Automobiles and homes both contribute to pollution, but in different ways. Automobiles are a significant source of air pollution, particularly in urban areas, due to the combustion of fossil fuels and the emission of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and carbon dioxide. The transportation sector, including cars, trucks, and buses, is responsible for a substantial portion of nitrogen oxide and particulate matter emissions. On the other hand, homes contribute to pollution through the use of fuels for heating and electricity generation, which can also have a significant impact on air quality. While individual cars may have smaller emissions compared to industrial sources, the large number of automobiles and traffic congestion in urban areas lead to a significant cumulative impact on air pollution. Additionally, the production of electricity by coal-fired power plants can contribute more pollution than most cars. Overall, both automobiles and homes contribute to pollution, but the specific types and extent of pollution vary between the two sources.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Do automobiles use more pollution than homes? | It is difficult to say exactly what percentage of air pollution comes from automobiles, as many other human activities contribute to air pollution. However, the personal automobile is the single greatest polluter. |
| Which emits more pollution, older or newer vehicles? | Newer vehicles generally emit less pollution and use less gasoline, while older vehicles generally emit more pollution and use more gasoline. |
| What are the main pollutants emitted by automobiles? | Carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) |
| How does automobile pollution affect human health and the environment? | Automobile pollution contributes to global warming, climate change, and air pollution, which can have adverse effects on human health, including impacts on nearly every organ system in the body. |
| How can automobile pollution be reduced? | By driving fuel-efficient vehicles, maintaining vehicles in good repair, and reducing the number of miles driven. |
What You'll Learn

Transportation's impact on NOx emissions
While it is challenging to pinpoint the exact percentage of air pollution that comes from cars, there is no denying that vehicles are major contributors to air pollution. The transportation sector is responsible for over 55% of NOx total emissions inventory in the US, with on-road vehicles contributing to 52% of transportation-related NOx emissions in the country in 2023.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are a group of gases that include nitrogen dioxide (NO2). When fuel burns, nitrogen and oxygen react to form nitrogen oxides. These gases have harmful direct effects on human health and indirect effects on agricultural crops and ecosystems. Vehicle NOx emissions have been regulated since the 1960s, and while newer vehicles emit less pollution than older vehicles, NOx emissions remain a significant issue.
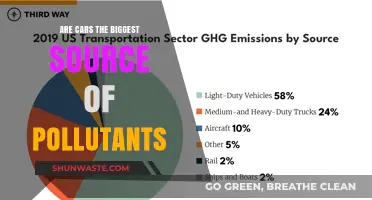
In 2023, transportation in the United States emitted 4.8 million tons of NOx, a decrease of over 70% since 2006. However, the transportation sector continues to be one of the largest contributors to US greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Cars, trucks, commercial aircraft, and railroads are among the sources of transportation end-use sector emissions. Passenger cars alone are responsible for more than 20% of the transportation sector's GHG emissions in the US.
In addition to NOx, vehicles emit carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). While CO2 is not inherently harmful and is necessary for life on Earth, burning gasoline and other fossil fuels releases far more CO2 into the atmosphere than the planet can handle. This excess CO2 forms a heat-trapping layer, contributing to global warming and climate change.
To address the impact of transportation on NOx emissions, it is essential to minimize the creation of NOx during the combustion process and remove NOx from vehicle exhaust through aftertreatment devices. Lowering the combustion temperature and using chemical reactions to convert NOx into nitrogen and water or CO2 are common strategies. Additionally, transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs) can help reduce tailpipe emissions and improve air quality.
Jellyfish Filters: Innovative Solution to Clean Polluted Waters
You may want to see also

Fossil fuel combustion
CO2 emissions from fossil fuels have been rising, with record levels reported in 2023. The concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has increased from 278 parts per million in 1750 to 420 parts per million in 2023. This rise in heat-trapping CO2 and other greenhouse gases is the primary driver of increasing global temperatures, with 2023 being the hottest year on record. The combustion of fossil fuels is also responsible for the formation of smog and acid rain.
Vehicles are significant contributors to air pollution through the combustion of gasoline and other fossil fuels. In the US, vehicles are responsible for over 55% of NOx emissions and less than 10% of VOCs emissions. When gasoline is burned in cars, it emits carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter, methane, and nitrous oxide. Carbon monoxide is particularly harmful, as it affects critical organs like the heart and brain. The transportation sector, including cars, is a major source of nitrogen oxide emissions, which contribute to smog and acid rain.
While modern vehicles are more fuel-efficient, the increased popularity of less fuel-efficient SUVs and pickup trucks, along with higher mileage, has led to a rise in gasoline usage. Electric vehicles (EVs) offer a solution, as they produce no tailpipe emissions, although they are still associated with emissions during the production and distribution of electricity.
The combustion of fossil fuels has severe health impacts, particularly on children's health and development. Exposure to toxic air pollutants and climate change caused by fossil fuel combustion can lead to respiratory illness, cognitive and behavioral development issues, and other chronic diseases. Fossil-fuel combustion disproportionately affects vulnerable communities, including children, the poor, and minorities, exacerbating global inequality and environmental injustice.
Nitrates and Phosphates: Pollutants in Eutrophication?
You may want to see also

