Air pollution particles, also known as particulate matter (PM) or soot, are a mix of tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the air we breathe. These particles vary in size, shape, and chemical composition, with some being so small that they are invisible to the naked eye. While air quality has improved due to cleaner power plants, industrial sites, and vehicles, many people still live with unhealthy levels of particle pollution, which has been linked to various adverse health effects, including respiratory and cardiovascular issues. To combat this, individuals can take measures such as using air filters, limiting outdoor activity on high pollution days, and advocating for clean air programs. Additionally, policies promoting cleaner energy, transport, and industrial practices can significantly reduce particle pollution on a larger scale.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition of particle pollution | Particle pollution, also called "particulate matter" or "soot," is a mix of tiny solid and liquid particles in the air. |
| Composition | Particles vary in size, shape, and chemical composition, and may contain inorganic ions, metallic compounds, elemental carbon, organic compounds, and compounds from the earth's crust. |
| Health Risks | Exposure to fine particulate matter causes cardiovascular and respiratory disease, asthma, acute and chronic bronchitis, and cancers. |
| Global Impact | In 2019, 99% of the world's population lived in places where WHO air quality guidelines were not met. Ambient air pollution was associated with 6.7 million premature deaths annually, with 4.2 million due to outdoor air pollution. |
| Sources of Particles | Particles are formed through mechanical and chemical processes. Sources include vehicle emissions, industrial sites, power plants, construction, agriculture, wildfires, and natural sources such as trees and vegetation. |
| Treatment and Prevention | Policies promoting clean technologies, improved waste management, energy-efficient homes, cleaner transport, and better municipal waste management can reduce air pollution. Individuals can use air filters, limit outdoor activity on high pollution days, and wear respirators or masks. |
What You'll Learn

Reducing emissions at their sources
For industry, clean technologies can significantly reduce emissions from smokestacks. Improved waste management practices, such as capturing methane gas from waste sites instead of incinerating it, can also help reduce particle pollution. Additionally, the use of cleaner technologies and fuels in industrial processes can minimize the release of harmful pollutants.
In the transport sector, a shift towards cleaner modes of power generation is crucial. This includes promoting electric vehicles, low-emissions vehicles, and fuels with reduced sulfur content. Encouraging the use of public transportation, walking, and cycling networks in cities can also help reduce vehicle emissions. Additionally, policies that prioritize rapid urban transit and interurban rail travel can contribute to decreasing emissions from the transport sector.
Power generation is another significant source of air pollution. Increasing the use of renewable and combustion-free power sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, can effectively reduce emissions. At the same time, improving the energy efficiency of buildings and promoting compact and green urban planning can lower the demand for power generation, thereby reducing overall emissions.
Agricultural activities, such as dust storms, construction, demolition, and mining operations, contribute to particle pollution. Implementing measures such as improved land management practices, dust control techniques, and the use of cleaner agricultural machinery can help minimize emissions from these sources.
Overall, reducing emissions at their sources requires a combination of policy interventions, technological advancements, and behavioral changes. By targeting the major sources of air pollution and implementing effective strategies, significant improvements in air quality can be achieved, leading to positive health and environmental outcomes.
US Air Pollution: Time for Tougher Action?
You may want to see also

Reducing exposure to air pollutants
Air pollution is a serious global public health problem that demands collective action to control emissions. While waiting for systemic change, individuals can take measures to reduce their exposure to air pollutants, especially on high-pollution days. Here are some ways to reduce exposure to air pollutants:
Outdoor Air Pollution
On days with high levels of outdoor air pollution, staying indoors, reducing outdoor air infiltration, and limiting physical exertion, especially near sources of air pollution, can reduce personal exposure. Utilizing public air quality alert systems can help individuals stay informed about pollution levels. Additionally, wearing respirators may be effective in certain situations.
Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollutant levels can often be higher than outdoors due to chemicals released from consumer products, gas appliances, building materials, smoking, and furniture. To minimize indoor air pollution, it is recommended to use ventilation with outdoor air and minimize the use of strongly scented products, such as air fresheners. Avoid cleaning products and fragrances with pine or citrus scents, as they can react with ozone to form particles and formaldehyde. Minimize the use of products containing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), found in some non-stick pans and water-repellent treatments. Use high-emitting products, such as paint, outdoors whenever possible, or increase ventilation when using them indoors.
Transportation
Transportation is a significant contributor to outdoor air pollution. To reduce exposure, individuals can opt for cleaner commutes by sharing rides, using public transportation, walking, or cycling. Keeping car engines properly tuned, maintaining proper tire inflation, and avoiding excessive idling can also help. Additionally, consider refuelling during cooler periods, such as in the evening, and following gasoline refuelling instructions to prevent spillage.
Energy and Waste Management
Access to clean household energy solutions, such as affordable alternatives for cooking, heating, and lighting, can significantly reduce ambient air pollution. Individuals can also contribute by conserving electricity and using energy-efficient appliances. Proper waste management strategies, including waste reduction, separation, recycling, and improved biological waste management methods, are crucial in reducing air pollution.
It is important to note that while individual actions can reduce exposure and health risks, effective policies and collective efforts are necessary to address the root causes of air pollution and achieve long-term solutions.
Air Pollution's Impact: Devastating Agricultural Consequences
You may want to see also

