Air and water pollution are two pressing issues that have detrimental effects on the environment. Air pollution is caused by harmful chemicals or particles in the air, which can take the form of gases, solid particles, or liquid droplets. These pollutants can be released into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and oil, and have been a significant issue since the Industrial Revolution. Water pollution, on the other hand, occurs when harmful substances, often chemicals or microorganisms, contaminate bodies of water, degrading water quality and rendering it toxic and unusable. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including stormwater runoff, agricultural practices, and the improper storage and transportation of oil. Both air and water pollution have far-reaching consequences, impacting the health of humans, animals, and plants, as well as the economy and social development.
What You'll Learn

Air pollution and its impact on human health
Air pollution refers to the emission of pollutants into the air, which are detrimental to human health and the planet as a whole. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution kills around seven million people globally each year. Ninety-nine per cent of people currently breathe air that exceeds the WHO's guideline limits for pollutants, with those in low- and middle-income countries suffering the most.
The energy choices we make as a society influence our air quality. Researchers are studying the potential health impacts of using different energy sources. For example, the combustion of fuels emits mercury and other heavy metal compounds, which can accumulate in plants, animals, and, ultimately, humans.
Air pollution can cause or exacerbate various health issues, including respiratory and lung diseases, coughing, itchy eyes, cancer, neurological damage, and even premature death. People with pre-existing conditions such as asthma, COPD, or emphysema are especially vulnerable, as air pollution can trigger asthma attacks, worsen breathing difficulties, and cause wheezing and coughing.
Additionally, wood smoke, which contains wood tars, gases, soot, and harmful chemicals, poses serious health risks. Short-term exposure to fine particles in the air can aggravate lung diseases, trigger asthma, acute bronchitis, and respiratory infections. Long-term exposure increases the likelihood of developing chronic conditions such as COPD, chronic bronchitis, cardiovascular disease, or lung cancer.
Climate change also exacerbates the problem by increasing pollen production and mould growth, which can trigger allergies and asthma attacks.
Interventions to reduce air pollution include limiting hazardous waste disposal, improving air quality monitoring, and implementing policies to reduce vehicle emissions and industrial pollution.
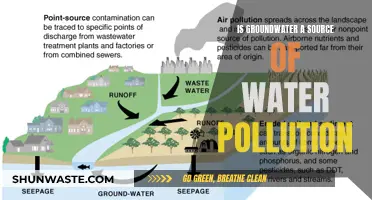
Sources of Water Pollution: Point vs Nonpoint
You may want to see also

Water pollution and its effect on wildlife
Water pollution is caused by the presence of harmful substances, often chemicals or microorganisms, in a body of water. These pollutants contaminate rivers, reservoirs, lakes, seas, and oceans, degrading water quality and rendering it toxic to both humans and the environment. While water pollution has severe consequences for human health, it also has a detrimental impact on wildlife.
One of the primary sources of water pollution is agricultural practices. Fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste from farms wash into waterways during rainfall, leading to nutrient pollution. This excess of nitrogen and phosphorus in water causes algal blooms, which produce toxins harmful to wildlife. These toxins accumulate in the tissues of aquatic organisms, such as fish, birds, sea turtles, and aquatic mammals like dolphins and manatees. As a result, these organisms can suffer from impaired reproductive abilities, reduced lifespan, and increased vulnerability to diseases.
Heavy metals, such as mercury, are another significant water pollutant. Mercury is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct of coal-fired power plants and waste incineration. Once emitted, mercury eventually finds its way into bodies of water, where it builds up in the tissues of wildlife. As mercury increases in concentration as it moves up the food chain, large predator fish like walleye and trout can have mercury levels far exceeding those in the surrounding water. This accumulation of mercury adversely affects the immune systems of wildlife and poses serious health risks to both wildlife and humans who consume these fish.
In addition to agriculture and heavy metals, sewage, trash, industrial emissions, and chemicals from households and farms also contribute to water pollution. These pollutants can create "dead zones" in bodies of water, where oxygen levels are depleted due to excessive plant and algae growth. Aquatic life in these zones, including fish and crabs, cannot survive due to the lack of oxygen. Furthermore, the trash dumped in the ocean can infect and harm marine animals, further threatening their survival.
The effects of water pollution on wildlife are far-reaching and often devastating. It disrupts the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems, impairing the ability of wildlife to reproduce, hunt, and survive. As a result, water pollution poses a severe threat to the biodiversity and survival of various species, including fish, birds, mammals, and aquatic plants.
Preventing Water Contamination: Strategies for a Safe Future
You may want to see also

