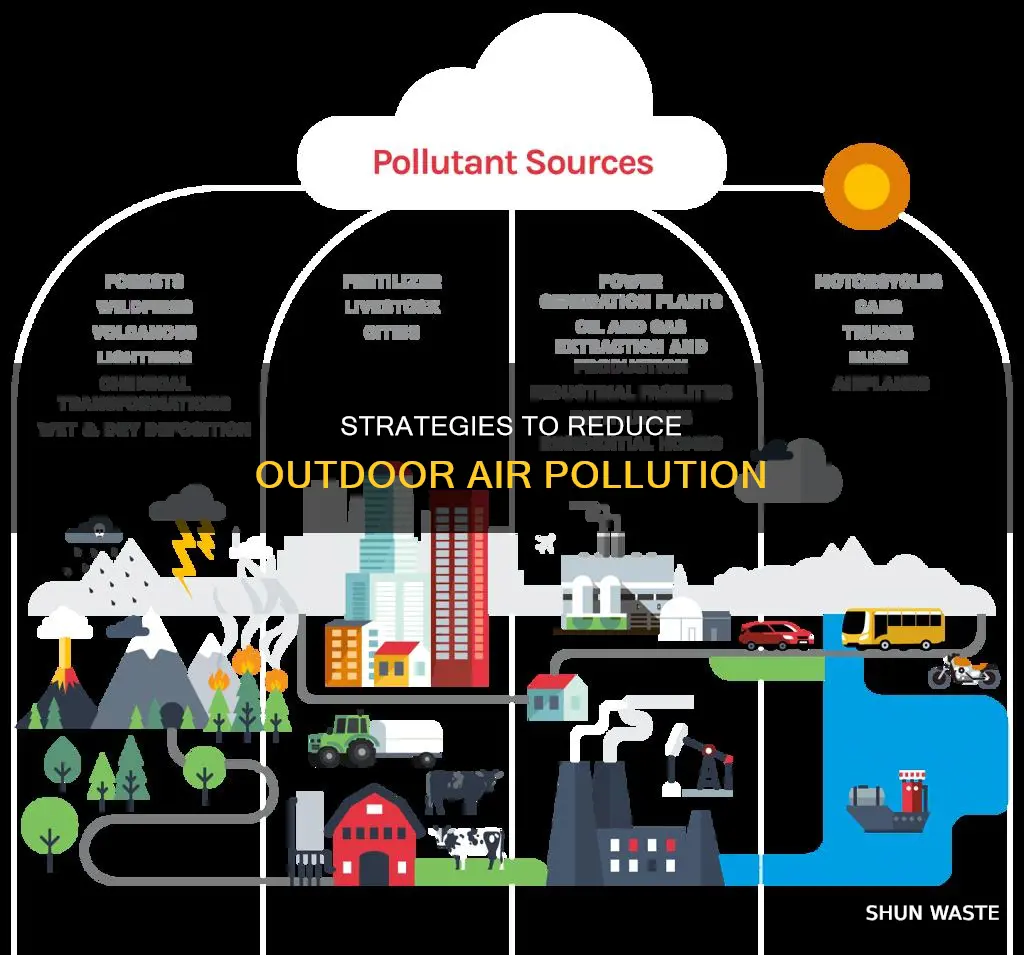
Outdoor air pollution is a pressing issue that demands concerted action from policymakers and individuals alike. While sources of outdoor air pollution often extend beyond individual control, certain personal interventions can effectively reduce exposure and health risks. This includes staying indoors, limiting outdoor physical activity during periods of elevated pollution, using air filters, and wearing respirators. However, these personal interventions are secondary to the need for systemic change, with policies and investments in cleaner transport, energy-efficient homes, power generation, industry, and waste management being crucial to reducing outdoor air pollution.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cleaner transport | Using electric vehicles, carpooling, using public transportation, walking, cycling, using cleaner heavy-duty diesel vehicles, and low-emission vehicles |
| Energy-efficient homes | Using energy-efficient appliances and heating systems, turning off electrical items, using LED bulbs, air-drying clothing, using less energy |
| Power generation | Using cleaner modes of power generation, reducing energy intake |
| Industry | Using clean technologies, improved waste management |
| Municipal waste management | Capturing methane gas emitted from waste sites, using biogas |
| Access to clean household energy | Using clean household energy solutions for cooking, heating, and lighting |
| Urban planning | Prioritizing rapid urban transit, walking and cycling networks in cities, promoting cleaner modes of transportation |
| Agriculture | Improved management of agricultural waste |
What You'll Learn

Reduce vehicle usage and opt for cleaner modes of transport
Reducing vehicle usage and opting for cleaner modes of transportation are crucial steps in decreasing outdoor air pollution. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
Encourage Active Mobility and Public Transportation:
Promoting active mobility options such as walking and cycling can significantly reduce private vehicle usage. Well-designed urban infrastructure that prioritizes dedicated walking and cycling paths, as seen in Copenhagen, can encourage these cleaner modes of transport and decrease transport-related emissions. Additionally, investing in efficient and affordable public transportation systems, such as buses, trains, and trams, can further reduce the number of private vehicles on the road, lowering congestion and transport-related pollution.
