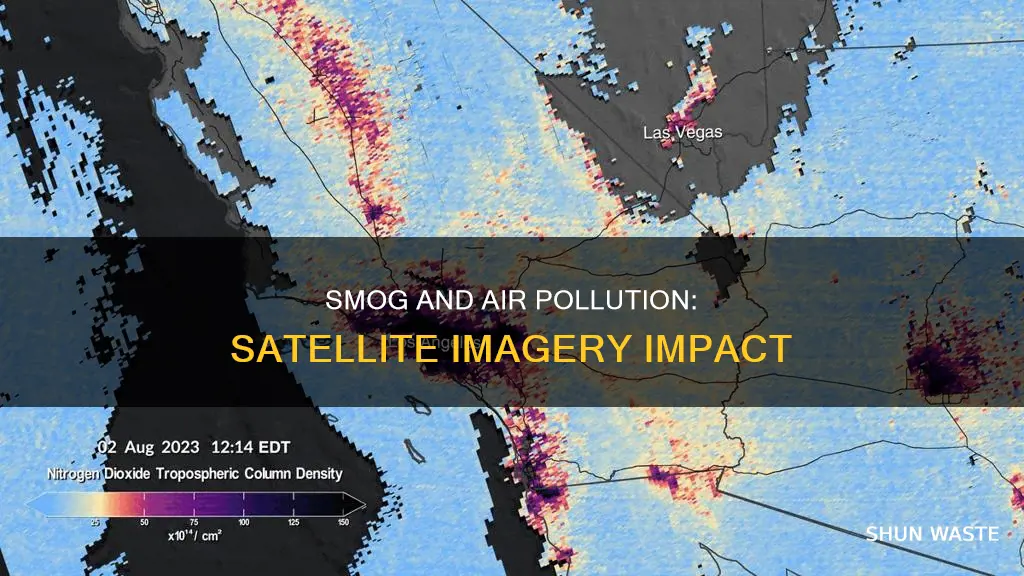
Satellite imagery has become an invaluable tool for monitoring air quality and pollution. The technology allows researchers to measure the concentration of pollutants in the atmosphere and track their movement over large areas. Recent satellite imagery released by NASA, for example, exposed the alarming spread of toxic smoke over Delhi, leading to a deterioration in air quality. Similarly, in Lahore, Pakistan, toxic smog was visible from space, with pollution levels reaching record-breaking numbers. The use of satellite imagery to monitor air quality and pollution levels is especially beneficial in areas where ground-based monitoring is not feasible or cost-prohibitive. Despite some challenges, such as the resolution and accuracy of the imagery, satellite technology is becoming increasingly important for monitoring air quality and pollution levels around the world.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Use of satellite imagery | Monitoring air quality and pollution levels |
| Benefits of satellite imagery | Cost savings, greater coverage, timely data |
| Advantages of satellite imagery | Avoidance of ground-based monitoring systems, more comprehensive monitoring |
| Drawbacks of satellite imagery | Resolution, cost of analysis, accuracy, interpretation |
| Impact of satellite imagery | Revolutionized air quality and pollution monitoring policies |
What You'll Learn
- The impact of smog and air pollution on satellite imagery accuracy
- The economic benefits of using satellite imagery to monitor air quality
- How satellite imagery can be used to identify sources of air pollution?
- The challenges of using satellite imagery to monitor air quality
- How satellite imagery is helping to inform policy decisions?

The impact of smog and air pollution on satellite imagery accuracy
Satellite imagery is a powerful tool for monitoring air quality and pollution levels, offering a broad overview of large areas and tracking the movement of pollutants. However, the accuracy of these images can be impacted by smog and air pollution, which can reduce visibility and affect the data collected.
The benefits of satellite imagery
Satellite imagery has revolutionized air quality and pollution monitoring by providing a comprehensive view of large areas. This technology offers greater coverage than ground-based monitoring systems, allowing for the detection of pollution in remote or inaccessible regions. For example, satellite imagery has been used to track dust storms, wildfire smoke, and agricultural pollution from sugar beet farms in France. It is also useful for monitoring areas prone to rapid changes in pollution levels, as it can collect data quickly and in real time.
The challenges of smog and air pollution
While satellite imagery is a valuable tool, smog and air pollution can impact its accuracy. Thick smog and haze, such as that caused by industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural burning, can reduce visibility and make it difficult to obtain clear images. This was evident in satellite images of Lahore, Pakistan, which showed a dense grey smog blanket caused by record-breaking pollution levels.
Impact on data collection
The presence of smog and air pollution can affect the data collected by satellites. One challenge is that satellites must look through the entire column of air underneath them to measure air pollution, making it difficult to estimate pollution levels in the lowest few meters where people live. Additionally, satellites rely on reflected sunlight, so they can only make measurements during the daytime, and clouds can obstruct their view.
Addressing the challenges
Despite the challenges posed by smog and air pollution, advancements in satellite technology have improved the accuracy of imagery. High-resolution imagery can now detect small-scale features, such as smoke plumes from fires, and measure pollutant concentrations in the atmosphere. This improved accuracy helps identify sources of air pollution, such as factories and power plants, and track their impact on air quality.
While smog and air pollution can impact the accuracy of satellite imagery by reducing visibility and affecting data collection, advancements in technology have helped address these challenges. Satellite imagery remains a valuable tool for monitoring air quality and pollution levels, providing a broad overview of large areas and tracking pollutant movement.
Pollution's Impact on Estuaries: A Delicate Balance Disrupted
You may want to see also

