Traffic pollution, also known as traffic-related air pollution (TRAP), is a major source of exposure to harmful pollutants in urban areas. It is caused by vehicle emissions, including tailpipe emissions from combustion engines, and non-tailpipe emissions such as brake and tyre wear. These emissions release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and fine particles, which can have adverse effects on human health and the environment. The health risks associated with traffic pollution include respiratory issues, cardiovascular disease, and increased mortality rates, with populations living and working near roads being most at risk.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Congestion | Recurring congestion, such as rush hour traffic, increases travel time and exposure to pollutants. |
| Vehicle Emissions | Carbon Monoxide (CO), Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Unburned Hydrocarbons (HC), Ozone (O3), and Fine Particles (FP) are all released from vehicles and contribute to air pollution. |
| Health Risks | Short-term morbidity (emergency doctor visits), long-term mortality, asthma, cardiovascular disease, respiratory issues, cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, and more. |
| Population Exposure | Populations living and working near roads are at higher risk of exposure to pollutants and adverse health effects. |
| Environmental Impact | Traffic-related air pollution contributes to climate change and negatively affects the environment. |
| Global Statistics | Traffic and mobility are the largest contributing factors to 4.2 million annual deaths from ambient air pollution. |

Vehicle emissions
Non-tailpipe emissions include brake and tire wear, as well as road dust. These fine friction particles are a result of physical friction and do not change their composition when they come into contact with other pollutants in the atmosphere. Unlike tailpipe emissions, these particles will remain a source of pollution even with the increasing popularity of electric vehicles. The finer the particle, the further it can penetrate inside the body, causing various health issues such as oxidative stress, respiratory or cardiovascular disorders, cancers, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The health risks associated with vehicle emissions have been widely studied. In France, air pollution exposure causes 40,000 deaths each year, with road transport being a primary source of pollutants. Similarly, in China, traffic congestion has been linked to increased mortality rates, with an average of 46 additional deaths in major cities. In Canada, the population residing near major roadways is regularly exposed to traffic-related air pollution, which has been associated with adverse health effects. These health impacts include respiratory, cardiovascular, immunological, reproductive, and neurological issues.
To mitigate the health risks and environmental impacts of vehicle emissions, comprehensive vehicle emission control policies and regulations are necessary. This includes the development of effective emission models that directly account for congestion and the implementation of stricter fuel and engine standards to reduce the release of harmful pollutants.
Thermal Pollution: Nuclear Power Plants' Impact and Influence
You may want to see also

Congestion
Traffic congestion is a major cause of air pollution, particularly in urban areas. The problem is exacerbated by the rapid increase in the number of vehicles on the road. For instance, in China, the number of vehicles has increased significantly in the last decade, causing severe traffic congestion and worsening air pollution.
A study by the Harvard School of Public Health found that emissions from traffic congestion in 83 of the largest urban areas in the US contributed to over 2,200 premature deaths annually, with a financial cost to the health system of at least $18 billion. The study, "Evaluation of the Public Health Impacts of Traffic Congestion: A Health Risk Assessment," is believed to be the first to quantify the damage caused by emissions from vehicles idling in crowded roadways.
Traffic congestion increases vehicle emissions and degrades ambient air quality. It leads to an increase in O3 precursor emissions, which raises O3 concentration and has adverse health effects. A study in China found that traffic congestion aggravates air pollution and the health burden, particularly in urban clusters such as the North China Plain and the Sichuan Basin. Another study in Beijing found that when the traffic congestion index increased by 20%, the emergency ambulance call rate for heart disease increased by 2.9%.
The impact of traffic congestion on air pollution is not limited to a specific type of vehicle. However, a case study in Chennai found that motorcycles had the highest count among all vehicles, and they contributed more CO2 and particulate matter compared to passenger cars. This indicates that different types of vehicles may have varying levels of impact on air pollution.
To address the issue of air pollution caused by traffic congestion, effective vehicle emission control policies and regulations are necessary. The development of emission models that directly account for congestion and the implementation of comprehensive driving patterns that reflect congestion can help mitigate the problem. Additionally, it is important to consider the populations living and working near roads, as they are at a higher risk of exposure to pollutants.
Aquaculture's Water Pollution: Impact and Solutions
You may want to see also

