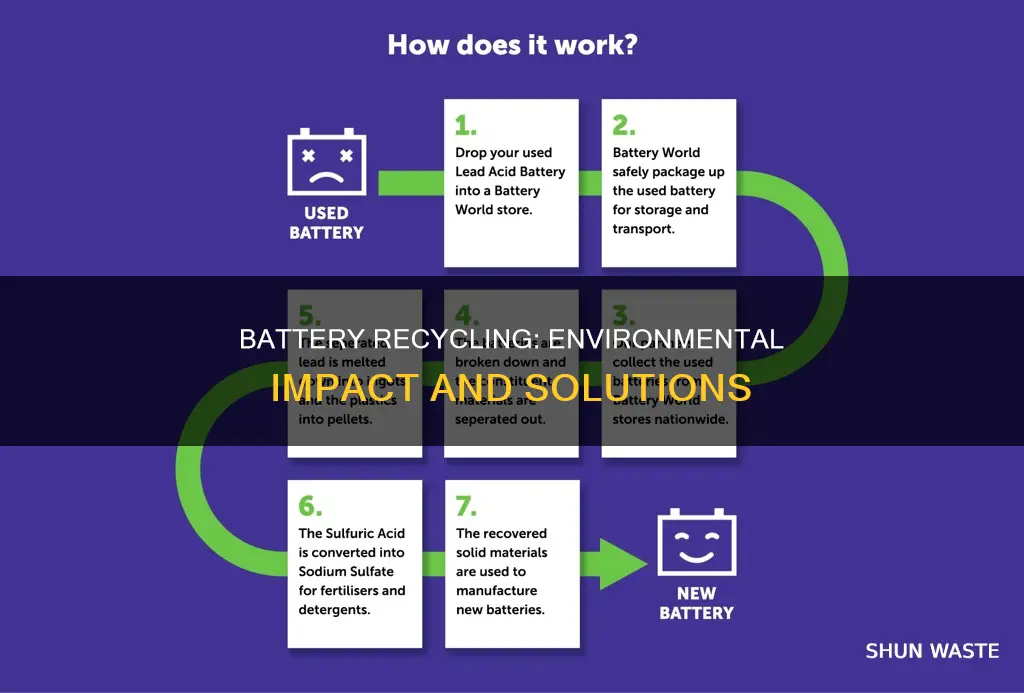
Improper disposal of batteries is harmful to the environment. Batteries that end up in landfills may corrode and decay, releasing dangerous chemicals into the environment, including battery acid. These chemicals can contaminate soil, water sources, and even the air, causing serious environmental damage and posing risks to human health. Recycling batteries is a crucial solution to this problem. It keeps batteries out of landfills and prevents the release of toxic materials into the environment. Additionally, recycling enables the reuse of valuable materials such as copper and aluminum, reducing the need for resource extraction and minimizing the environmental footprint of battery production. While the recycling process for certain battery types, like lithium-ion, is not yet widespread, efforts are being made to improve recycling technologies and develop standards for responsible waste management.
Does recycling batteries pollute the environment?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Batteries in landfills | May corrode and decay, releasing dangerous chemicals into the environment, including battery acid, which can seep into the soil, water sources, and air |
| Recycling batteries | Keeps them out of landfills, preventing environmental damage and reducing the need for new resources |
| Recyclable battery materials | Copper and aluminum can be recycled and reused endlessly |
| Toxic materials in batteries | Can enter water sources and cause pollution if not properly recycled or disposed of |
| Improper incineration | Can release toxic fumes into the air |
| Improper disposal | Certain batteries can explode, causing injury and property damage |
| Rechargeable batteries | More environmentally friendly and cost-effective than disposable batteries |
| Battery recycling challenges | The process of recycling lithium-ion batteries is not widespread, and the most environmentally-friendly recycling processes are unclear |
| Environmental impact of battery production | Varies depending on the source of electricity used to power them; fossil fuels used to power batteries contribute to environmental degradation |
| Metal extraction for batteries | Can cause environmental degradation and hazards, as seen with nickel and cobalt mines |
| Benefits of recycling batteries | Reduces energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and natural resource use compared to landfill |
What You'll Learn
- Batteries in landfills release dangerous chemicals into the environment
- Recycling batteries reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions
- Improper disposal of batteries can cause explosions and property damage
- Reusing batteries can reduce the environmental impact of mining
- Recycling batteries can help preserve natural resources and prevent shortages