The economic benefits of using satellite imagery to monitor air quality
Satellite imagery has been used to monitor air quality in several parts of the world, including India, Pakistan, and Ghana. This technology has proven to be a cost-effective solution for monitoring air pollution and has helped raise alarms about hazardous air quality in heavily populated cities.
Cost Savings for Developing Countries:
Satellite imagery provides developing countries with a cost-effective way to monitor air quality and obtain critical data. For example, collecting household survey data to monitor socioeconomic targets over the lifetime of the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) could cost up to USD 253 billion. In contrast, Earth Observation (EO) satellite programs like Landsat by NASA and Sentinel by ESA offer free access to high-resolution images and updated information. This enables developing countries to save significant time and money while still extracting valuable insights.
Improved Public Health Outcomes:
By monitoring air quality with satellite imagery, governments can identify areas with hazardous levels of air pollution and take timely action to mitigate its health impacts. This is especially important for vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and those with respiratory conditions. By reducing the incidence of respiratory and other health issues related to air pollution, countries can reduce healthcare costs and improve the overall health of their citizens.
Informing Policy Decisions:
Satellite imagery provides valuable data that can inform policy decisions related to air quality management, urban planning, and environmental protection. For example, India's National Satellite Imagery provides data on the impact of industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural burning on air quality. This data can inform policies to reduce pollution, such as regulating emissions, promoting cleaner technologies, or implementing traffic management measures.
Disaster Management and Resource Allocation:
Satellite imagery can help predict and manage natural disasters such as floods, volcanic eruptions, wildfires, and cyclones. By providing real-time data on environmental changes, governments can allocate resources more efficiently and effectively to areas that need it the most. This proactive approach can help reduce the economic impact of disasters and improve emergency response capabilities.
Monitoring Economic Activity:
Satellite observations, combined with machine learning techniques, can provide daily snapshots of economic activity by tracking indicators such as greenhouse gas emissions. This is especially useful for monitoring economic slowdowns and recoveries, as demonstrated during the COVID-19 outbreak. By analyzing changes in emissions from cities, industrial facilities, and agricultural areas, governments and economic policymakers can make more informed decisions to support economic growth and environmental sustainability.
In conclusion, using satellite imagery to monitor air quality offers a range of economic benefits, including cost savings, improved public health, informed policy decisions, enhanced disaster management, and more effective monitoring of economic activity. By leveraging this technology, countries can make more data-driven decisions to improve the well-being of their citizens and the environment.
Wind Energy: Reducing Noise Pollution?
You may want to see also

How satellite imagery can be used to identify sources of air pollution
Satellite imagery has become an invaluable tool for identifying sources of air pollution and assessing its impact on the environment. Here are some ways in which satellite imagery can be used to identify sources of air pollution:
Visualising Air Pollution
Satellite imagery can capture visual evidence of air pollution, such as smog, and help identify its sources. For example, NASA's satellite imagery exposed the spread of toxic smog in Delhi, India, and Lahore, Pakistan, which was caused by industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural burning. This visual evidence raises awareness and prompts authorities to take action, such as implementing restrictions and closures to protect public health.
Tracking Pollutants
Satellite technology can track and monitor various air pollutants, including greenhouse gases, methane, carbon dioxide, and fine particulate matter (PM2.5). By collecting data over time, satellites can identify specific sources of pollution, such as landfills, dairy farms, leaking pipelines, and power plants. This information can then be used to develop targeted strategies to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
Environmental Impact Assessments
Satellite imaging plays a crucial role in environmental impact assessments (EIAs) by providing a comprehensive overview of project areas and their surrounding environments. This detailed view helps assessors identify existing infrastructure, vegetation, or other features that may be impacted by proposed projects. Additionally, satellite imaging allows for the monitoring of project sites over time, ensuring that any changes or impacts on the local environment are addressed.
Identifying Pollution Hotspots
Satellite imagery can be used to identify areas with high levels of air pollution, or "pollution hotspots." By analysing the data collected, scientists and policymakers can pinpoint specific regions or facilities that contribute significantly to air pollution. This information is crucial for developing effective policies and interventions to mitigate pollution and protect vulnerable communities.
Monitoring Climate Change Effects
In addition to identifying sources of air pollution, satellite imagery is invaluable for monitoring the effects of climate change. It can track changes in sea levels, glacier retreat, desertification, and other environmental indicators. This data informs decisions and strategies to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change, ensuring a more sustainable future.
Air Pollution's Human Cost: Factory Emissions' Impact
You may want to see also

