As air pollution continues to worsen, it is important to understand how environmental factors such as humidity affect the number of pollutants in the air. Humidity is a naturally occurring phenomenon that influences air quality and can have both positive and negative impacts on human health and respiratory systems. It can affect the dispersion of pollutants, reactions between chemicals, and the movement of pollutants, ultimately influencing the overall air quality in different regions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Effect on air pollution | Humidity affects air pollution in ways that make it more harmful to humans and our respiratory health. |
| Effect on health | Humidity can cause stress to individuals with weakened respiratory systems, particularly those with preexisting conditions like asthma. |
| Effect on temperature | Humidity is a significant cause of drastic temperature changes in our immediate environment. |
| Effect on weather | Humidity plays a crucial role in directing our daily weather and climate conditions. |
| Effect on air quality | Humidity can affect the flow of air pollutants over long distances. |
| Effect on indoor air quality | Humidity can worsen indoor air quality by degrading materials over time and increasing irritating odors, particles, and vapors. |
| Effect on biological pollutants | Humidity can cause the growth of harmful molds and bacteria that trigger negative respiratory responses. |
| Effect on pollutant dispersion | Humidity can impact the dispersion of pollutants, with high humidity causing pollutants to stick to water droplets and other particles in the air, removing them from the atmosphere. |
| Effect on ozone pollution | While heatwaves and sunny, hot weather increase ozone pollution, humidity can help to decrease it by blocking sunlight and destroying formed ozone. |
| Effect on particulate matter | Urban areas with high levels of particulate matter may experience increased fog and haze due to high humidity, contributing to air pollution. |
What You'll Learn

Humidity increases the rate of harmful chemicals in the air
Humidity is a naturally occurring phenomenon that is common in certain climates and seasons across the world. It is the amount of water vapour in the atmosphere, and it plays a crucial role in determining the weather and climate conditions of a region. While humidity is essential for human life, as it ensures sufficient breathable air, it also has a significant impact on air quality and pollution.
High humidity can increase the rate of harmful or toxic chemicals in the air. This is because humidity affects the flow of air pollutants, as water molecules attach to air particles and make them heavier, causing them to settle. In some regions, this can lead to the formation of fog and haze, which can negatively impact air quality. Urban areas with high levels of particulate matter are particularly vulnerable to this issue. Additionally, high humidity can enhance the negative effects of harmful air pollutants like smog.
The relationship between humidity and indoor air quality is also important to consider. High humidity levels indoors can worsen emission rates and increase exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can have adverse health effects. These compounds are found in thousands of household products and materials and can cause headaches, nausea, and eye, nose, and throat irritation. High humidity can also promote the growth of harmful moulds and bacteria, which can trigger negative respiratory responses, especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions like asthma.
Furthermore, humidity affects the dispersion of pollutants. When humidity is high, pollutants can adhere to water droplets and other particles in the air, causing them to be removed from the atmosphere. This process can lead to the formation of clouds and precipitation, which helps to cleanse the air of pollutants. However, it is important to note that humidity does not directly cause an increase in the number of pollutants, but rather influences their movement and dispersion.
Overall, while humidity plays a critical role in ensuring breathable air, it can also increase the rate of harmful chemicals in the air and negatively impact air quality, particularly in urban areas with high pollution levels.
The Clean Energy Debate: Nuclear Power Plant Pollution
You may want to see also