Batteries in landfills release dangerous chemicals into the environment
Batteries that end up in landfills can release dangerous chemicals into the environment. Improper disposal of batteries can cause serious environmental damage. Landfills are not 100% contained, and chemicals from batteries can leach into groundwater and soil. These chemicals include toxic metals such as lead, cobalt, nickel, manganese, iron, chromium, and copper. Lead exposure, for example, can cause memory loss, damage the cardiovascular system, and lead to miscarriages and premature deliveries in pregnant women. Nickel is the most common allergic metal and can cause respiratory disorders and cancer at higher concentrations.
Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in consumer electronic products, also contain potentially toxic materials, including metals such as copper, nickel, and lead, and organic chemicals such as electrolytes containing LiClO4, LiBF4, and LiPF6. These batteries are often small and disposed of at a high rate, leading to environmental pollution and adverse health impacts. Under simulated landfill conditions, these batteries can leach out concentrations of metals that exceed regulatory limits, rendering them hazardous waste.
In addition to the release of toxic chemicals, batteries in landfills can also contribute to the generation of leachate, a mixture of dissolved organics, inorganic salts, ammonia, heavy metals, and xenobiotic organic compounds. Leachate can act as a transportation medium for hazardous species, polluting soils or groundwater and transporting contaminants over long distances.
To prevent the release of dangerous chemicals from batteries into the environment, it is important to recycle or properly dispose of batteries. Recycling batteries can help keep them out of landfills and reduce the environmental and health risks associated with battery disposal. Some materials in batteries, such as copper and aluminum, can be recycled and reused endlessly, reducing the consumption of natural resources.
Primary Pollutants: Synergistic Effects and Impacts
You may want to see also

Recycling batteries reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions
Recycling batteries is essential to reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Batteries are used in many everyday electronics, from bicycles and cars to telephones and solar panels. They are also found in UPS equipment and electric vehicles (EVs). The average person might not think twice about tossing old batteries in the trash, but this practice can have serious environmental repercussions. Most unrecycled batteries end up in landfills, contributing to environmental damage and releasing dangerous chemicals, such as battery acid, into the soil, water sources, and air.
Recycling batteries help to keep them out of landfills and mitigate the release of harmful substances. Some core battery materials, such as copper and aluminum, can be recycled and reused endlessly, reducing the need to extract new resources from the environment. This ensures that batteries remain plentiful and affordable while also conserving natural resources and preventing shortages. Recycling can also help reduce the carbon footprint associated with battery production, which is predominantly fueled by fossil fuels.
While recycling batteries is beneficial, the specific methods employed can impact energy consumption and emissions. For example, pyrometallurgical recycling involves subjecting battery materials to extremely high temperatures, requiring significant energy input. On the other hand, hydrometallurgical recycling uses chemical solutions to extract metals but necessitates further breakdown of components beforehand. Additionally, in some cases, the current technology for recycling lithium-ion batteries may lead to higher energy consumption and air emissions compared to primary production.
Despite these challenges, recycling batteries remain a crucial step towards reducing environmental impacts. It is important to note that electric vehicles, despite being a cleaner alternative to gasoline or diesel-powered cars, still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions during the production and recycling phases. As such, recycling batteries can help mitigate these emissions and support the transition to a low-carbon energy system.
Overall, recycling batteries play a vital role in reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. By keeping batteries out of landfills, conserving natural resources, and reducing the need for new resource extraction, recycling helps to lessen the environmental footprint of battery-powered products. Additionally, recycling can contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing the carbon emissions associated with battery production and supporting the development of clean energy technologies.
The View Outside: A Real-Time Perspective
You may want to see also

Improper disposal of batteries can cause explosions and property damage
Improper disposal of batteries can have serious consequences for the environment, human health, and safety. Batteries contain chemicals such as mercury, lead, cadmium, nickel, and silver, which can be harmful to the environment and human health if not properly managed. When batteries are thrown away in the trash, they often end up in landfills, where they can corrode and decay, releasing these dangerous chemicals into the soil, water sources, and even the air. This can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting plants, animals, and people who rely on these resources for drinking or irrigation. In some cases, animals may ingest discarded batteries, causing serious health problems or even death.
Additionally, improper disposal of batteries can cause explosions and property damage. Certain types of batteries, such as 9V batteries, pose a significant fire risk if not properly stored or disposed of. The terminals of these batteries can create a circuit if they come into contact with metal objects or other batteries, generating sparks that can ignite flammable materials and potentially lead to electrical fires. Negligence in storing or disposing of batteries properly is a common cause of electrical fires, which can have devastating consequences for homes and businesses.
To mitigate the risk of fires and explosions, it is crucial to take preventive measures such as proper storage and disposal of batteries. This includes taping the terminals or ends of batteries to prevent contact with conductive objects or other batteries. It is also important to store batteries in a safe place, away from flammable materials and out of the reach of children.
Furthermore, recycling batteries is a crucial step in preventing the negative impacts of battery disposal. By recycling batteries, we can keep them out of landfills and properly dispose of any harmful chemicals they may contain. Many battery retailers and local waste management companies offer battery recycling services, making it convenient for individuals and businesses to dispose of their batteries responsibly.
Overall, improper disposal of batteries can have far-reaching consequences, including explosions and property damage. It is essential to prioritize proper storage, disposal, and recycling of batteries to protect the environment, human health, and safety.
The Ocean's Trash Problem: An Annual Crisis
You may want to see also