Adopt Cleaner Vehicle Technologies:
Governments and individuals can play a role in transitioning to cleaner vehicle technologies. This includes incentivizing and adopting electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid vehicles, and newer models with improved emissions standards. Since the 1970s, policies to reduce lead in gasoline and stricter emissions standards have resulted in newer vehicles being up to 99% cleaner for common pollutants compared to older models. These efforts have contributed to improved air quality in cities, despite increasing vehicle miles traveled.
Optimize Delivery and Route Planning:
Individuals can contribute by opting for longer delivery time windows, allowing delivery companies to optimize their routes and reduce extra trips. Additionally, when shopping online, consider consolidating purchases into one shipment to minimize packaging and the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
Maintain Vehicles and Reduce Idling:
Proper vehicle maintenance, including regularly checking tire pressure and fixing exhaust issues, can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Unnecessary idling of vehicles, especially diesel engines, contributes to air pollution and can be avoided by turning off engines when not in use.
Promote Carpooling and Shared Mobility:
Encouraging carpooling and shared mobility options, such as ride-sharing services, can decrease the number of vehicles on the road. This reduces congestion and lowers overall emissions from transportation.
Kern Air Pollution: What's the District's Role?
You may want to see also

Use energy-efficient appliances and heating systems
Energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of reducing outdoor air pollution, as it addresses both indoor and outdoor pollutant concentrations. By reducing the demand for electricity generation, energy efficiency directly contributes to lowering air pollution levels. This is especially pertinent given that the energy system is essential for global economic and social progress.
One effective strategy to enhance energy efficiency is to prioritize the use of energy-efficient appliances and heating systems. These systems play a pivotal role in mitigating air pollution, particularly within residential contexts. For instance, advanced designs for new homes are increasingly incorporating mechanical features that introduce outdoor air into the home through the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) system. This innovation not only improves indoor air quality but also reduces the need for energy-intensive cooling and heating processes, thereby conserving energy and diminishing pollution.
Energy-efficient heat recovery ventilators, also known as air-to-air heat exchangers, are a prime example of these innovative systems. They recover the thermal energy from outgoing air to preheat or precool incoming outdoor air, thereby reducing the energy required for heating or cooling. This technology is particularly effective in temperate climates, where it can significantly decrease the energy consumption associated with maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures.
To further enhance the efficiency of heating systems, individuals can take several proactive measures. One such action is to adjust gas stoves to decrease emissions, as recommended by the US EPA. Another suggestion is to opt for a fan instead of air conditioning, as air conditioners are significant energy consumers. Programmable thermostats can also be used to regulate temperatures efficiently, with settings of 78°F in summer and 68°F in winter.
Additionally, when replacing appliances, it is advisable to look for energy-efficient alternatives, often denoted by an "energy star" label. These products are designed to minimize energy consumption, thereby reducing the environmental footprint and contributing to lower pollution levels. By adopting these energy-efficient appliances and heating systems, individuals can play a proactive role in mitigating outdoor air pollution while also enjoying the economic benefits of reduced energy costs.
Air Quality in Roseburg, Oregon: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Improve waste management practices
Improving waste management practices is crucial for reducing outdoor air pollution, which currently causes an estimated 4.2 million premature deaths worldwide annually. Here are some ways to enhance waste management practices:
Strategies for Waste Reduction and Separation
Implementing waste reduction strategies at the municipal and agricultural levels is essential. This includes encouraging recycling, reusing, and waste reprocessing. For instance, the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency provides education, guidance, and incentives for businesses, cities, and communities to reduce waste and emissions. Similarly, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) assists local waste management teams in adopting safer and more environmentally friendly practices, which benefit both the workers and the communities they serve.
Improved Methods for Waste Management
Biological waste management methods, such as anaerobic waste digestion to produce biogas, offer a feasible and low-cost alternative to open incineration. Capturing methane gas emitted from waste sites can also be used as an alternative energy source. Additionally, when incineration is unavoidable, strict emission controls are critical to minimize the environmental impact.
Regulations for Waste Management
Governments play a vital role in establishing strong regulations to prevent dumping and burning of waste. They can invest in better waste handling methods, such as providing access to affordable clean household energy solutions for cooking, heating, and lighting. This contributes to cleaner air and a safer environment for everyone.
Corporate Responsibility
Companies can also contribute by reducing waste. They can achieve this by using less packaging, designing products that are easily recycled, and supporting regulations for improved waste management. By minimizing waste and adopting sustainable practices, companies can positively impact outdoor air quality.
Education and Community Engagement
Educating communities about waste management practices is essential. Local businesses, city offices, and school districts should be directed towards programs that help them reduce waste and become more sustainable. For example, the Small Business Environmental Assistance Program in Minnesota helps businesses comply with environmental rules and reduce waste. Community engagement and collaboration are key to ensuring effective waste management practices.
