
Noise pollution is any undesirable sound that causes discomfort to the ears and negatively impacts our health and quality of life. It can lead to hearing loss, sleep disturbances, increased stress levels, cardiovascular issues, cognitive impairment, and aggressive behaviour. To reduce noise pollution, we can implement various strategies such as upgrading insulation with soundproofing materials, using noise-cancelling headphones or earplugs, and placing furniture strategically to absorb sound. Additionally, we can advocate for stricter noise regulations, improved urban planning, and better product design to minimise noise pollution in our communities.
What You'll Learn

Soundproof your space
Soundproofing your space can be an effective long-term solution to noise pollution. Here are some ways to soundproof your space:
Acoustic Testing
Before implementing soundproofing measures, it is advisable to conduct acoustic or sound insulation testing to identify the areas of sound transfer. There are two types of sound tests: impact tests, which assess noise levels on separating ceilings and floor divides, and airborne tests, which measure sound reverberation through party walls and floors.
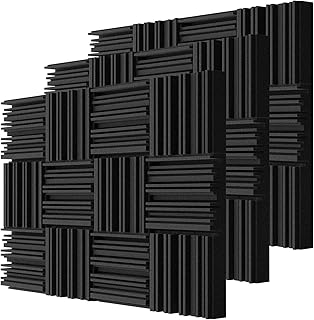
Acoustic Wall Panels
Acoustic wall panels are a great way to reduce noise levels in your property. There are various options available on the market, and they can dramatically lessen the amount of noise in your home or office.
Carpets and Rugs
Carpets and rugs can effectively reduce noise pollution, especially on hard floors. Carpets can decrease noise by up to 34 decibels, compared to laminate or wooden flooring, which only reduces sound by up to 6 decibels. Additionally, carpets help to reduce reverberation time, creating a quieter indoor environment.
Noise-Cancelling Headphones and Earplugs
While not a permanent solution, noise-cancelling headphones and earplugs can be a short-term remedy for construction or street noise, allowing you to get a good night's sleep.
Wall Coverings
If you have large empty walls, consider hanging wall coverings such as blankets or canvas paintings. These can help absorb sound and reduce echo, minimizing the impact of noise pollution.
Window Shutters
High-quality window shutters can be a long-term solution to outdoor noise by creating a barrier between external noises and your windows.
Strategic Furniture Placement
Strategic placement of furniture can help reduce noise pollution. For example, placing large bookshelves or drawers along adjoining walls can help absorb sound and create a quieter atmosphere. Additionally, keeping noisy electrical appliances away from bedrooms can improve sleep quality and provide a more peaceful environment.
Fencing
Installing fencing can help reduce unwanted sounds due to their barrier properties. Fences interrupt sound waves and vibrations as they pass through the air, lessening the impact of noise pollution.
Doors
Solid wood doors are recommended for tackling noise pollution. Ineffective doors that cannot block out unwanted sounds can easily be replaced to create a quieter indoor space.
Windows
Simply closing windows can be an effective way to reduce outdoor noise, especially if your property has double or triple glazing. Additionally, consider installing dual-paned windows, which can significantly reduce noise levels, improve energy efficiency, and reduce heating and cooling bills.
Trees and Greenery
Planting trees and bushes around your property can help reduce noise levels, especially in urban areas near busy roads. Greenery acts as a natural sound buffer and also improves air quality.

Upgrade your insulation
Upgrading your insulation is an effective long-term solution to noise pollution. Soundproofing your space can help to create a quieter and more peaceful environment, improving your quality of life.
Insulation acts as a barrier to sound waves, absorbing or reflecting them and preventing them from travelling further. This is particularly useful for blocking high-frequency sounds. There are several types of insulation that can be used to reduce noise pollution, each with its own unique properties and applications.
Absorption
Fibreglass, cellulose, or foam insulation materials can absorb sound waves by converting them into heat energy, thus reducing their intensity. Fibreglass batts, for example, have a spongey design that absorbs sound waves and diminishes their power. This type of insulation is also one of the most affordable and commonly used options.
Damping
Insulation materials such as mass-loaded vinyl or rubber can dampen sound waves by dissipating their energy and reducing their amplitude, preventing them from travelling further and causing a disturbance.
Blocking
High-density or thick insulation materials such as concrete, brick, or gypsum board create a physical barrier that blocks sound waves from passing through. These materials are excellent at preventing sound from entering or leaving a space, maintaining privacy and confidentiality.
Reflection
Insulation materials with smooth surfaces, such as metal or glass, reflect sound waves back to their source. This prevents sound from entering or exiting a space and is particularly useful for managing high-frequency sounds.
When upgrading your insulation, it is important to consider the type and density of the materials used, their placement and thickness, and the frequency and intensity of the sound you want to address. For example, fibreglass and mineral wool are good at absorbing high-frequency sounds but have limited blocking capabilities. On the other hand, concrete or brick offer excellent blocking but have limited absorption properties.
Additionally, the placement of insulation is critical to its performance. Insulation installed in walls or floors can effectively reduce airborne noise, while ceiling insulation is ideal for reducing impact noise from upstairs neighbours or mechanical equipment. Thicker or denser materials generally provide better noise reduction, but cost or space limitations may need to be considered.
Upgrading your insulation is a great way to create a quieter and more peaceful environment, reducing the negative impacts of noise pollution on your health and well-being.