Reusing batteries can reduce the environmental impact of mining
Mining is an essential part of modern society, providing the building blocks for many everyday items. However, it is also a highly environmentally invasive process, with a significant carbon footprint. The extraction of minerals and metals from the earth often involves the use of fossil fuels, the disruption of natural habitats, and the pollution of water sources and surrounding areas.
Battery production, in particular, has come under scrutiny for its environmental impact. The manufacturing of electric vehicle (EV) batteries, for example, requires minerals like cobalt and lithium, which are obtained through energy-intensive mining processes. These mines can cause ecological degradation, contaminating large areas of land and water sources with toxic chemicals.
Recycling and reusing batteries can play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of mining. Firstly, recycling keeps batteries out of landfills, preventing the release of toxic chemicals into the environment. Batteries that end up in landfills can corrode and decay, allowing harmful substances, such as battery acid, to seep into the soil, water sources, and even the air. By recycling, we can properly dispose of these toxic chemicals and prevent environmental contamination.
Secondly, recycling and reusing batteries help reduce the demand for newly mined materials. Mining for metals and minerals can have far-reaching consequences, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and adverse effects on local communities. By reusing and recycling batteries, we can extend the lifespan of these finite resources, reducing the need for further extraction and minimizing the ecological footprint of mining.
Additionally, recycling batteries can lead to a more sustainable and circular economy. Some materials in batteries, such as copper and aluminum, can be recycled and reused endlessly. This not only ensures a steady supply of these resources but also helps conserve natural resources and prevent shortages. By encouraging the recycling and reuse of batteries, we can reduce our reliance on mining, minimizing both the environmental and social impacts of extraction.
Furthermore, reusing batteries can provide economic benefits while reducing environmental harm. Rechargeable batteries, for example, offer a cost-effective alternative to disposable batteries, minimizing the quantity sent for disposal and recycling. By investing in rechargeable and reusable batteries, we can reduce waste and lower the overall environmental impact of battery production and disposal.
Explore Ambient Data: Understanding its Diverse Types and Applications
You may want to see also

Recycling batteries can help preserve natural resources and prevent shortages
The importance of recycling batteries cannot be overstated. Improper disposal of batteries can cause serious environmental damage. Most unrecycled batteries end up in landfills, where they corrode and decay, releasing dangerous chemicals into the environment, including battery acid. These chemicals can contaminate soil, water sources, and even the air, causing harm to both the environment and human health.
Recycling batteries is a crucial step in preserving natural resources and preventing shortages. Batteries contain valuable materials such as copper and aluminum, which can be recycled and reused endlessly. By recycling these materials, we can reduce our reliance on finite natural resources and ensure that batteries remain plentiful and affordable. Aluminum, for example, has been used in batteries since 1888, and its potential as a replacement for lead-acid batteries is only recently being explored. Copper, another important metal in battery creation, has been used in batteries since 1887 but requires further research.
The demand for batteries is increasing, especially with the rising popularity of electric vehicles. This, in turn, puts pressure on natural resources. Recycling batteries can help alleviate this pressure by providing a sustainable source of materials for new batteries. It also reduces the need for extracting and processing raw materials, which can be environmentally damaging and energy-intensive.
Additionally, recycling batteries help prevent the release of toxic materials into the environment. Batteries contain harmful substances such as lead and lithium, which can cause pollution and pose risks to human health if not properly disposed of. Recycling ensures that these toxic materials are safely handled and kept out of landfills.
Finally, recycling batteries contribute to climate change mitigation efforts. The production and disposal of batteries can result in significant carbon emissions, contributing to global warming. By recycling batteries, we can reduce the need for new battery production, thereby lowering carbon emissions and helping to preserve the environment for future generations.
Florida's Estuaries: Polluted Paradise?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Recycling batteries keeps them out of landfills, which can cause serious environmental damage. It also helps to reduce the extraction of natural resources and prevents shortages.
Batteries that end up in landfills can corrode and decay, releasing toxic chemicals and heavy metals like lead into the environment. These pollutants can contaminate soil, water sources, and the air, causing harm to both the environment and human health.
Recycling batteries helps to reduce environmental degradation by minimizing the extraction of natural resources and lowering carbon emissions. It also enables the recovery and reuse of valuable materials such as copper and aluminum, reducing the need for new resource consumption.
Lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries are the most common types of batteries that can be recycled. However, the recycling infrastructure for different battery types varies, and not all batteries are widely recycled yet.
Contact your local municipality or battery retailers to find the best battery recycling options in your area. Tape the terminals or ends of the batteries to reduce the risk of fire during transportation. Some organizations and retailers provide battery recycling containers or accept batteries for recycling.