Fossil fuels
Additionally, the combustion of fossil fuels produces ultra-fine particles and aromatic hydrocarbons, which have been linked to asthma, cancer, heart disease, and premature death. Fossil fuel pollution disproportionately affects communities of colour and low-income communities, with Black and Hispanic Americans exposed to significantly higher levels of particulate matter pollution. Furthermore, the extraction, transportation, and refining of fossil fuels can lead to oil spills that harm wildlife, destroy habitats, and erode shorelines.
Another significant issue is plastic pollution, as the majority of plastics are made from fossil fuels. Approximately 300 million tons of plastic waste are produced globally each year, with 14 million tons ending up in the ocean, causing wildlife deaths and contaminating the food chain. The plastic industry also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, with the US industry alone producing 232 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent annually.
The use of fossil fuels results in significant climate, environmental, and health costs. For example, in 2018, 350,000 premature deaths in the United States were attributed to fossil fuel-related pollution, particularly in states like Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. Similarly, in California in 2017, toxic air pollution from wildfires was exacerbated by traffic pollution, affecting millions of people.
To mitigate these issues, researchers have urged country leaders to commit to phasing out fossil fuels and transitioning to clean, renewable energy sources. It is estimated that phasing out fossil fuels could prevent about 3.85 million deaths in South, Southeast, and East Asia annually and up to 460,000 deaths in high-income countries.
Dams' Dark Side: Unveiling Thermal Pollution's Impact
You may want to see also

Tyre and brake wear
The particles released from tyre and brake wear are extremely small and can be easily inhaled by humans, penetrating deep into the lungs and causing respiratory issues. In addition to respiratory problems, exposure to these particles has been linked to oxidative stress, cardiovascular disorders, cancers, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. The toxicity of these particles is further increased by the presence of transition metals.
The problem of tyre and brake wear pollution is exacerbated by the lack of regulation and control measures. While exhaust emissions have been the focus of attention and have been tightly regulated, tyre and brake wear emissions are completely unregulated. This is due in part to the difficulty in measuring and controlling non-exhaust sources of pollution. However, as the transport sector moves towards electric vehicles, the relative contribution of tyre and brake wear to overall vehicle emissions is expected to increase.
To address this issue, there have been calls for stricter regulations and industry challenges to reduce vehicle weight and improve tyre quality. For example, fitting higher-quality tyres and ensuring proper tyre inflation can help reduce non-exhaust emissions. Additionally, advancements in brake technology, such as the development of iDisc brake discs coated in tungsten-carbide, can significantly reduce brake dust emissions.
Overall, tyre and brake wear is a significant and often underestimated contributor to traffic pollution, posing serious health and environmental risks. Addressing this issue requires a combination of regulatory measures, industry innovations, and consumer awareness to reduce the impact of non-exhaust emissions on air quality and human health.
Acid Rain: Understanding the Key Pollutants and Their Impact
You may want to see also