The challenges of using satellite imagery to monitor air quality
While satellite imagery has revolutionized the way air quality and pollution are monitored, there are some challenges and limitations to this technology. One key challenge is the resolution of the imagery. Satellite images can provide a broad overview of an area but often lack the detail needed to accurately measure air quality and pollution levels. This can be a problem when trying to identify specific sources of pollution or assess the impact on a local scale.
Another challenge is the cost of obtaining and analyzing satellite imagery. While the images themselves may be free or low-cost, the specialized software and expertise required to interpret them can be expensive. This can be a barrier, especially for smaller organizations or those in less economically developed regions.
Additionally, the accuracy of satellite imagery can be impacted by various factors, including weather conditions and cloud cover. The presence of clouds, for instance, can obstruct the satellite's view and make it difficult to collect data. Similarly, the satellite's ability to accurately estimate pollution levels in the lower atmosphere, where people live, is limited because it has to look through the entire column of air underneath it.
Moreover, satellite imagery can be complex and difficult to interpret, requiring specialized knowledge and training. The data collected by satellites needs to be carefully analyzed and interpreted to derive meaningful insights about air quality and pollution levels. This complexity can make it challenging for those without the necessary expertise to make sense of the information.
Despite these challenges, satellite imagery remains a valuable tool for monitoring air quality and pollution. It offers a cost-effective way to monitor large areas and can provide timely data, making it particularly useful for tracking rapid changes in pollution levels. By understanding the limitations of satellite imagery and combining it with other data sources, we can effectively utilize this technology to address air quality issues and protect the health of people and the environment.
Air Pollution's Impact: Goods and Services Endangered
You may want to see also

How satellite imagery is helping to inform policy decisions
Satellite imagery has become an invaluable tool for monitoring air quality and pollution, and is helping to inform policy decisions in a number of ways.
Firstly, satellite imagery offers a cost-effective method of monitoring air quality and pollution levels over a large area. By using satellites, organisations can avoid the need to deploy and maintain ground-based monitoring systems, which can be costly and may not be feasible in certain areas. This makes it possible to monitor air quality in remote or inaccessible regions, providing a more comprehensive picture of pollution levels.
The data provided by satellite imagery is also highly timely. Satellites can collect data quickly and in real time, making it easier to track rapid changes in pollution levels. This is particularly useful for monitoring areas prone to fluctuating pollution levels, ensuring that policy decisions are based on up-to-date information.
Another benefit of satellite imagery is its ability to identify sources of air pollution. By detecting smoke plumes or industrial sites, for example, scientists can pinpoint the origins of pollution. This information can then be used to develop strategies to reduce emissions and improve air quality, such as implementing regulations or policies to target specific sources of pollution.
Satellite imagery also helps to track the movement of pollutants over large areas. By monitoring the spread of pollution, researchers can predict where it may cause problems and take steps to mitigate its impact. This can inform policy decisions by highlighting areas that require intervention and enabling the targeting of resources to where they are most needed.
Finally, satellite imagery can be used to assess the effectiveness of existing policies. By monitoring changes in air quality over time, policymakers can evaluate whether their interventions are having the desired effect. This allows for evidence-based adjustments to be made, ensuring that policies are optimised to effectively address the issue of air pollution.
Air Pollution's Impact: Millions Suffer in Silence
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Satellite imagery offers a broader overview of an area than ground-based monitoring systems, allowing for more comprehensive monitoring of air quality and pollution levels. This is especially useful in areas where ground-based monitoring is not feasible or cost-prohibitive.
Satellite imagery can detect smoke plumes from industrial sites, large fires, or agricultural burning, as well as identify factories and power plants as sources of pollution.
One of the main limitations is the resolution of the imagery, which may not be detailed enough to accurately measure air quality. Additionally, the cost of obtaining and analyzing satellite imagery can be high, and the accuracy of the data can be affected by weather and cloud cover.