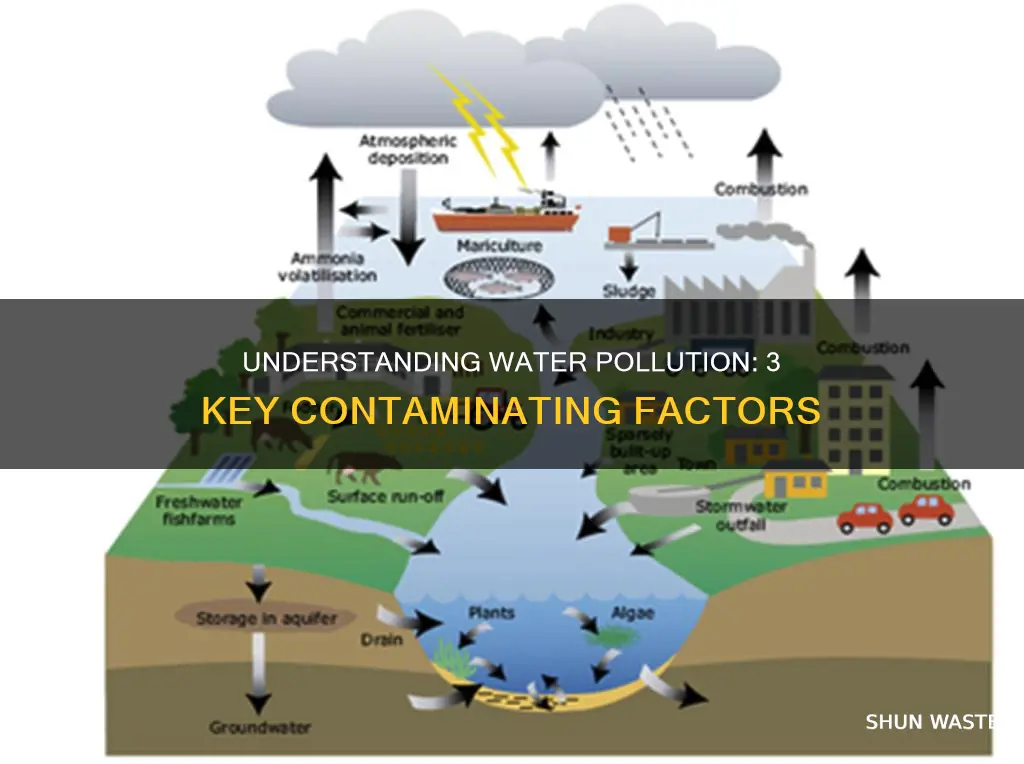
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies such as oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, aquifers and groundwater. It is often caused by human activity, such as the direct release of waste and dangerous by-products into water supplies by factories, waste management facilities, refineries and sewage treatment plants. Farming and fossil fuel power plants can also cause water pollution, as can rising global temperatures caused by CO2 emissions, which heat the water and reduce its oxygen content.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Direct inputs | Factories, sewage treatment plants, waste management facilities, refineries |
| Widespread sources | Nutrients, pesticides, pollutants from industry |
| Point source pollution | Sewage, waste water treatment |
| Diffuse pollution | Farming, fossil fuel power plants |
| Natural causes | Mercury filtering from the Earth's crust |
| Human causes | CO2 emissions, farm waste, fertilizer runoff, industrial waste, chemicals, heavy metals |
What You'll Learn

Human activity, including waste management facilities, factories, and refineries
Human activity is the most common cause of water pollution. Waste management facilities, factories, and refineries are all sources of direct pollution, also known as 'point source pollution'. These facilities release waste and dangerous by-products into the closest water supply without treating them. This includes contaminants such as chemicals, nutrients, and heavy metals.
Wastewater treatment plants are the main point source of water pollution. These plants release sewage and wastewater into water sources, which can carry bacteria and viruses that cause diseases such as typhoid, cholera, and giardia.
Factories are another major source of water pollution. They release a variety of contaminants into water sources, including chemicals, nutrients, and heavy metals. These contaminants can be carried by streams and rivers into bays and estuaries and eventually out to sea.
Refineries are also a source of water pollution, as they release dangerous by-products into water supplies. These by-products can include a range of pollutants, such as chemicals and heavy metals.
In addition to these direct sources of pollution, human activity also contributes to so-called "diffuse pollution". This type of pollution comes from widespread sources, such as nutrients and pesticides from farming activities and pollutants released by industry into the air, which then fall back to land and sea. Farming is the main source of diffuse pollution, with fossil fuel power plants also contributing significantly.
How Poor Air Quality Impacts Your Health
You may want to see also