Humidity affects the dispersion of pollutants
Humidity is a naturally occurring phenomenon that is common in certain climates and seasons across the world. It is the amount of water vapour in the atmosphere, a combination of dry air and water vapour. The degree of this combination determines the temperature.
Humidity also affects the movement of pollutants. Water molecules attach to air particles and make them heavier, so they are more likely to settle. This can impact the flow of air pollutants over long distances. In addition, humidity can increase the negative effects of harmful air pollutants like smog and can cause the growth of harmful moulds and bacteria that trigger negative respiratory responses.
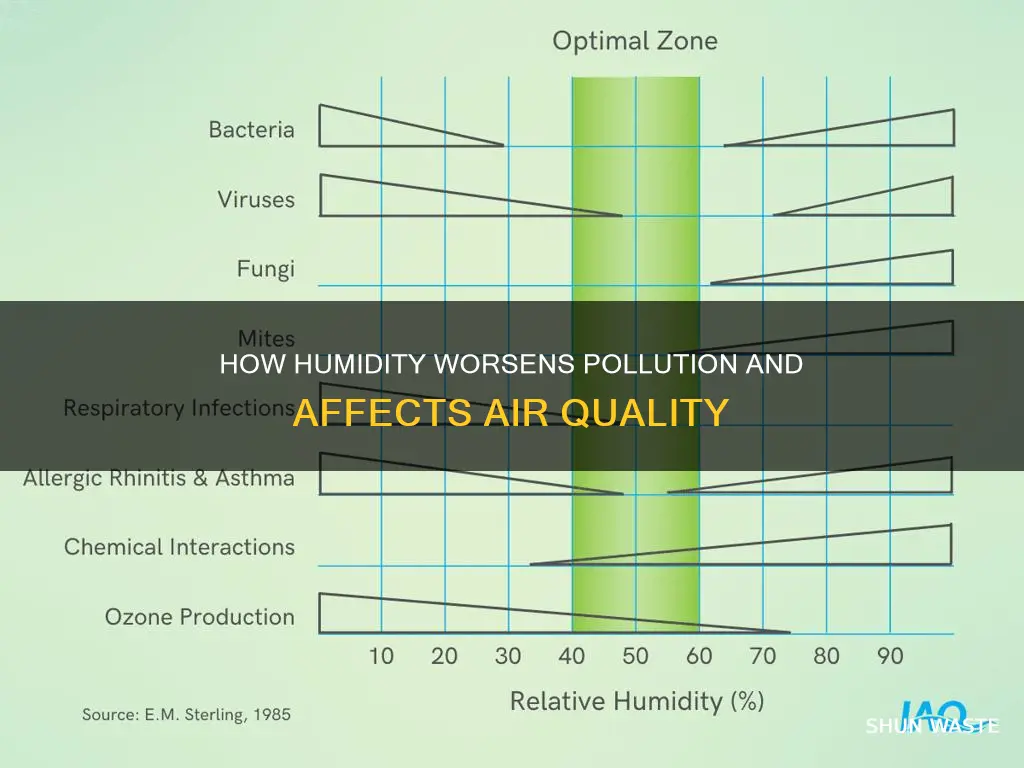
Indoor humidity can also affect air quality. Excessive indoor dampness can degrade materials over time, worsening indoor air pollution. It can also increase the presence of biological pollutants such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, mites, and mould.
The Ocean's Pollution: Sources and Solutions
You may want to see also

Humidity impacts the movement of pollutants
Secondly, humidity affects the weight of air particles. Water molecules attach to air particles, making them heavier and more likely to settle. This can impact the dispersion of pollutants over long distances, as well as their ability to reach higher altitudes. The direction and speed of the wind also play a significant role in the transport of pollutants, with higher wind speeds dispersing pollutants and particles over a wider area, reducing local pollution levels.
Additionally, humidity influences the reactions between chemicals in the atmosphere. For example, in the case of ground-level ozone, humidity can help to decrease pollution levels. Afternoon thunderstorms block sunlight, slowing down ozone production, while the moisture from the storm destroys the ozone that has already formed.
Humidity also plays a role in precipitation formation, which affects air pollution. High humidity levels contribute to cloud formation and subsequent rainfall, which helps remove pollutants from the air. However, in indoor environments, excessive humidity can worsen air quality by promoting the growth of biological pollutants such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, mites, and mold.
How Fabrics Absorb and Filter Smoke Pollutants
You may want to see also

