The question of whether diesel or gasoline engines are more polluting is a complex one. While diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than petrol engines, they produce more toxic emissions and fine particulate matter, which is associated with poor heart health. Newer diesel engines are equipped with diesel particle filters that help to trap particulate matter, but the amount of nitrogen oxide emitted from diesel engines remains an issue. The type of engine, injection system, vehicle type, usage, and purpose all impact pollution levels, and the fast-evolving nature of engine technologies adds further complexity to the comparison.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| CO2 emissions | Diesel engines emit less CO2 than gasoline engines |
| Greenhouse gases | Diesel engines emit less greenhouse gases than gasoline engines |
| Fuel consumption | Diesel engines use less fuel to travel the same distance as gasoline engines |
| Fine particulate matter | Diesel engines emit more fine particulate matter than gasoline engines, which is associated with poor heart health |
| Nitrogen oxides | Diesel engines emit more nitrogen oxides than gasoline engines |
| Torque | Diesel engines generate more torque than gasoline engines |
| Fuel costs | Diesel engines have lower total fuel costs than gasoline engines |
| Maintenance | Diesel engines can run twice as long as gasoline engines before requiring serious service |
| Fuel composition | Diesel fuel contains about 12% more energy per gallon than ordinary gasoline |
| Newer diesel engines | Newer diesel engines are equipped with diesel particle filters that reduce particulate emissions, making them cleaner than gasoline engines |
| Older diesel engines | Older diesel engines are more polluting than newer diesel engines and will continue to impact human health in the coming years |
What You'll Learn
- Diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than petrol engines
- Diesel engines emit more nitrogen oxides, which are harmful to human health
- Diesel engines are used in trucks and heavy equipment due to their greater torque and efficiency
- Petrol engines are self-regulating, needing less driver input than diesel engines
- Newer diesel engines are cleaner than gasoline engines, but older diesel engines are more polluting

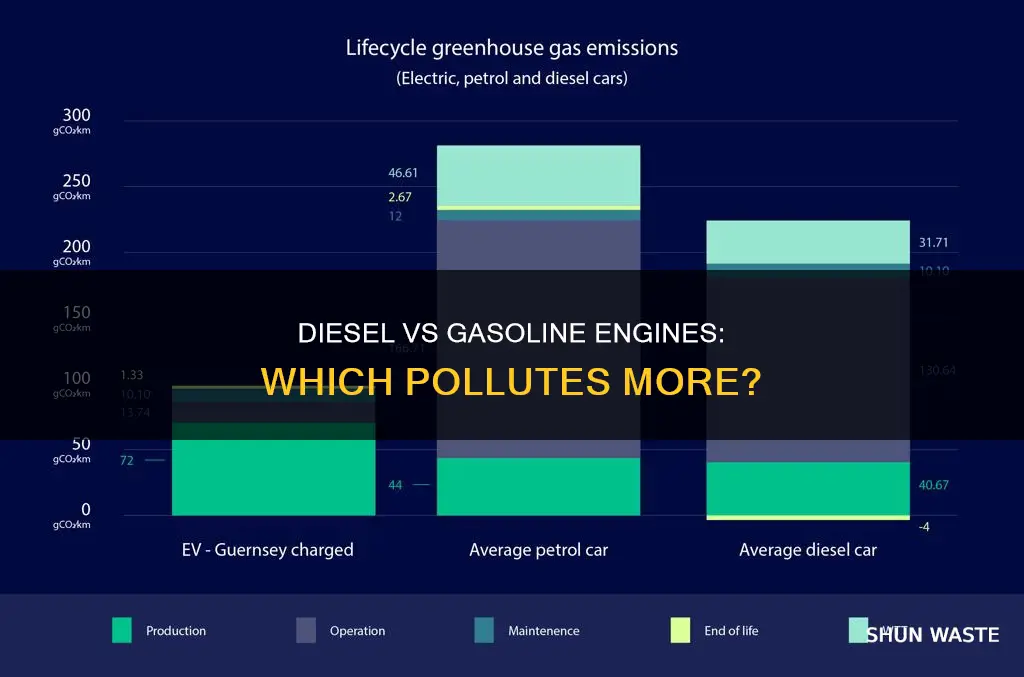
Diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than petrol engines
The question of whether diesel or petrol engines are more polluting is a complex one, and the answer depends on several factors. While diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than petrol engines, they produce more toxic emissions and fine particulate matter, which is associated with poor heart health.
Firstly, it is important to consider the type of pollution in question. Different types of engines may pollute more in some areas and less in others. For example, diesel engines typically emit fewer greenhouse gases and CO2 than petrol engines. This is due to the higher compression ratio of diesel fuel, which allows for better fuel efficiency and less fuel used to travel the same distance, resulting in lower CO2 emissions.
However, diesel engines produce more toxic emissions and fine particulate matter, which can have negative impacts on human health. The fine particulate matter emitted from diesel engines has been linked to increased hospital admissions and deaths from heart attacks. Additionally, the amount of nitrogen oxide emitted from diesel engines remains a concern.
The evolution of engine technologies and standards also plays a role in the pollution debate. The recent introduction of the direct injection system in petrol engines has increased the number of fine particulate pollutants, causing the emission rates of petrol engines to rise. On the other hand, newer diesel engines are often equipped with diesel particle filters that help trap particulate matter, making them cleaner than older diesel models.
Other factors that contribute to the complexity of the issue include the different models and uses of petrol and diesel vehicles. Diesel vehicles are usually bigger, heavier, and more efficient, and they are often used to travel greater distances. As a result, diesel engines may emit more CO2 over their life cycle, despite having lower CO2 emissions per distance travelled.
In summary, while diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than petrol engines, they excel in other types of pollution, such as toxic emissions and fine particulate matter. The overall impact of diesel and petrol engines on the environment and human health depends on a variety of factors, including engine technology, vehicle type, usage patterns, and maintenance.
Understanding Nonpoint Pollution: A Complex Environmental Issue
You may want to see also

