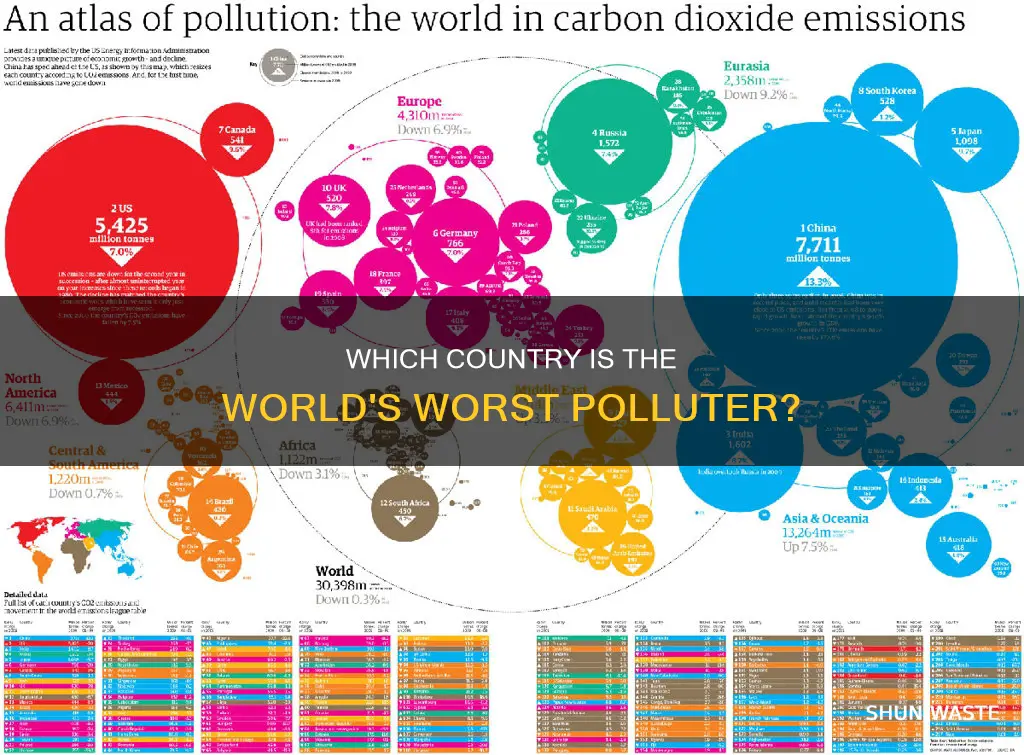
Climate change is an increasingly pressing issue, with global warming being everyone's business. Countries with the highest carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are typically the most industrialised, with China, the United States, and India being the top three emitters. However, when considering CO2 emissions per capita, the United States and China's positions are reversed, with the US having higher emissions per person. Germany is the European country with the highest CO2 emissions, contributing over a quarter of the entire European Union's total CO2 emissions. While India is the third most polluting country in terms of CO2 emissions, it does not appear in the ranking of the 10 most polluting countries per capita, as it has a large population. The three most polluting countries per capita are all located in the Arabian Peninsula, due to their large share of the oil industry and small populations.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Country with the highest carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions | China |
| CO2 emissions | 9.9 billion tonnes |
| Reason for high emissions | Export of consumer goods and heavy reliance on coal |
| Second-highest CO2 emissions | United States |
| CO2 emissions | 4.4 billion tonnes |
| Reason for high emissions | Car-dependent infrastructure and unsustainable lifestyle |
| Third-highest CO2 emissions | India |
| CO2 emissions | 2.3 billion tonnes |
| Reason for high emissions | Industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, reliance on fossil fuels, and weak regulations |
| European country with the highest CO2 emissions | Germany |
| CO2 emissions | N/A |
| Reason for high emissions | Heavy dependence on coal |
What You'll Learn