Use noise-cancelling headphones
Noise-cancelling headphones are a popular solution to noise pollution, but they are not suitable for everyone. Active noise cancellation can cause discomfort for some people, with symptoms including eardrum pain, headaches, dizziness, and nausea. The more powerful the noise cancellation, the more intense these symptoms may become. This discomfort is likely due to the way some people's brains process the sudden and uneven change in sound when active noise cancellation is turned on.
However, for those who do not experience these negative side effects, noise-cancelling headphones can be an effective way to reduce noise pollution, especially in very noisy environments. They work by emitting an anti-noise signal to contrast the external sounds, allowing you to hear music or other audio at a moderate level without having to increase the volume to unsafe levels.
If you are considering purchasing noise-cancelling headphones, it is important to first understand how noise-cancelling technology works and what side effects may occur. Try to test out different models, if possible, to see if you experience any discomfort. Some people may find that adjustable active noise cancellation or milder forms of noise cancellation are better tolerated. Additionally, noise-cancelling earbuds tend to cause fewer issues than over-ear headphones.
It is also important to remember that noise-cancelling headphones are most effective at reducing lower-frequency sounds, such as those produced by jet engines or motors. They are less effective at blocking out higher-frequency sounds, such as human voices or barking dogs. In these cases, passive noise-isolating headphones or earbuds may be a better option.
Overall, while noise-cancelling headphones can be a useful tool for reducing noise pollution, it is crucial to consider potential side effects and the types of noise you are trying to block out to determine if they are the right choice for you.

Plant trees and vegetation
Trees and vegetation are a natural solution to noise pollution, acting as "natural noise blockers". They can reduce noise levels by up to 50% and are particularly effective in urban areas.
Trees and plants achieve noise reduction through a phenomenon called sound attenuation, which is the damping of sound. Sound attenuation occurs when sound waves dissipate over longer distances until there is no energy left to vibrate the air. Trees and plants attenuate noise through four mechanisms: absorption, deflection, refraction, and masking.
Firstly, trees and plants absorb sound waves. The thicker and rougher the bark, and the fleshier the leaves, the better they are at sound absorption. The dynamic surface area of these parts of the plant contributes to their sound-absorbing capabilities.
Secondly, when sound waves hit massive tree trunks, they are deflected or reflected off the trunks and back towards the source. This is because the trunks are rigid and do not vibrate. In contrast, when sound hits flexible surfaces like leaves, they vibrate and transform sound waves into other forms of energy. This can cause interference in sound waves, leading to a reduction in noise.
Thirdly, sound refraction occurs when sound waves change direction as they pass through different mediums. For example, ground-covering plants, vines on walls, and green walls can help to dissipate sound waves and dampen noise, similar to how carpets and curtains reduce echoes in a room.
Lastly, trees and plants can mask annoying noises. The rustling of leaves, the creaking of stems, and the swaying of branches create sounds that are more pleasant to the human ear. Additionally, trees and shrubs attract birds and squirrels, whose chirping and squeaking help mask noise pollution.
The effectiveness of trees and vegetation as noise barriers depends on several factors, including the intensity, frequency, and direction of the sound, as well as the location, height, width, and density of the vegetation. According to the USDA, a 100-foot-wide planted buffer can reduce noise by 5 to 8 decibels (dBA). The width of the vegetation barrier and its distance from the source of noise are crucial factors in its noise-blocking effectiveness.
Evergreen trees, such as Southern Magnolia, Leyland Cypress, Pittosporum, Abies, and Arborvitae, are excellent choices for noise reduction as they are dense, grow quickly, and provide year-round noise filtration.

Turn off electrical appliances
Turning off electrical appliances is an effective way to reduce noise pollution in your home. While some electrical items might produce only a barely audible noise, others can be quite high-pitched. Turning them off will help you create a quieter home.
Electrical appliances such as TVs, computers, games, and other similar items can create unnecessary stress on your ears. Turning them off when not in use will not only reduce noise pollution but also save electricity.
It is recommended to keep noisy electrical appliances, such as tumble dryers, air conditioning units, and washing machines, as far away as possible from bedrooms. This will help improve the quality of your sleep and create a more peaceful atmosphere in your home.
In addition to turning off electrical appliances, you can also shut the door when using noisy machines. For example, you can close the door to the room where your dishwasher or washing machine is located, or you can turn them on before leaving the house to reduce your exposure to loud noises.
By taking these simple steps, you can effectively reduce noise pollution in your home, improve your quality of life, and protect your physical and mental health from the negative effects of unwanted noise.
Frequently asked questions
There are several ways to reduce noise pollution in your home, including:
- Turning off electrical appliances when not in use.
- Closing windows to keep out external noise.
- Using rugs and carpets to absorb sound.
- Investing in noise-cancelling headphones or earplugs.
- Upgrading your insulation with soundproofing materials.
- Installing acoustic wall panels.
- Placing furniture strategically to absorb sound.
To reduce noise pollution in your community, you can:
- Advocate for stricter noise regulations and their enforcement.
- Support the use of electric vehicles to reduce traffic noise.
- Promote community education and awareness about noise pollution.
- Plant trees and create green spaces to act as natural sound buffers.
- Encourage the use of noise-reducing technologies and appliances.
Noise pollution can have several negative impacts on your health, including:
- Increased stress levels and impaired cognitive functioning.
- Sleep disturbances, leading to fatigue and reduced concentration.
- Hearing damage from prolonged exposure to loud noises.
- Cardiovascular issues, including increased blood pressure and heart rate.
- Aggressive behaviour and negative psychological impacts.












![Acoustic Panels 12-Pack Soundproof Wall Panels 12"X10.4"X0.4" Sound Panels High Density Sound Dampening Panels - [Light Turquoise Hexagon]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/91eSZ1vF1dL._AC_UL320_.jpg)