Energy choices and their influence on air and water quality
The energy choices we make as a society have a significant impact on our air and water quality. The energy system is a vital contributor to economic and social progress worldwide, but it also has negative side effects. Fossil fuel combustion, for instance, releases toxic air pollution and greenhouse gases, which not only affect air quality but also have long-term consequences for climate health. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that a staggering 92% of the global population lives in areas where local air pollution exceeds WHO limits. This has dire consequences for human health, with air pollution being responsible for one in nine deaths globally, and, according to estimates from Harvard, as many as one in five deaths may be attributed to air pollution from fossil fuels.
Water quality is also greatly affected by energy choices. The global energy system consumed around 370 billion cubic meters of freshwater in 2021, accounting for nearly 10% of total global freshwater withdrawals. Fossil fuel and nuclear power plants are among the largest consumers of freshwater, and the water used in these processes is often sourced from lakes, rivers, and underground aquifers. This heavy reliance on freshwater sources puts immense stress on our water reserves, especially considering the increasing unpredictability of water availability due to changing weather patterns.
To address these issues, a shift towards renewable energy sources is crucial. Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and geothermal power are naturally replenished and emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants. Wind energy, generated through wind turbines, does not directly contribute to air pollution emissions and does not require water for cooling, making it one of the cleanest sources of energy. Solar energy, while having some emissions associated with the manufacturing of solar panels, does not produce air pollutants or contribute to greenhouse gas emissions once operational. Geothermal energy, which utilizes the Earth's internal heat to produce electricity, generates only a fraction of the carbon dioxide produced by natural gas power plants and has minimal NO2 or SO2 pollution.
By embracing renewable energy options, we can reduce our dependence on dwindling and expensive fossil fuel resources, improve air and water quality, and drive inclusive economic growth. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimates that 90% of the world's electricity can and should be derived from renewable sources by 2050. This transition will not only mitigate climate change but also bring about a range of social and economic benefits, including reduced healthcare costs, job creation, and a more resilient electrical grid.
Fracking's Impact: Is Our Water at Risk?
You may want to see also

Air pollution's contribution to water pollution
Air pollution has a significant impact on water quality, with airborne contaminants finding their way into bodies of water and causing widespread harm. This is a pressing issue as soil and water are the cornerstones of all life on Earth, providing homes and essential nutrients for most organisms.
Airborne pollutants can be carried by wind and deposited into water sources, a process known as atmospheric deposition. This is particularly evident in the case of mercury, which cycles through various phases, much like the water cycle, and can be found in high concentrations in the atmosphere. When mercury is deposited during wet weather, it contaminates water bodies, leading to health warnings in certain areas due to high levels of mercury in fish. Other contaminants that contribute to water pollution include polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
In addition, air pollution can indirectly harm water sources by affecting the soil. Acid precipitation from rain, snow, and particulate matter can alter soil chemistry, making it more difficult for soils to retain essential nutrients, minerals, and elements such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium. As a result, these nutrients are leached from the soil by water, reducing their availability for plant growth and impacting water quality. This process of acidification can have dramatic short-term effects on aquatic ecosystems, with "acid shock" proving lethal to many fish and other aquatic organisms.
Furthermore, air pollution contributes to nutrient pollution in water bodies. Excess nitrogen and phosphorus in the air, largely from farm waste and fertilizer runoff, can cause algal blooms, which are toxic to both people and wildlife. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and sulfur, resulting from air pollution, is a major stressor on natural ecosystems, often leading to eutrophication and reduced biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems.
The impact of air pollution on water quality is not always immediately visible. Some rivers, lakes, or coastal areas may appear clean but are still polluted. Climate change and increasing wildfire frequency are expected to exacerbate the problem by releasing previously bound contaminants back into the atmosphere. Overall, the complex interplay between air and water pollution underscores the urgent need for effective pollution control strategies to protect the environment and human health.
Agricultural Runoff: Water Pollution's Unseen Threat
You may want to see also