China's CO2 emissions
China, the United States, and India are the top three countries with the highest carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. China's CO2 emissions are largely due to the export of consumer goods and its heavy reliance on coal. In 2022, China emitted 9.9 billion tonnes of CO2, accounting for approximately 14% of global CO2 emissions.
While China's recent efforts to reduce CO2 emissions are promising, the country still faces challenges. China's emissions remain only 1% below the latest peak, indicating that any surge in demand or economic growth could push emissions to a new record high. Additionally, China's international climate pledge for 2035 and the five-year plan for 2026-2030 will play a crucial role in shaping the future path of its CO2 emissions.
It is worth noting that when assessing a country's contribution to global warming, per capita emissions provide a more accurate representation than absolute emissions. China's large population and role as a major producer and exporter of goods impact its overall emissions. Correcting for trade and considering consumption-based emissions, which account for the CO2 emitted in the production of imported goods, offer a more comprehensive view of a country's carbon footprint.
Finding Your Zip Code: A Quick Guide
You may want to see also

India's air pollution
India is one of the world's most polluted countries, with 11 of the top 20 most air-polluted cities in the world. In 2019, 21 of the 30 most polluted cities were in India. Delhi, India's capital and most populous city, is the most polluted capital city in the world. The air pollution in Delhi shortens the life expectancy of its residents by 11.9 years. Overall, an average Indian's life expectancy is reduced by 5.3 years due to air pollution.
The main contributors to India's air pollution include industrial and vehicular emissions, construction dust and debris, thermal power plants, waste burning, and the use of wood and dung for cooking and heating. In rural areas, biomass burning for cooking and heating is a significant source of pollution. India's reliance on fossil fuels, weak regulations, and seasonal weather patterns also contribute to the country's air pollution. For example, during the autumn and spring months, large-scale crop residue burning in agricultural fields is a major source of smoke, smog, and particulate pollution.
India has recognized the severity of its air pollution problem and has taken steps to address it. In 2019, the country declared a "war against pollution" and launched its National Clean Air Programme (NCAP), aiming to reduce particulate pollution by 20-30% by 2024. The Indian government has also set more ambitious targets for NCAP, aiming for a 40% reduction in particulate pollution by 2025-26. Additionally, India is investing in renewable energy sources and has partnered with organizations like the Clean Air Fund to improve air quality.
Despite these efforts, India continues to struggle with severe air pollution. The country's fast-growing economy and industrialization contribute to the challenge of reducing air pollution. However, there is a growing public awareness of air pollution as a problem, and initiatives like the India CEO Forum for Clean Air are gaining traction. India is also working to improve the availability and accessibility of data on air pollution, which is crucial for addressing the issue effectively.
Wind Energy: Pollution or Clean Power?
You may want to see also

US consumption habits
The United States is one of the world's top three most polluting countries in terms of CO2 emissions, alongside China and India. In 2020, the US emitted 4.4 billion tonnes of CO2. However, when measured per capita, the US has a higher carbon footprint than China.
Americans also have a high consumption of natural resources. The average person in North America consumes nine times as many natural resources as the average person in Africa. This is due in part to the country's heavy reliance on cars, with limited public transport options due to specific policy choices and urban design. The US also has a high consumption of meat, which has risen dramatically over the past few decades. Cattle farming is one of the most environmentally destructive forms of food production, requiring 15000 litres of water to produce one kilogram of beef.
Racial and ethnic disparities in pollution exposure and consumption habits have also been documented in the US. On average, black and Hispanic minorities bear a disproportionate burden from air pollution caused mainly by non-Hispanic whites. This is due in part to differences in pollution concentrations at locations of residence, with minority groups often living in areas with higher pollution levels.
While some Americans are taking steps to reduce their consumption, such as by buying used items or reducing waste during the COVID-19 pandemic, overconsumption remains a significant issue. To address this, experts have suggested implementing policies such as tax rebates for repair services and "pay as you throw" waste collection to encourage more sustainable consumption habits.
The Seine's Pollution Problem: Why It's So Dirty
You may want to see also