Humidity affects reactions between chemicals
Humidity is gaseous water in the air, and it affects the quality of the air we breathe. It is a combination of dry air and water vapour, and the degree of this combination determines the temperature. Humidity increases the rate of harmful or toxic chemicals in the air. It also causes dust mites, mould, and bacteria in our homes, which negatively affect air quality.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air at a specific temperature. The warmer the air, the greater its capacity to hold moisture. Humidity above 65% will cause mould to grow, and humidity below 25% will cause structurally important water loss in artifacts. High humidity can also cause metal corrosion, and low humidity can make materials brittle.
Temperature directly affects the rate of a chemical reaction. As temperature increases, molecules gain more energy, move faster, and collide more often, which increases the reaction rate. The opposite is also true; as temperature decreases, molecules lose energy, move slower, and collide less often, which decreases the reaction rate.
Humidity also affects the rate of chemical reactions. A study on the effect of humidity on the reaction kinetics of an oxygen scavenger based on gallic acid found that the reaction rate coefficient and the stoichiometric factor increased at higher relative humidity, with the threshold between 54% and 75% relative humidity. Below 54% relative humidity, there was no detectable reaction.
In cities, motor vehicle exhausts increase humidity as water vapour is a product of the combustion of hydrocarbons. Therefore, cities tend to be more humid than rural areas due to the heat island effect, which results from modifying land surfaces and the generation of waste heat.
Repairing Gross Polluters: Getting Your Vehicle Back on Track
You may want to see also

Humidity can cause mould and bacteria to grow
Humidity can have a significant impact on air pollution, particularly regarding respiratory health. High humidity can increase the rate of harmful or toxic chemicals in the air and cause dust mites in our homes, further degrading air quality.
One of the critical ways humidity affects our health is by causing the growth of mould and bacteria, which can trigger negative respiratory responses. Humidity provides the moisture required for mould and bacteria to grow and thrive. This growth can occur on various surfaces, including walls, window frames, carpets, and insulation.
Mould gradually destroys whatever surface it grows on, and if left unaddressed, it can lead to structural damage. For example, mould can weaken floors and walls by feeding on wet wood. This damage can become so severe that it compromises the structural integrity of a building, requiring the intervention of a structural engineer or other professionals.
To prevent mould growth, it is essential to address moisture problems in buildings promptly. Proper maintenance of the building envelope, including walls, windows, floors, and roofs, is crucial to prevent water intrusion. Vapour barriers can also be incorporated into the design of walls and floors to prevent the absorption or release of moisture, reducing the risk of mould growth.
Additionally, relative humidity (RH) should be maintained below 60% indoors to inhibit mould growth. Humidity levels above 55% can activate mould growth, with the ideal moisture level for mould being 70% or higher. Therefore, it is recommended to keep indoor humidity levels between 30% and 50% if possible. Dehumidifiers and proper ventilation can help achieve this, improving air quality and reducing the health risks associated with mould exposure.
Onondaga Lake: Pollution's Lingering Legacy?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Humidity can make pollution worse in certain circumstances. For example, in urban areas with high levels of particulate matter, high humidity can cause fog and haze, which contribute to air pollution. Humidity can also increase the rate of harmful or toxic chemicals in the air.
Water molecules attach to air particles and make them heavier, so they are more likely to settle. Humidity can also cause the growth of harmful molds and bacteria that trigger negative respiratory responses.
Yes, humidity and indoor air quality are directly related. Humidity affects the levels of biological and chemical pollutants in the air.
High humidity can cause negative health effects such as headaches, nausea, and eye, nose, and throat irritation. It can also cause liver damage, central nervous system issues, and increased cancer risk.
You can improve indoor air quality by controlling humidity levels. For example, you can use a furnace filter to collect dust, lint, and fibers, or use spot ventilation to provide quick ventilation to specific places in your home.