Farming and fossil fuel power plants
Fossil fuel power plants, on the other hand, release pollutants into the air, which then fall back to land and water, a process known as "diffuse pollution". This type of pollution can impact water quality in rivers, lakes, and seas, as well as groundwater.
In addition to the direct release of pollutants, farming and fossil fuel power plants can also contribute to water pollution through their impact on the environment. For example, rising global temperatures caused by CO2 emissions can heat water, reducing its oxygen content. This, in turn, can create favourable conditions for the growth of harmful bacteria and viruses, which can contaminate water sources and pose risks to human health.
Furthermore, the use of pesticides and fertilisers in farming can have indirect effects on water quality. When these chemicals are released into the environment, they can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, impacting the relationships between species and potentially leading to the decline or extinction of certain organisms. This, in turn, can affect the quality and safety of water sources, as a healthy ecosystem is crucial for maintaining water purity.
To mitigate the impact of farming and fossil fuel power plants on water pollution, it is essential to implement sustainable practices and regulations. This may include improving waste management systems, reducing the use of harmful chemicals, and transitioning to cleaner energy sources. By addressing these issues, we can help protect water sources and ensure their safety for human and animal consumption, as well as preserve the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Soil Pollution: Groundwater's Unseen Danger?
You may want to see also

Sewage and wastewater treatment
Wastewater can also contain outside substances, such as pollutants, which can disrupt the relationships between species in an ecosystem. These pollutants can include fertilisers, pesticides, pharmaceutical products, nitrates, phosphates, plastics, and faecal waste.
Fertilisers and pesticides can enter water sources through farm waste and fertiliser runoff. Eighty per cent of ocean pollution originates on land, with contaminants such as chemicals, nutrients and heavy metals carried from farms, factories and cities by streams and rivers into bays and estuaries, and then out to sea.
Water pollution can also be caused by rising global temperatures, which heat the water and reduce its oxygen content.
Breathing at 500 AQI – Deadly or Not?
You may want to see also

Industrial waste
One of the main concerns with industrial waste is its impact on freshwater sources, which are essential for human and animal consumption. As industrial waste discharges toxins and pollutants into rivers and lakes, it can lead to the contamination of potable water. This can have severe consequences for communities that rely on these water sources for their daily needs.
Furthermore, industrial waste can contribute to nutrient pollution, which includes nitrates and phosphates. While these nutrients are essential for plant and animal growth, they can become pollutants when present in excessive amounts due to farm waste and fertilizer runoff. This type of pollution can lead to excessive algae growth, reducing oxygen levels in the water and creating "dead zones" where aquatic life cannot survive.
To address the issue of industrial waste polluting water sources, it is crucial to implement proper waste management practices. This includes treating industrial waste before releasing it into water bodies and ensuring that harmful substances are removed or reduced to safe levels. By adopting sustainable practices and responsible waste management, we can mitigate the impact of industrial activities on water quality and protect our precious water resources.
How Pollution is Killing Plant Life
You may want to see also

Natural causes, such as mercury filtering from the Earth's crust
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies, such as oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, aquifers and groundwater. While water pollution is often caused by human activity, there are also natural causes, such as mercury filtering from the Earth's crust.
Mercury is a naturally-occurring element that can be found in the Earth's crust. Over time, it can filter into water sources, including oceans, rivers, lakes, canals and reservoirs. This can be harmful to humans and animals, as mercury is a toxic substance that can cause damage to the brain, nervous system and kidneys. It can also accumulate in the bodies of fish and other aquatic organisms, which can then be passed on to humans through the food chain.
Natural causes of water pollution can also include bacteria, viruses and parasites. These can be found in human and animal waste, which can contaminate water supplies and cause the spread of diseases such as typhoid, cholera and giardia. Outside substances, such as pollutants found in wastewater, can also disrupt the relationships between species in an ecosystem, which can have a detrimental effect on the environment.
Another natural cause of water pollution is nutrient pollution, which includes nitrates and phosphates. While plants and animals need these nutrients to grow, they can become pollutants when they are present in high concentrations due to farm waste and fertiliser runoff. This can lead to an overgrowth of algae and other aquatic plants, which can deplete the oxygen levels in the water and create "dead zones" where other organisms cannot survive.
In addition to mercury, other heavy metals can also be natural pollutants of water sources. These metals can be released from rocks and minerals in the Earth's crust through processes such as weathering and erosion. They can then be carried by streams and rivers into larger water bodies, where they can accumulate and have toxic effects on aquatic life.
Preventing Chemical Water Pollution: Strategies for a Cleaner Future
You may want to see also



