Interventions to reduce air and water pollution
Air and water pollution have devastating effects on the environment, with air pollution causing approximately 4 million deaths in 2016 and 4.2 million in 2019, and unsafe water killing more people each year than war and other forms of violence combined.
Air Pollution Interventions
Air pollution is a serious public health problem, and unhealthy levels of air pollution are breathed by billions of people worldwide. To reduce exposure to air pollution, personal interventions include avoiding sources of pollution, staying indoors, filtering indoor air, using face masks, and limiting physical activity when and where air pollution levels are elevated. However, compared to upstream reduction or control of emissions, personal interventions place burdens and the risk of adverse unintended consequences on individuals.
To reduce air pollution levels, the WHO's Air Quality and Health Unit works in three cross-cutting areas: knowledge, evidence, and measuring progress; institutional capacity building and technical support; and leadership and coordination. Successful policies and solid governance depend on coordinated action between a variety of stakeholders and sectors, such as energy, transport, waste management, urban planning, and agriculture.
Some examples of successful policies include:
- Clean technologies that reduce industrial smokestack emissions
- Improved management of urban and agricultural waste, including capturing methane gas emitted from waste sites as an alternative to incineration (for use as biogas)
- Ensuring access to affordable clean household energy solutions for cooking, heating, and lighting
- Shifting to clean modes of power generation
- Prioritizing rapid urban transit, walking, and cycling networks in cities, as well as rail interurban freight and passenger travel
- Adopting cleaner heavy-duty diesel vehicles and low-emissions vehicles and fuels, including fuels with reduced sulfur
Water Pollution Interventions
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances, often chemicals or microorganisms, contaminate a body of water, degrading water quality and rendering it toxic to humans or the environment. Our rivers, reservoirs, lakes, and seas are filled with chemicals, waste, plastic, and other pollutants.
Nutrient pollution, caused by excess nitrogen and phosphorus in water or air, is the number-one threat to water quality worldwide. More than 80% of the world's wastewater flows back into the environment without being treated or reused. To improve water quality, interventions are needed to reduce the discharge of untreated wastewater and to manage the use of nitrogen and phosphorus more sustainably.
Dams' Impact: Water Pollution and Environmental Concerns
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Air pollution has a detrimental impact on both human health and the planet. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution is responsible for nearly seven million deaths worldwide each year. It can cause and worsen lung diseases, leading to hospitalizations, cancer, respiratory issues, neurological damage, and even premature death. Additionally, air pollution contributes to climate change, which exacerbates the effects of mold and allergens from trees, weeds, and grass.
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances, often chemicals or microorganisms, contaminate bodies of water such as streams, rivers, lakes, and oceans. This degradation of water quality renders it toxic to humans and the environment. Unsafe water is a significant health hazard, causing various diseases and claiming more lives annually than war and all other forms of violence combined. Water pollution also affects aquatic ecosystems, reducing biodiversity and harming fish and other aquatic life.
There are various sources of air pollution, including vehicle exhaust, smoke, road dust, industrial emissions, pollen, gas-fueled yard equipment, and chemicals used in homes. Energy choices, such as the use of fossil fuels, also contribute to air and water pollution. Water pollution sources include wastewater from households, commercial, industrial, and agricultural activities, as well as stormwater runoff carrying pollutants from impermeable surfaces into waterways.
Exposure to air and water pollution poses significant health risks, including respiratory diseases, cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular disease. Pollutants can enter the bloodstream, causing coughing, itchy eyes, and lung problems. Water pollution can lead to diarrheal diseases and impact the health of vulnerable communities, such as people of color, who are more likely to reside in areas with poor air quality due to historical racism and discriminatory policies.