinks, washing machines, and dishwashers). When sewage systems fail or are absent, this waste can end up in natural water bodies, polluting them with harmful bacteria, viruses, nutrients, and toxins. Wastewater is also produced by various industrial operations, such as manufacturing, mining, and agriculture, and can contain high levels of pollutants.
Agricultural Activities
Agricultural activities are a leading cause of water degradation worldwide. Farming and livestock production account for about 70% of the earth's surface water consumption and are major water polluters. Agricultural runoff carries pesticides, fertilizers, and animal waste into water bodies, leading to harmful algal blooms and dead zones. In the United States, agricultural pollution is the top source of contamination in rivers and streams, the second-biggest source in wetlands, and the third main source in lakes. It also contributes significantly to contamination in estuaries and groundwater.
Oil Spills and Leakage
Oil spills and leakage are significant contributors to water pollution. While major tanker spills often make headlines, consumers account for the vast majority of oil pollution in our seas. Oil and gasoline drips from millions of cars and trucks each day, and land-based sources such as factories, farms, and cities contribute significantly to the estimated 1 million tons of oil that reaches marine environments annually. Accidental oil releases from drilling, transportation, and storage activities can also contaminate water bodies.
Chemical Pollutants
Various chemical pollutants, including pesticides, fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and heavy metals, find their way into water bodies. These substances can originate from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, or improper disposal of household chemicals. They can have toxic effects on aquatic life and humans, with exposure to nitrates linked to stunted growth and increased salinity reducing agricultural yields.
Water Filtration: Ocean Pollution Solution?
You may want to see also

How to prevent water pollution
Water pollution is a pressing issue, with our rivers, reservoirs, lakes, and seas inundated with chemicals, waste, plastic, and other pollutants. While we are all accountable to some degree for this problem, there are numerous ways to prevent water contamination and reduce our contribution to it.
One of the most effective ways to prevent water pollution is to be mindful of what we pour into storm sewers. Waste that goes down these sewers often ends up untreated in local waterways, so it's important to properly dispose of chemical cleaners, oils, and non-biodegradable items. Additionally, maintaining our vehicles to prevent leaks and disposing of pet waste responsibly can help reduce water pollution.
Another way to prevent water pollution is to reduce our plastic consumption and reuse or recycle plastic whenever possible. We can also minimize the use of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, and ensure that these substances, along with motor oil and other automotive fluids, do not enter sanitary sewer or storm sewer systems.
Water conservation is another important aspect of preventing water pollution. We can install water-efficient toilets, showerheads, and appliances, and adopt water-saving practices such as taking shorter showers, drawing less water for baths, and running washing machines and dishwashers only with full loads.
Furthermore, we can take action in our communities by volunteering for riverbank plantings, creating buffers of native plants along stream banks, and advocating for regulations that address modern-day challenges, including microplastics, pharmaceuticals, and other contaminants.
By implementing these measures and encouraging others to do the same, we can make a significant impact in preventing water pollution and protecting our precious water resources.
Lake Water: A Haven for Harmful Bacteria and Viruses?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Water pollution is the release of substances into bodies of water that makes water unsafe for human use and disrupts aquatic ecosystems.
Water pollution can be caused by a wide range of different contaminants, including toxic waste, petroleum, fertilisers, pesticides, pharmaceutical products, plastics, faecal waste, and even radioactive substances. The main point source of pollution is sewage and wastewater treatment, while for diffuse pollution, the main sources are farming and fossil fuel power plants.
Water pollution endangers the health of millions of people around the world. The WHO estimates that about 2 billion people have no option but to drink water contaminated by excrement, exposing them to diseases such as cholera, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, and dysentery. Water pollution also affects ecosystems, with sewage promoting algae growth that eventually results in eutrophic "dead zones" where aquatic life cannot survive due to a lack of oxygen.
There are several measures that can be taken to prevent water pollution:
- Reduce CO2 emissions to prevent global warming and acidification of the oceans.
- Reduce the use of chemical pesticides and nutrients on crops.
- Reduce and safely treat wastewater so that it can be reused for irrigation and energy production.
- Restrict the use of single-use plastics that often end up in rivers, lakes, and oceans as microplastics.
- Learn about the unique qualities of water in your local area and discover where your actions will have the most impact.
- Reduce your plastic consumption and properly dispose of chemical cleaners, oils, and non-biodegradable items.