Water and air pollution are pressing issues that have detrimental effects on human health, the environment, and the economy. Water pollution occurs when harmful microorganisms and chemical substances contaminate bodies of water, decreasing water quality and potentially making it toxic. Sources of water pollution include oil spills, agricultural runoff, sewage, and industrial waste. Air pollution, on the other hand, refers to the contamination of the atmosphere by harmful gases and solid or liquid particles, which can come from vehicle exhaust, factories, wildfires, and the combustion of fossil fuels. Both types of pollution have severe consequences and contribute to significant health risks, including respiratory issues, heart diseases, and cancers.
How does water and air pollution occur?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Air pollution | Contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere |
| Sources of air pollution | Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities, forest fires, residential energy for cooking and heating, power generation, agriculture/waste incineration |
| Health impact of air pollution | Respiratory and other diseases, strokes, heart diseases, lung cancer, acute and chronic respiratory diseases, asthma attacks, cancer, heart attacks, developmental problems for children, dementia |
| Water pollution | Harmful microorganisms and chemical substances contaminate bodies of water, causing the water quality to decrease and potentially making it toxic |
| Sources of water pollution | Sewage, stormwater runoff, chemicals, waste, plastic, oil spills, leaks from oil drilling operations or ships, nuclear energy waste, coal and gas industries, agricultural runoff, global warming, saltwater intrusion |
What You'll Learn

Oil spills and leaks
The release of oil into coastal waterways and oceans is a significant problem, impacting the environment, people, communities, and industries that depend on a clean marine environment for survival, commerce, and recreation. Oil spills can contaminate beaches, sediments, and water, causing serious harm to marine wildlife. Oil penetrates the structure of the plumage of birds and the fur of mammals, reducing its insulating and waterproofing abilities, making them more vulnerable to temperature changes and less buoyant in the water. Ingesting oil can be toxic to birds and marine mammals, and it can also cause liver and immune system damage in humans.
Oil spills can block light from reaching photosynthetic plants in the water, and they reduce the level of dissolved oxygen in the water, which is harmful to aquatic life. Oil spills can also contaminate seafood, making it unsafe to eat. Oil spills on land can be washed down storm drains, including spills in fuel depots, oil leaks from vehicles, and non-accidental pouring of oil or paint. Oil spills on land can also reach the oceans through runoff from roads during rainstorms or via rivers.
Cleanup and recovery from an oil spill are challenging and can take weeks, months, or even years. While various methods exist to contain and remove oil, such as using floating booms, skimming, and sorbents, no entirely satisfactory method has been developed for cleaning up major oil spills. Additionally, cleanup activities must be carefully executed to avoid causing further harm. Oil spills can have long-lasting impacts, and even with restoration projects, the affected ecosystems may not fully recover.
To address oil spills, the United Nations treaty known as the Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) came into effect in 1983. MARPOL requires tankers and ships to use oil-pollution prevention equipment, such as double hulls, reliable navigation, and communication equipment. This has led to a significant reduction in oil spills, with individual tank sizes limited to minimize the damage caused by leaks.
Natural Gas Extraction: Water Pollution's Unseen Threat
You may want to see also

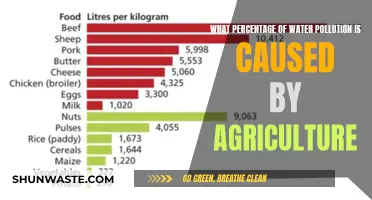
Agricultural runoff
The impact of agricultural runoff varies depending on factors such as the type of farming operation, landscape conditions, soils, climate, and farm management practices. However, some common consequences include increased levels of nitrogen and phosphorus, which can stimulate harmful algal blooms, leading to hypoxic conditions that are detrimental to aquatic life and recreational activities. Excessive sedimentation from erosion can smother breeding areas and degrade coastal and marine ecosystems, including coral reefs.
Bacteria and nutrients from livestock and poultry manure can contaminate drinking water supplies and cause beach and shellfish bed closures. Pesticide runoff poses risks to aquatic life, fish-eating wildlife, and drinking water sources. Additionally, manure management is a significant contributor to air pollution, emitting ammonia that combines with other air pollutants to form harmful solid particles, leading to respiratory and cardiovascular health issues.
To address these issues, organizations like the US EPA and state agencies have developed initiatives such as the National Water Quality Initiative (NWQI) and the Clean Water Guidance. These programs provide recommendations and best management practices to farmers and landowners, helping them minimize water quality impacts and meet clean water standards.
The effects of agricultural runoff are widespread and have significant ecological, economic, and public health implications. By implementing sustainable practices and following guidelines, the agricultural community can play a crucial role in mitigating these impacts and ensuring clean water for future generations.
Water Pollution: Sources and Impacts on Our Resources
You may want to see also