Using air filters
Air pollution is a pressing issue, with 99% of the world's population living in places where the WHO air quality guidelines are not met. Airborne particulate matter is a complex mixture of solids and aerosols composed of small droplets of liquid, dry solid fragments, and solid cores with liquid coatings. These particles can induce adverse health effects, especially when inhaled into the lungs.
To combat this, air filters and portable air cleaners can be used to improve indoor air quality and reduce the presence of harmful particles. Here are some key points to consider when using air filters to treat air pollution particles:
Types of Air Filters
There are two main types of air filters used to treat air pollution particles: portable air cleaners and furnace or HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) filters.
Portable Air Cleaners
Portable air cleaners, also known as air purifiers or air sanitizers, are designed to filter the air in a single room or area. They can be effective in reducing indoor air pollution, but it is important to note that they cannot remove all pollutants from the air. When selecting a portable air cleaner, look for one with a high clean air delivery rate (CADR) that is suitable for the size of the room. The higher the CADR, the more particles the air cleaner can filter. Some air cleaners have additional features like multiple filters or UV-based reactions to capture and destroy pollutants.
HVAC Filters
Upgrading the air filter in your furnace or central HVAC system can also help improve indoor air quality. These filters can capture particles from the air that passes through them, including small particles of significant health concern (PM2.5). When choosing an HVAC filter, consider the type of particles you want to filter and the size of the area it needs to cover. Additionally, ensure regular replacement of the filter, as a dirty and overloaded filter will not work effectively.
HEPA Filters
Both portable air cleaners and HVAC filters may use HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, which are particularly effective at capturing small particles. According to the US HEPA standard, a true HEPA filter removes at least 99.97% of airborne particles of 0.3-micron diameter in a single pass. This includes particles that are difficult to intercept, as they are small enough to bypass other filters.
Alternative Filters
While HEPA filters are commonly used, there are alternative options, such as the H14 filters used in some PuroAir models. These filters are marginally more efficient at capturing particles than true HEPA filters, achieving a 99.995% capture rate in lab testing. However, in real-world use, there may be little practical difference between the two types of filters.
In conclusion, using air filters is an effective way to treat air pollution particles, especially when combined with source control and proper ventilation. By selecting the appropriate type of air filter, ensuring regular maintenance, and considering features like HEPA filtration, individuals can improve their indoor air quality and reduce their exposure to harmful particulate matter.
Air Pollution's Deadly Impact: Understanding Emphysema
You may want to see also

Improving waste management
To improve waste management, it is essential to reduce, reuse, and recycle. Individuals can play a significant role by reducing waste generation, reusing items whenever possible, and recycling materials properly. Separating waste correctly and avoiding littering are also important steps in improving waste management.
Companies and governments also have a crucial role in improving waste management practices. Companies can contribute by reducing packaging, designing products for easy recyclability, and supporting regulations for improved waste management. Governments can implement policies to promote better waste management, such as providing access to basic waste management services and ensuring proper protective gear and safety information for waste management workers.
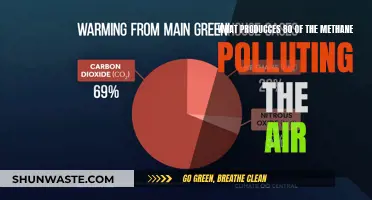
Additionally, waste collection and sorting can be enhanced through simple technologies, such as the Black Soldier Fly facilities, which reduce methane emissions from organic waste. Methane emissions from food and plant waste are largely preventable and should be a key focus area. Open burning of waste, a common practice, should be eliminated, as it releases harmful pollutants like dioxins, furans, and black carbon into the atmosphere.
By addressing these issues and implementing improved waste management practices, we can significantly reduce air pollution and its associated health and environmental impacts.
Creating an Air Purifier: Filtering Out Pollution
You may want to see also

Promoting cleaner transport
One effective strategy is to encourage the use of public transportation, such as buses, trains, and trams, which have lower per capita emission rates compared to private cars. By investing in and improving public transportation systems, cities can make them more efficient, affordable, and attractive to commuters, thereby reducing the number of private vehicles on the road and lowering transport-related pollution.
Developing infrastructure for active mobility options like cycling and walking is another important aspect of promoting cleaner transport. Creating dedicated cycling lanes, pedestrian zones, and safe, convenient pathways encourages individuals to choose these environmentally friendly modes of transport. This not only reduces traffic congestion and pollution but also promotes physical health and well-being.
Transitioning to cleaner fuels and technologies is essential for reducing emissions from traditional transport systems. Governments worldwide are promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and providing incentives for alternative fuels, such as biofuels (e.g., ethanol and biodiesel) and hydrogen, which can replace conventional petrol and diesel in internal combustion engines.
Educational campaigns and public engagement also play a vital role in encouraging the use of cleaner transport options. By raising awareness about the health and environmental risks of transport-related pollution, individuals can be motivated to make behaviour changes that contribute to cleaner air.
Additionally, implementing policies such as London's Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ), which charges older, more polluting vehicles to enter certain areas, can effectively reduce pollution from vehicles and improve air quality in urban environments.
Air Quality Alert: Is Any Air Truly Clean?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Particles that are 10 micrometres or smaller in diameter, known as PM10, can be inhaled into the lungs and cause serious health issues, especially for children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing heart or lung conditions. PM2.5, or particles that are 2.5 micrometres or smaller in diameter, are even more dangerous and are associated with premature mortality, asthma, and other adverse health effects.
There are several ways to minimise exposure to air pollution particles. On high pollution days, stay indoors with the windows closed and use air filters to clean indoor air. Avoid physical exertion, especially outdoors or near pollution sources. Wear an N95 particle mask when outdoors in smoky or dusty conditions. Check air quality levels and forecasts for your area to plan your activities accordingly.
Implementing policies and technologies that reduce industrial emissions, improve waste management, promote cleaner transportation and energy sources, and enhance urban planning can effectively decrease air pollution. Individuals can also contribute by adopting cleaner personal transport options, using environmentally friendly products, reducing waste, and conserving energy.