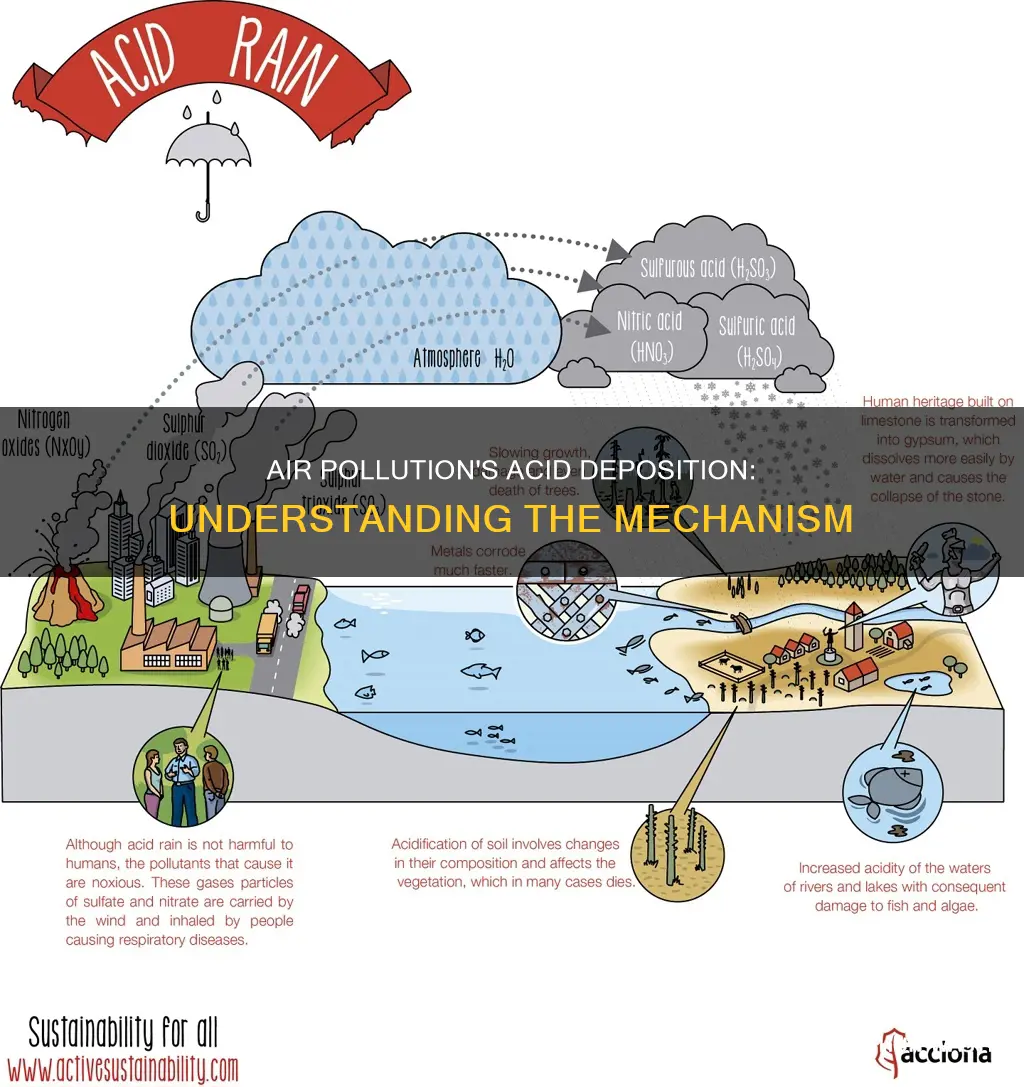
Acid deposition, or acid rain, is a broad term for any form of precipitation with acidic components that fall to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. Acid deposition is caused by air pollution, specifically the release of sulphur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the atmosphere, which occurs when humans burn fossil fuels for energy. These air pollutants are transformed into acid particles that are carried by the wind and fall to the earth as wet and dry depositions, causing harmful effects on soil, forests, lakes, and other environments.
What You'll Learn
- Burning fossil fuels releases sulphur and nitrogen oxides, causing acid rain
- Acid deposition makes soils, lakes and ponds more acidic
- Acid deposition can be carried by wind over long distances
- Acid rain can damage physical structures like buildings and cars
- Acid rain can cause health issues, including eye irritation and asthma