Diesel engines emit more nitrogen oxides, which are harmful to human health
The question of whether diesel or gasoline vehicles are more polluting is complex and depends on various factors. While diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than gasoline engines due to higher fuel efficiency, they emit more harmful nitrogen oxides.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are a family of poisonous, highly reactive gases that are harmful to human health. Diesel engines emit more NOx than gasoline engines, and this has become an increasing concern for human health. NOx gases can cause respiratory problems and contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain.
The higher emissions of nitrogen oxides from diesel engines have been a persistent issue, even with the introduction of newer diesel technologies. While newer diesel engines are equipped with diesel particulate filters that help trap particulate matter, the issue of NOx emissions remains unresolved.
The health impacts of diesel engine emissions are significant. Fine particulate matter emitted from diesel engines has been linked to poor heart health. Research has shown that increases in particulate matter concentrations lead to more hospital admissions and deaths from heart attacks, particularly for those already at risk. As a result, the promotion of diesel vehicles over petrol vehicles in recent years has been criticized for neglecting human health considerations in air pollution policies.
In summary, while diesel engines emit less CO2, they produce more harmful nitrogen oxides. This has negative consequences for human health, particularly in terms of cardiovascular issues. Therefore, it is important to consider the trade-offs between reduced CO2 emissions and the increased presence of toxic nitrogen oxides when assessing the overall environmental and health impact of diesel engines compared to gasoline engines.
Cars: Understanding Their Pollution Impact
You may want to see also