Health risks
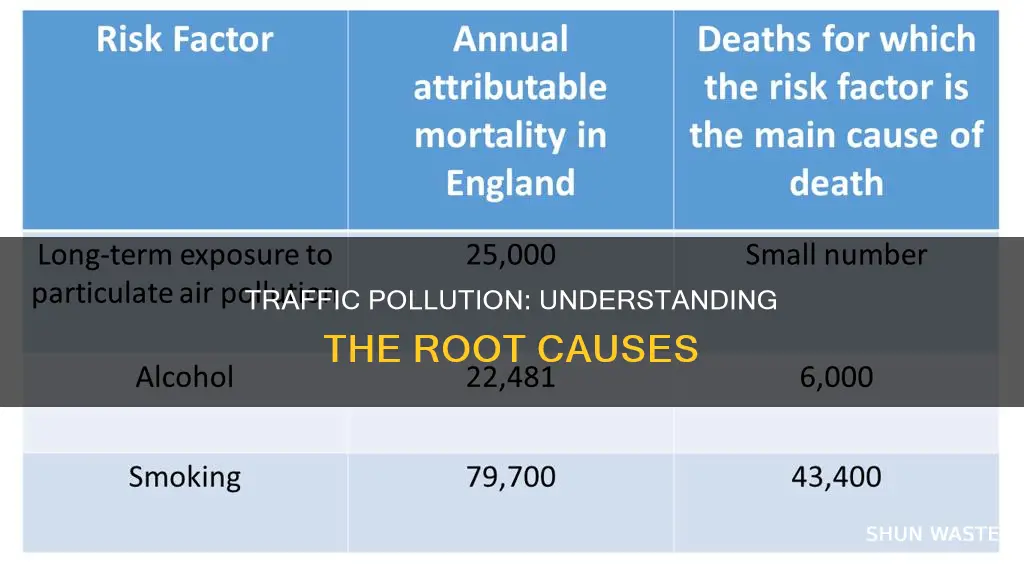
Traffic pollution is a major concern for public health, with populations living and working near roads at risk of adverse health effects. The pollutants emitted by vehicles during chemical and physical reactions, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and fine particles, pose significant risks to human health.
Traffic-related air pollution (TRAP) has been linked to a wide range of adverse health effects, including respiratory, cardiovascular, immunological, reproductive, developmental, and neurological problems. The fine particles (FP) in exhaust fumes and from tyre and brake wear are toxic due to their composition, shape, and size. These fine particles can penetrate deep into the body, causing oxidative stress, respiratory issues, cardiovascular disorders, cancers, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Carbon monoxide (CO), a poisonous gas released during fossil fuel combustion, is another major concern. Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels also produces nitrogen oxides (NOx), which contribute to the formation of harmful compounds and acids. Unburned hydrocarbons (HC) are yet another source of pollution, leading to the formation of ozone (O3), which is associated with asthma, breathing difficulties, and an increased risk of stroke.
The impact of traffic congestion on air quality and health cannot be overstated. Congestion increases travel time and exposure to pollutants, and lowers the dispersion of vehicle emissions. This results in higher concentrations of O3 and other harmful emissions, aggravating health risks, especially in urban areas. Studies have shown that traffic congestion is linked to increased emergency ambulance call-outs and hospital admissions, with higher rates of heart disease and premature mortality.
The health effects of traffic pollution are not limited to physical ailments. Exposure to traffic-related air pollution has been linked to anxiety, and noise pollution from traffic can also have adverse effects on mental health and well-being.
Furthermore, the health risks associated with traffic pollution are not evenly distributed. Certain populations, such as pregnant women, children, and older individuals, may be more vulnerable to the adverse effects of air pollution. Socioeconomic factors, proximity to major roadways, and access to green spaces can also influence the health outcomes related to traffic pollution exposure.
Guyana's Water Pollution: Causes and Effects
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Traffic-related air pollution (TRAP) is a mixture of secondary pollutants formed in the atmosphere from exhausts, evaporative emissions, and non-combustion emissions (e.g. road dust, tyre wear). TRAP is considered the leading cause of poor air quality in cities and urban areas.
The main causes of traffic pollution are vehicle emissions and traffic congestion. Vehicle emissions include carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOX), unburned hydrocarbons (HC), and fine particles (FP) from exhaust fumes. Traffic congestion increases traffic flow, leading to more emissions and poorer air quality.
Traffic pollution has been associated with a wide range of adverse health effects, including respiratory, cardiovascular, immunological, reproductive, and neurological issues. Short-term exposure to traffic pollution can lead to emergency doctor visits and hospital admissions, while long-term exposure increases the risk of mortality.


