Burning fossil fuels releases sulphur and nitrogen oxides, causing acid rain
Acid deposition, or acid rain, is any form of precipitation with acidic components with a pH level of less than 5.6, which falls to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. Burning fossil fuels releases sulphur and nitrogen oxides, which are transformed into sulphuric and nitric acid in the atmosphere, causing acid rain.
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are emitted into the atmosphere and transported by wind and air currents. These compounds are released when fossil fuels such as oil and coal are burned, as well as from exhaust gases from vehicles. SO2 and NOx react with water, oxygen, and other chemicals to form sulphuric and nitric acids. These acids then mix with water and other materials before falling to the earth's surface, causing harmful effects.
Acid rain can fall on buildings, vehicles, and trees, and can make lakes and ponds acidic. It can also be inhaled by people, causing potential health problems. The acids in the rain can dissolve calcite in marble and limestone, leading to the removal of material and the loss of carved details.
The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of SO2 and NOx emissions, contributing to the formation of smog and acid rain. Conserving energy and reducing the use of cars, trucks, and buses can help decrease the release of these compounds into the atmosphere, mitigating the occurrence of acid rain.
Emails and Pollution: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also

Acid deposition makes soils, lakes and ponds more acidic
Acid deposition, also known as acid rain, is any form of precipitation with acidic components that fall to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. Acid deposition occurs when sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, typical air pollutants, are transformed into sulfuric and nitric acid compounds in the atmosphere. These acid compounds are then carried by the wind and fall to the earth's surface, making the environment more acidic. This includes soils, lakes, and ponds.
When sulphur and nitrogen compounds are released into the atmosphere, they react with water, oxygen, and other chemicals to form various acidic compounds. These compounds then mix with water and other materials before seeping into the ground, causing harmful effects. As acid rain flows through soils, it releases aluminium from soil clay particles, which then flow into lakes and streams. This process causes the pH in lakes and streams to decrease, making them more acidic.
Some lakes and streams are naturally acidic, but acid deposition can further increase their acidity. This is particularly true in areas with poor soil-buffering capacity, such as the Northeastern United States, where some lakes have a pH of less than 5. Acid deposition can also cause episodic acidification, where lakes that are not normally acidic experience temporary effects due to melting snow or heavy rainfall bringing greater amounts of acidic deposition.
The effects of acid deposition on lakes and ponds are well documented. Acidic water can be toxic to fish, causing a decrease in population numbers or even the disappearance of certain species. It can also affect other wildlife, such as frogs and aquatic plants, by increasing their sensitivity to environmental conditions and reducing their food sources. In addition, acid deposition can remove minerals and nutrients from the soil, impacting the growth of plants and trees in the surrounding area.
The impact of acid deposition on soils is also significant. Soils that undergo acidification can negatively impact agriculture, as some crops may be sensitive to low pH levels. Acid deposition can also contribute to the release of aluminium, which can be harmful to plants and animals. Additionally, it can strip nutrients from trees, leaving them more vulnerable to freezing temperatures.
Fitbits and EMF Pollution: A Health Risk?
You may want to see also

Acid deposition can be carried by wind over long distances
Acid deposition, or acid rain, is a broad term for any form of precipitation with acidic components that fall to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. Acid deposition is caused by the release of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the atmosphere, which occurs when fuels like oil and coal are burned. These gases are transformed into sulphuric and nitric acid compounds, which are then carried by wind and air currents over long distances.
The process of acid deposition begins with the emission of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which are transported by wind and air currents as fine particles. These particles can be carried over long distances, sometimes across borders, meaning that acid deposition is a problem for everyone, not just those living near the sources of these emissions. On sunny days, these acid compounds are carried as fine particles, while on rainy days they dissolve in raindrops or within clouds.
Acid deposition can fall to the earth's surface in both wet and dry forms. Wet deposition, or acid rain, is the most well-known form of acid deposition and includes rain, snow, fog, or hail that has been made acidic by sulphuric and nitric acid compounds. Dry deposition, on the other hand, includes gases and dust particles that contain acidic components. Both wet and dry deposition can be carried by wind over long distances, allowing acid deposition to impact areas far from the sources of these emissions.
The impact of acid deposition is widespread and can affect soils, lakes, ponds, streams, forests, and other environments. It can also cause damage to buildings, cars, and trees, and can have negative effects on human health. By understanding the process of acid deposition and the role of wind in its transport, we can better address the issue of air pollution and its impact on the environment and human well-being.
Globalization's Dark Side: Air Pollution's Global Reach
You may want to see also