Poor waste disposal
The improper disposal of solid waste, including garbage, rubbish, electronic waste, trash, and construction and demolition debris, is a major source of water pollution. When these wastes are not properly managed, they can find their way into oceans and other bodies of water. As it breaks down in the water, it releases toxins, choking aquatic life and raising the toxicity of the water, making it unsafe for human consumption and swimming. This contaminated water can also serve as a breeding ground for disease-causing organisms that affect animals, plants, and people.
In addition to water pollution, poor waste disposal contributes to air pollution. When waste is disposed of through open dumping and burning, it releases harmful substances into the air, causing respiratory issues and worsening existing health problems. This mismanagement of waste, including the unsafe handling of radioactive waste, can lead to radiation poisoning in nearby areas.
Furthermore, waste disposal contributes to global climate change. Greenhouse gases emitted through waste disposal thicken the ozone layer, leading to extreme weather events, melting ice caps, and rising sea levels. The impact of climate change on habitats also affects the survival of various animal species.
To address these issues, it is essential to promote proper waste management practices, such as recycling, composting, and safe treatment of waste. By improving waste management plans and preventing waste from ending up in places that pollute the air and water, we can protect both human health and the environment.
Polluted Water: Deprived of Oxygen?
You may want to see also

Fossil fuel combustion
The health impacts of fossil fuel combustion disproportionately affect certain communities, with children, the poor, and minorities bearing a heavier burden. Children are more susceptible to the harmful effects due to their higher air and food intake per kilogram of body weight compared to adults. Globally, it is estimated that more than 40% of environmentally-related diseases and over 88% of the impacts of climate change are shouldered by children under five, despite this age group making up only 10% of the global population. The combustion of fossil fuels also has significant environmental justice implications, as the health and economic costs disproportionately affect developing countries and vulnerable communities.
In addition to air pollution, fossil fuel combustion also contributes to water pollution. Oil spills, for example, can have devastating impacts on aquatic ecosystems, contaminating water sources and harming marine life. Furthermore, the fracking process used to extract fossil fuels requires a significant amount of water, and the resulting wastewater can be toxic, containing substances like arsenic, lead, chlorine, and mercury, which further contaminate groundwater and drinking water sources. Power plants that burn fossil fuels also affect water ecosystems by withdrawing freshwater from local sources for cooling, and the subsequent release of warmer water can cause stress for local species.
The combustion of fossil fuels has far-reaching consequences, impacting both the environment and human health. It is a significant contributor to global warming, with coal, oil, and natural gas being the main types of fossil fuels in use. The burning of these fuels releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, which has led to an average global temperature increase of 1°C, with more severe temperature rises in certain regions. This, in turn, has resulted in melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and more frequent and severe extreme weather events, including wildfires, hurricanes, wind storms, flooding, and droughts.
To mitigate the impacts of fossil fuel combustion, it is essential to transition to renewable energy sources and improve energy efficiency. Leading businesses are taking steps to manage their greenhouse gas emissions and set targets for reduction. Additionally, individuals can play a role by conserving energy, reducing their driving miles, and opting for more energy-efficient equipment and transportation options. By addressing fossil fuel combustion and its associated pollution, we can work towards a more sustainable and equitable future for all, especially for the most vulnerable members of our global community.
Water-Soluble Pollutants: A Complex Environmental Challenge
You may want to see also

Industrial facilities
Water Pollution from Industrial Facilities
Water pollution from industrial facilities has intensified since the Industrial Revolution, when factories began releasing pollutants directly into rivers and streams. Today, industrial waste continues to be dumped into water sources, with up to 500 million tons of heavy metals, solvents, and toxic sludge entering the global water supply annually. This includes chemicals, waste, plastics, and other pollutants that contaminate our rivers, reservoirs, lakes, and seas.
In developing countries, the situation is even more dire, with up to 70% of industrial waste being dumped untreated into water sources. This has severe consequences for human health, as unsafe water can cause illnesses such as cholera, giardia, and typhoid. It is estimated that contaminated water caused 1.8 million deaths in 2015, and every year, unsafe water sickens about 1 billion people.
Air Pollution from Industrial Facilities
The burning of fossil fuels and industrial processes are major contributors to air pollution, releasing large amounts of organic compounds, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and chemicals into the atmosphere. The release of human-produced sulfur and nitrogen compounds, for example, can negatively impact plants, fish, soil, forests, and even building materials.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the impacts of industrial pollution, it is essential to implement waste treatment strategies that aim to eliminate priority pollutants at their source. This can be achieved by utilizing indigenous microorganisms found in industrial effluents to resist, process, metabolize, and detoxify pollutants. Additionally, investing in new ambient air pollution control technologies can help reduce air pollution levels and protect the health of residents in industrial areas.
Water Pollution: Our Actions, Our Responsibility
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Air pollution is caused by solid and liquid particles, gases, and certain chemicals that are suspended in the air. These particles and gases can come from car and truck exhaust, factories, dust, pollen, mould spores, volcanoes, and wildfires.
Water pollution occurs when harmful microorganisms and chemical substances contaminate bodies of water, decreasing the water quality and potentially making it toxic. Sources of water pollution include chemicals, waste, plastic, and other pollutants.
The major sources of outdoor air pollution include residential energy for cooking and heating, vehicles, power generation, agriculture/waste incineration, and industry.
Air pollution has been linked to various health issues such as respiratory problems, heart diseases, lung cancer, strokes, and other respiratory diseases. It can also aggravate existing breathing conditions and increase the risk of asthma attacks, leading to more hospital admissions.