Diesel engines are used in trucks and heavy equipment due to their greater torque and efficiency
The question of whether diesel or gasoline vehicles are more polluting is a complex one. It depends on several factors, including the type of pollution (e.g. air pollution, noise pollution), the injection system, the type of vehicle, and its usage patterns.
However, it is important to consider the health impacts of diesel engine emissions. Diesel vehicles emit fine particulate matter, which has been linked to poor heart health and increased hospital admissions for heart attacks. The latest emissions technology for diesel engines requires the addition of a urea mixture, which can be inconvenient for drivers.
While newer diesel engines are generally cleaner and emit less dangerous visible emissions, they still produce higher levels of nitrogen oxide, which remains an issue. On the other hand, gasoline engines with direct injection systems are becoming more common, but these increase fine particulate pollutants, potentially bringing them closer to the emission rates of diesel engines.
In summary, diesel engines are favored in trucks and heavy equipment due to their higher torque and efficiency, but the pollution and health impacts of both diesel and gasoline engines are complex and depend on various factors.
The Nile River: A Polluted Paradise?
You may want to see also

Petrol engines are self-regulating, needing less driver input than diesel engines
The question of whether diesel or petrol engines are more polluting is complex and depends on several factors. While diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than petrol engines due to their higher compression ratio and better fuel efficiency, they produce more toxic emissions and fine particulate matter, which have negative impacts on human health.
Petrol engines, on the other hand, have self-regulating emissions systems that require less driver input. The recent introduction of a direct injection system in petrol engines reduces fuel consumption but increases fine particulate pollutants. Despite this, petrol engines generally emit fewer fine particles and are considered less polluting, especially for smaller vehicles used for shorter distances.
Diesel engines are typically used in larger, heavier vehicles and are more efficient, resulting in lower fuel costs. However, they require more advanced technologies, such as particulate filters, to meet emission standards, which can be problematic for urban driving due to clogging issues.
Overall, while diesel engines may have a slight edge in CO2 emissions, the self-regulating nature of petrol engines and their generally lower fine particle emissions make them more favourable from an environmental and health perspective. The evolution of engine technologies and standards further complicates the comparison, and it is essential to consider multiple pollution aspects, including air pollution, fine particles, nitrogen oxides, and greenhouse gases.
The Impact of Oil Spills: Non-Point Pollution Sources
You may want to see also

Newer diesel engines are cleaner than gasoline engines, but older diesel engines are more polluting
The question of whether diesel or gasoline engines are more polluting is complex and depends on various factors. While newer diesel engines are generally cleaner than gasoline engines, older diesel engines are more polluting due to their higher emissions of harmful particulate matter.
Newer diesel engines are equipped with diesel particulate filters that trap obnoxious particulate matter, making their visible emissions less dangerous than those of gasoline engines. Additionally, diesel engines have a higher compression ratio and are more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines, resulting in lower carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions over their life cycle. This is because diesel fuel contains about 12% more energy per gallon than gasoline, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower CO2 emissions.
However, older diesel engines are more polluting, especially in terms of fine particulate matter and nitrogen oxide emissions. The higher emissions of fine particulate matter from diesel engines have been associated with poor heart health and increased hospital admissions for heart attacks. The accumulation of these older diesel vehicles on the roads has negatively impacted human health over the years.
The type of pollution considered is also important. While diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases, they produce more nitrogen oxides and fine particulate matter, which can have detrimental health effects. The frequent use of diesel engines for longer distances and their heavier weight contribute to their higher pollution impact in these areas.
It is worth noting that the technologies and standards for both diesel and gasoline engines are evolving rapidly. The direct injection system in gasoline engines, for example, reduces fuel consumption but increases fine particulate pollutants. As a result, the choice between diesel and gasoline engines depends on multiple factors, including the type of pollution considered, injection system, vehicle type, usage frequency, and purpose.
Humanity's Space Junk: Polluting the Final Frontier
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
It depends on the type of pollution we're talking about. Diesel engines emit less CO2 and greenhouse gases than petrol engines. However, diesel engines emit more nitrogen oxide and fine particulate matter, which is associated with poor heart health.
Diesel engines have a higher compression ratio than petrol engines, so less fuel is used to travel the same distance, resulting in lower CO2 emissions.
Newer diesel engines are equipped with diesel particle filters that trap most particulate matter, making them cleaner than gasoline engines in terms of visible emissions. However, the higher emission standards required for diesel engines can be challenging to maintain, especially in urban areas.