Acid rain can damage physical structures like buildings and cars
Acid rain is rain that has been made acidic by certain pollutants in the air. It is caused by the presence of sulphur and nitrogen particles in the wet components of rain. These particles are often the result of human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, vehicle emissions, and unethical waste emission disposal techniques.
Acid rain can cause significant damage to physical structures like buildings and cars. The acidic particles and gases can deposit onto surfaces, causing corrosion and deterioration. This is particularly true for metal structures, where acid rain can cause corrosion and paint peeling. For example, the calcite in marble and limestone can dissolve when it reacts with SO2 and NOx, resulting in the roughening of surfaces, material removal, and the loss of carved details.
Additionally, acid rain can also damage stone buildings and sculptures through dissolution and alteration. The type of stone and its composition determine its susceptibility to acidic deposition. Acid rain can also dirty the surfaces of buildings and other structures, causing them to lose their aesthetic appeal.
The effects of acid rain on physical structures can be long-lasting and challenging to reverse. While some materials may be more resistant than others, the cumulative impact of repeated exposure to acid rain can take its toll over time. Furthermore, the repair and restoration of damaged structures can be costly and time-consuming.
It is important to note that the impact of acid rain on buildings and cars is not just cosmetic. The structural integrity of these physical structures may be compromised, posing safety risks and requiring costly repairs or replacements.
Delhi's Air Pollution: Causes and Concerns
You may want to see also

Acid rain can cause health issues, including eye irritation and asthma
Acid deposition is caused by the release of pollutants into the atmosphere, primarily from the burning of fuels like oil and coal. Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide are the major culprits, which transform into sulphuric and nitric acid compounds, resulting in acid rain. This precipitation, with a pH of less than 5.6, leads to the acidification of soils, lakes, and ponds.
Acid rain, while not harmful to walk or swim in, poses risks to both the environment and human health. The particles that cause acid rain can be inhaled, potentially harming lung function and triggering or exacerbating respiratory conditions such as asthma. Asthma is a chronic disease characterised by airway inflammation and variable airflow obstruction. Air pollution, including acid rain, can induce asthma symptoms and negatively impact lung function, particularly in children. Maternal smoking during pregnancy, influenced by air pollution, is also a risk factor for asthma development in children.
The impact of acid rain on human health can also lead to eye irritation. While there is limited information on the direct link between acid rain and eye irritation, the presence of acidic components in the air and precipitation can potentially irritate the eyes, similar to how they irritate the lungs.
Additionally, acid rain contributes to environmental damage, which indirectly affects human health. It can destroy nutrients essential for trees' health, increase the toxicity of water bodies, and break down stone and metal structures. These impacts can have cascading effects on ecosystems and human communities, ultimately influencing overall health and well-being.
Trains and Pollution: What's the Real Damage?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Acid deposition is any form of precipitation with acidic components with a pH level of less than 5.6, such as sulphuric or nitric acid, that falls to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms.
Air pollution causes acid deposition when sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, released from burning fossil fuels, react with water, oxygen, and other substances to form sulphuric and nitric acid compounds. These compounds are then carried by the wind and fall to the earth's surface as wet or dry depositions, making the environment more acidic.
Acid deposition has harmful effects on the environment, including damage to soils, lakes, ponds, and forests. It also affects aquatic life by increasing the toxicity of waters, leading to a decline in fish populations. Additionally, it can cause health issues for humans, such as eye irritation and asthma, when inhaled as fog or rain.
Efforts to reduce acid deposition include implementing pollution control measures, such as the Clean Air Act in the US, and setting air quality standards to limit emissions of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. International agreements like the UNECE Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution (CLRTAP) have also contributed to substantial reductions in emissions.
The primary sources of these emissions are human activities such as burning fossil fuels for energy generation, with coal-burning power plants, factories, and vehicles being the biggest contributors. However, natural sources like rotting vegetation and volcanic activity also release these pollutants.



