Air Pollution: Condensation's Impact and Vice Versa
You may want to see also

Promote cleaner industrial technologies
Outdoor air pollution is a critical issue that affects people's health and well-being worldwide, causing an estimated 4.2 million premature deaths globally in 2019, with the majority occurring in low- and middle-income countries. To address this challenge, promoting cleaner industrial technologies is essential.
Cleaner industrial technologies play a pivotal role in mitigating outdoor air pollution. Industries are significant contributors to air pollution, particularly through industrial smokestack emissions. By embracing cleaner technologies, we can substantially reduce these emissions. This includes adopting advanced smokestack scrubbers, which remove pollutants from industrial exhaust gases, and implementing catalytic converters that transform toxic gases into less harmful substances. Additionally, the use of low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints and coatings in industrial processes can significantly reduce the release of harmful VOCs into the atmosphere.
Another crucial aspect is the improved management of industrial waste. Capturing methane gas emitted from waste sites and utilizing it as biogas instead of incinerating it can lead to substantial reductions in air pollution. This approach not only mitigates pollution but also provides a valuable energy source. Furthermore, industries can invest in cleaner production technologies, such as implementing closed-loop production systems that minimize waste generation and maximize resource efficiency, reducing the overall environmental impact.
The transition to cleaner industrial technologies also involves a shift towards renewable and alternative energy sources. This includes the increased use of solar, wind, and hydropower, which produce little to no air pollution compared to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation. Additionally, promoting energy efficiency in industrial processes can further reduce pollution levels. This can be achieved through the adoption of energy-efficient machinery and equipment, as well as the optimization of energy-intensive processes, such as heating and cooling systems.
To facilitate the adoption of cleaner industrial technologies, governments and organizations like the WHO and EPA play vital roles. They can provide incentives, grants, and subsidies to industries that invest in cleaner technologies, as well as establish and enforce emissions standards and regulations. By offering guidance, resources, and technical support, these entities can help industries navigate the transition to cleaner practices. Moreover, promoting research and development in this field will foster innovation and the creation of even more effective pollution-reduction technologies.
In conclusion, promoting cleaner industrial technologies is a critical component of the broader effort to reduce outdoor air pollution. By adopting cleaner production methods, waste management strategies, and energy sources, industries can significantly contribute to improving air quality and protecting public health on a global scale.
Air Pollutants: Common Toxins in Our Air
You may want to see also

Encourage the use of cleaner and more efficient vehicles
Encouraging the use of cleaner and more efficient vehicles is a crucial strategy to reduce outdoor air pollution, which has caused an alarming number of premature deaths worldwide, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Here are some detailed actions that can be taken to promote the adoption of cleaner and more efficient vehicles:
Promote Public Transportation and Active Mobility
One way to encourage the use of cleaner and more efficient vehicles is to prioritize public transportation and active mobility options. This includes investing in and promoting rapid urban transit systems, such as buses, light rail, and subways. Making public transportation more accessible, affordable, and efficient can incentivize people to leave their private vehicles at home. Additionally, creating safe and well-connected walking and cycling networks in cities can further reduce the reliance on private vehicles. This can be achieved through dedicated cycling lanes, improved pedestrian infrastructure, and initiatives like bike-sharing programs.
Incentivize Electric Vehicles
Governments and local authorities can provide incentives to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). This includes offering tax breaks, subsidies, or grants to individuals and businesses that purchase or lease electric cars, buses, trucks, and vans. Providing incentives for the installation of electric vehicle charging stations in residential and commercial areas can also accelerate the transition to electric mobility.
Raise Awareness about Fuel Efficiency
Educating consumers about the importance of fuel efficiency when choosing a vehicle can also contribute to reducing air pollution. Encouraging the use of tools like the EPA's Fuel Economy and Environment Label can help consumers make informed decisions. By comparing different vehicle models, individuals can select options that are not only environmentally friendly but also economically beneficial due to reduced fuel consumption.
Implement Anti-Idling Measures
Unnecessary idling of cars, trucks, and buses contributes significantly to air pollution and wastes fuel. Implementing anti-idling measures, such as anti-idling policies or "no-idling zones" near schools and public spaces, can reduce emissions and improve air quality, especially in densely populated areas. Educating drivers about the environmental impact of idling and encouraging them to turn off their engines when parked or waiting can also help.
Promote Carpooling and Telecommuting
Encouraging carpooling initiatives, such as ride-sharing programs and carpool lanes, can reduce the number of vehicles on the road, thereby decreasing overall emissions. Additionally, promoting telecommuting and flexible work arrangements can decrease the need for commuting altogether, reducing traffic congestion and associated air pollution.
Support Sustainable Commercial Practices
Commercial fleets and businesses can be encouraged to adopt cleaner and more efficient vehicles through various initiatives. Governments can offer incentives for the adoption of electric or low-emission commercial vehicles, such as delivery vans, taxis, and ride-sharing fleets. Additionally, providing support and guidance to businesses transitioning to cleaner technologies, such as electric or hand-powered landscaping equipment, can further reduce emissions from commercial activities.
Air Pollution: Causes and Concerns
You may want to see also