Cars are a major contributor to air pollution. Every time a car is driven, pollutants are emitted directly into the air, causing significant risks to human health and the environment. These pollutants are emitted from the exhaust pipe and are released during the combustion of gasoline. The pollutants emitted by cars include nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, volatile organic compounds, particulate matter, and greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide. These emissions contribute to global warming, climate change, and adverse health effects such as lung irritation, asthma, and heart disease. While electric and hybrid cars have a reduced environmental impact, the transportation sector as a whole, including airplanes, trains, and ships, contributes significantly to air pollution and heat-trapping gas emissions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cars create pollution | Yes |
| Types of pollution | Air pollution, noise pollution, water pollution |
| Pollutants | Nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), sulphur oxides (SOx), carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, benzene, formaldehyde, ozone, sulphur dioxide |
| Health impacts | Lung irritation, weakened defenses against respiratory infections, interference with oxygen transport in the blood, increased risk of pneumonia and influenza, eye irritation, asthma, heart disease, birth defects, psychological ill-health, premature death |
| Environmental impacts | Global warming, climate change, depletion of the ozone layer, acid rain |
| Sources of pollution | Exhaust emissions, combustion of gasoline, abrasion emissions, evaporative emissions, fuel production, car manufacturing, logistics, driving, scrapping, fuel spills, engine noise |
| Factors influencing pollution levels | Type of car (electric, hybrid, or fuelled), age and maintenance of the vehicle, fuel efficiency |
| Ways to reduce pollution | Transition to electric-powered vehicles, improve fuel efficiency, adopt clean vehicle and fuel technologies |
What You'll Learn

Cars are a major cause of air pollution
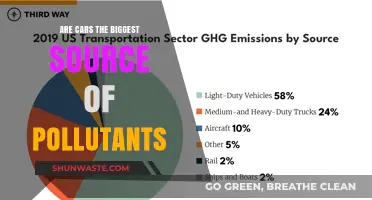
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, highway vehicles release about 1.5 billion metric tons of greenhouse gases annually, with each gallon of gasoline burned creating 9 kilograms of greenhouse gases. Cars are a significant contributor to these emissions, with transportation accounting for around 30% of all heat-trapping gas emissions. The Environmental Protection Agency estimates that vehicles cause nearly 75% of carbon monoxide pollution in the United States.
The pollutants emitted by cars have severe health consequences. Carbon monoxide, an odorless and colorless gas, interferes with the blood's ability to transport oxygen, posing a particular danger to infants and individuals with heart disease. Nitrogen oxides irritate the lungs and weaken defenses against respiratory infections. Particulate matter, a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets, can damage lungs and enter the bloodstream. Additionally, ozone, formed through the reaction of nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds, inflames lungs and causes breathing difficulties.
Furthermore, car pollution disproportionately affects Latinos, Blacks, and lower-income households. People in these communities are exposed to higher levels of air pollution, exacerbating existing health and environmental injustices.
While electric and hybrid vehicles offer reduced environmental impacts compared to traditional fueled cars, they still contribute to pollution through abrasion and evaporative emissions. Abrasion emissions arise from the corrosion of car parts and mechanical abrasion of tires, releasing particulate matter. Evaporative emissions, on the other hand, occur through vapors from the car's fuel system, even when the vehicle is parked with its engine turned off.
Outdoor Safety: Is it Safe to Venture Out?
You may want to see also

Car emissions and their effects on human health
Cars are a major contributor to air pollution. Every time a car is driven, pollutants are emitted directly into the air, causing significant health and environmental risks. The US Department of Energy reports that highway vehicles release about 1.7 billion tons of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere each year, mostly in the form of carbon dioxide. The Environmental Protection Agency estimates that vehicles cause nearly 75% of carbon monoxide pollution in the United States.
Vehicle emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone (smog), which can trigger health problems such as aggravated asthma, reduced lung capacity, and increased susceptibility to respiratory illnesses, including pneumonia and bronchitis. Motor vehicles, particularly those used for freight, are a major source of fine particulate matter, which has been linked to asthma, chronic bronchitis, heart attacks, and lung cancer. Diesel exhaust is of particular concern as it is suspected to be carcinogenic.
In addition to diesel and freight vehicles, passenger cars are a significant source of pollution. They produce nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and other harmful emissions. Poor air quality increases respiratory ailments, heightens the risk of cancer, and burdens healthcare systems with substantial costs. Particulate matter alone is responsible for up to 30,000 premature deaths each year. People living near busy roads or high-traffic volume areas are at an especially high risk of experiencing adverse health effects from vehicle emissions.
Vehicle emissions affect more than just the lungs. Studies have linked pollutants from vehicle exhaust to adverse impacts on nearly every organ system in the body. Exposure to pollution is inequitable, disproportionately affecting Latinos, Blacks, and lower-income households. Climate change, driven by vehicle emissions, also impacts human health. The increased frequency and intensity of heat waves, sea level rise, flooding, drought, and wildfires can devastate communities, especially children, the elderly, and low-income communities.
While cars are a significant source of pollution, advancements in clean vehicle and fuel technologies offer solutions. Zero-emissions vehicles, such as electric cars, can significantly reduce emissions and help transform transportation. Strong federal and state policies, such as vehicle emission standards, have already cut pollution from cars and trucks by about 90% since 1998. These efforts to reduce emissions protect the health of those living and working near busy roads and contribute to the fight against climate change.
Florida's Estuaries: Polluted Paradise?
You may want to see also