Oil industry in the Arabian Peninsula
The three countries with the highest carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions are China, the United States, and India. China's high emissions are attributed to its export of consumer goods and heavy reliance on coal. The United States and India also have high emissions due to industrial activities and the use of fossil fuels. However, when it comes to per capita emissions, the ranking changes. The three most polluting countries per capita are located in the Arabian Peninsula. This is due to the significant contribution of the oil industry to their economies and their small populations.
The Arabian Peninsula has the largest oil reserves in the world. Oil was first discovered in the region in Bahrain in 1932, which sparked an intensive search for oil in eastern Arabia. In 1938, oil was discovered in Saudi Arabia, followed by discoveries in Kuwait and Qatar in 1940. Over the years, oil has also been discovered in other areas of the Arabian Peninsula, including the United Arab Emirates, Oman, and Yemen.
The development of the oil industry in Saudi Arabia involved several international companies and concessions. The California Arabian Standard Oil Company (CASOC), a subsidiary of Standard Oil of California (SOCAL), played a significant role in the exploration and discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia. CASOC geologists identified a promising site named Dammam No. 7, and despite initial challenges, they eventually struck oil in 1938, revealing the largest source of crude oil in the world. The discovery of oil had a significant impact on the economy of Saudi Arabia, providing a crucial source of wealth for the kingdom.
The abundance of oil in the Arabian Peninsula has been both a blessing and a challenge for economic diversification. While oil revenues have contributed significantly to the region's economy, they have also disincentivized the exploration and development of other natural resources. Ancient mining sites indicate historical mineral production, such as gold, silver, and copper, but these industries have declined over time. The region also possesses other natural resources, including natural gas associated with oil fields, which can be commercially exploited or reinjected into oil-bearing strata for enhanced oil recovery.
The oil industry has been a dominant economic force in the Arabian Peninsula, and its impact on the global energy market has been significant. The region's vast oil reserves have shaped geopolitical dynamics and influenced international relations. The development of the oil industry in the Arabian Peninsula has also had social and environmental consequences, leading to urbanization, economic growth, and challenges associated with managing the environmental impact of oil extraction and consumption.
Sources of Wastewater: Where Does It All Come From?
You may want to see also

Europe's sustainability
Sustainability is about meeting the world's needs of today and tomorrow by creating systems that allow us to live well within the limits of our planet. Europe, the third most populated continent, is not spared by global warming and climate change. It is affected by issues such as air pollution, droughts, wildfires, and sea level rise. Europe still consumes more resources and contributes more to environmental degradation than other regions. About 75% of the land and 40% of the seas have been severely altered worldwide, and Europe is experiencing a rapid loss of biodiversity.
To address these issues, the EU has committed to long-term environmental and climate goals, such as the European Green Deal and the 8th Environment Action Programme (8EAP). These initiatives aim to enhance natural capital, achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, decouple economic growth from resource use, and create a toxic-free environment. Europe needs to transform key systems of food, energy, mobility, and buildings to reduce environmental pressures. This includes rethinking technologies, production processes, and consumption patterns.
Additionally, the EU has adopted policies to tackle plastic pollution, such as the Directive on single-use plastics, which bans the sale of certain products in member states. Individual European states have also implemented measures, such as France, Germany, and Spain, which have fully banned single-use plastics. The EU recognizes the urgency of taking immediate and decisive action across diverse policy areas and engaging society to create a sustainable future.
While China, the United States, and India are the top three countries with the highest carbon dioxide emissions, Europe is also contributing to global pollution. Germany, for example, has the highest CO2 emissions in Europe due to its heavy dependence on coal. However, Europe is taking steps towards sustainability and pollution reduction, with initiatives like the European Green Deal and policies addressing plastic pollution.
Preventing Particulate Matter: Strategies for Cleaner Air
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
China, the United States, and India are the top three countries with the highest carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. China has been emitting more CO2 than any other country since 2006.
Highly populated and industrialised countries tend to have higher pollution levels. The export market, burning of fossil fuels, and reliance on coal are significant contributors to a country's carbon emissions.
Air pollution is a significant health hazard, causing various health issues such as asthma attacks, respiratory problems, and adverse effects on pregnant people and newborns. It is also a leading cause of global warming and climate change, with carbon dioxide being the most important anthropogenic greenhouse gas.