Car exhausts emit a wide range of gases and solid matter
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Carbon monoxide, an odorless, colorless, and poisonous gas formed by the combustion of fossil fuels, blocks oxygen from reaching the brain, heart, and other vital organs when inhaled. It is particularly dangerous for infants and people with heart disease. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which irritates the lungs and weakens the body's defenses against respiratory infections. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) also play a role in creating ground-level ozone and photochemical smog, causing eye irritation, lung damage, and respiratory problems.
Particulate matter, or particle pollution, is a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. It contributes to atmospheric haze, damages lungs, and can enter the bloodstream. Hydrocarbons, such as petrol fuel vapors, emit outside all the time when there is fuel in the tank, even when the vehicle is parked with its engine turned off. Benzene and formaldehyde are other harmful pollutants emitted by car exhausts, with formaldehyde causing eye, nose, and throat irritation, and benzene linked to bone marrow and blood disorders.
Cars, trucks, and other forms of transportation are major contributors to air pollution, with vehicles being the single largest contributor in the United States. The production and burning of fossil fuels used in cars also contribute to environmental issues such as energy consumption, ecosystem damage, and occasional disasters like oil spills. However, it is important to note that electric and hybrid vehicles produce reduced environmental impacts as they do not burn fossil fuels.
Understanding PM2.5: Tiny Particles, Big Impact
You may want to see also

Cars contribute to global warming and climate change
Cars are a significant source of air pollution, particularly in urban areas. Vehicle exhaust emits a range of gases and solid matter, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and particulate matter. These pollutants have adverse effects on human health, causing lung irritation, chest pains, coughing, and respiratory issues. Additionally, carbon monoxide interferes with the blood's oxygen transport, posing a severe risk to infants and individuals with heart disease.
Furthermore, cars contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer. Ground-level ozone, formed through complex reactions involving nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds, acts as a respiratory irritant and poses health risks to individuals with asthma. The emissions from vehicles also lead to global warming, which has far-reaching consequences for the environment and human well-being. Climate change driven by heat-trapping emissions results in more frequent and intense heat waves, sea-level rise, flooding, droughts, and wildfires, impacting communities worldwide.
The transportation sector, including cars, airplanes, trains, and ships, accounts for a significant proportion of heat-trapping gas emissions. In the United States, transportation emits more than half of nitrogen oxide emissions and contributes to air pollution, particularly affecting Latinos, Blacks, and lower-income households. Additionally, the production and disposal of cars contribute to pollution, as do the abrasion and evaporation of car parts over time.
While electric and hybrid vehicles offer reduced environmental impacts, the extraction and shipping of fuels can still contribute to ecological damage and occasional disasters such as oil spills. Transitioning to clean vehicle technologies and improving fuel efficiency can help mitigate the effects of cars on global warming and climate change.
Jellyfish Filters: Innovative Solution to Clean Polluted Waters
You may want to see also

Electric cars produce less pollution than fuelled cars
Cars are one of the biggest contributors to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of gasoline and diesel fuels releases harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter. These emissions contribute to air pollution, global warming, and adverse health effects such as lung irritation, heart disease, and respiratory problems.
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained popularity as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fuelled cars. Unlike conventional internal combustion engines (ICEs), EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they do not emit pollutants directly into the air during operation. This is a significant advantage as tailpipe emissions from ICEs contribute to a significant portion of global warming pollution and have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
However, it is important to consider the emissions associated with the production and charging of EVs. The manufacturing of EV batteries, specifically the large lithium-ion batteries, can result in higher carbon emissions compared to the production of traditional fuelled cars. This is due to the energy-intensive process of mining and heating the required minerals, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Additionally, the charging of EV batteries can contribute to emissions, depending on the energy sources used for electricity generation in different regions.
Despite these considerations, EVs generally produce less pollution over their lifetime compared to fuelled cars. While the manufacturing and charging of EVs may result in higher emissions in certain regions, the absence of tailpipe emissions gives them a significant advantage during their operation. This is particularly true in geographic areas that use relatively low-polluting energy sources for electricity generation, where EVs have a substantial life cycle emissions advantage over conventional vehicles.
Furthermore, the range of EVs has improved significantly, making them a practical choice for many households. Most EV models can now travel over 200 miles on a fully charged battery, and advancements in battery technology have led to low failure rates. Additionally, smart planning for how and when to charge EVs can help manage the increased demand for electricity and further reduce their environmental impact.
The Pink Sky: Pollution's Impact and Influence
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, cars are one of the biggest causes of pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Cars emit a wide range of gases and solid matter, including:
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Particulate matter (PM)
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Ozone
- Benzene
- Formaldehyde
Cars create pollution through exhaust emissions, abrasion emissions, and evaporative emissions. Exhaust emissions are created by the combustion of fuels when the vehicle engine is running or idling. Abrasion emissions are caused by the corrosion of car parts and mechanical abrasion of tyres, for example. Evaporative emissions are created from vapours from the car's fuel system, which emit outside all the time when there is fuel in the tank, even when the vehicle is parked with its engine turned off.
Car pollution contributes to global warming as greenhouse gases heat the planet and deplete the ozone layer. It also causes acid rain and harms human health. Pollutants from vehicle exhausts have been linked to adverse impacts on nearly every organ system in the body.
Car owners can reduce their vehicle's effects on the environment by switching to electric, hybrid, or other clean, fuel-efficient cars.