Electric cars vs. gasoline-powered cars
While it is challenging to pinpoint the exact percentage of air pollution that comes from automobiles, there is no denying that vehicles are major contributors to air pollution. This is especially true for cars that run on gasoline, which emit pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. These emissions contribute to global warming, the depletion of the ozone layer, and the formation of atmospheric haze, which can have detrimental effects on human health.
In contrast, electric vehicles (EVs) have no tailpipe emissions. Instead, they are powered by electricity generated by power plants, which may produce emissions depending on the energy source. However, even when accounting for these electricity emissions, research shows that EVs are generally responsible for lower levels of greenhouse gases than gasoline-powered cars. This is because, while EV manufacturing may create more emissions, their operational emissions are significantly lower.
The environmental impact of EVs also depends on the region. In areas with relatively low-polluting energy sources, such as renewable energy, EVs have a significant life cycle emissions advantage over gasoline-powered cars. On the other hand, in regions with higher-emissions electricity, the life cycle emissions benefit of EVs may not be as pronounced.
Furthermore, the production of gasoline is not renewable or carbon-free, and it contributes to GHG emissions during various stages, including extraction, refining, and transportation. While the same is true for electricity generation, the electric grid can become cleaner as the world transitions to cleaner energy sources, reducing upstream emissions for EVs.
Overall, while both types of vehicles contribute to pollution, gasoline-powered cars produce higher levels of certain pollutants and GHG emissions, whereas EVs have the potential to significantly reduce emissions, especially in regions with cleaner energy sources.
Land Pollution: A Threat to Our Planet's Health
You may want to see also

Vehicle exhaust's health impact
Vehicle exhausts have a significant impact on health. While it is challenging to determine the exact percentage of air pollution that comes from cars, there is no denying that vehicles are major contributors. The burning of gasoline emits pollutants such as particulate matter, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide, which is the principal greenhouse gas. These emissions have severe consequences for the environment and public health.
Particulate matter, a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets, contributes to atmospheric haze, damages lungs, and enters the bloodstream. Carbon monoxide affects critical organs like the heart and brain, with motor vehicle exhaust accounting for up to 95% of all carbon monoxide emissions in cities. Nitrogen dioxide, formed when nitrogen and oxygen react during fuel burning, creates nitrogen oxides, which contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer.
The release of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases from vehicle exhausts leads to global warming. This heat-trapping layer around the planet prevents heat from escaping, causing rising global temperatures, rising sea levels, an increase in natural disasters, and other detrimental effects. The impact of these emissions is particularly evident in the oceans, which absorb the extra heat, resulting in unprecedented ocean temperature rises.
The health consequences of vehicle exhaust emissions are dire. A 2021 study by the International Council on Clean Transportation and academic institutions linked vehicle emissions to approximately 361,000 premature deaths worldwide in 2010 and 385,000 in 2015. On-road diesel vehicles were responsible for nearly half of these premature deaths, with the global financial cost of these transportation-attributable health impacts reaching approximately US$1 trillion.
In the United States, vehicle pollution is responsible for 17,000 to 20,000 deaths each year, with one in three people exposed to unhealthy air. People of color are disproportionately affected, breathing more air pollution from cars and trucks in certain regions. The high levels of air toxics and carcinogens in vehicle emissions have severe health implications, as highlighted by organizations such as the Health Effects Institute, the International Agency for Research on Cancer, and the National Toxicology Program.
Dust: What's in the Air We Breathe?
You may want to see also

Climate change and health
Automobiles and homes both contribute to pollution, which has a significant impact on climate change and health. While automobiles are major contributors to air pollution, the production of electricity by coal-fired power plants and heating homes with non-electric fuels can also cause more pollution than most cars. The transportation sector, including automobiles, is responsible for a significant portion of NOx emissions, VOCs, and particulate matter. These emissions contain pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) from air conditioners.
The impact of these emissions on climate change is significant. Carbon dioxide pollution has led to warming land and ocean temperatures, resulting in more severe storms, droughts, and other weather events. The rise in ocean temperatures has particularly alarming consequences, as the oceans have been absorbing about 90% of the extra heat caused by carbon dioxide. This contributes to the intensification of weather events and the degradation of environmental and social determinants of health.
Climate change poses a severe threat to human health, and the impact is already being felt. Research indicates that 3.6 billion people live in areas highly susceptible to climate change, and the direct damage costs to health are estimated to be between US$2-4 billion per year by 2030. Climate change increases the risk of deaths, non-communicable diseases, infectious diseases, and health emergencies. It also exacerbates existing health threats, such as respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, and creates new ones, like the increased risk of asthma attacks. Vulnerable regions have experienced a significantly higher death rate from extreme weather events.
To protect public health, it is crucial to address the impacts of climate change. Reducing emissions of greenhouse gases through improved transport, food, and energy choices can have significant health benefits, particularly by reducing air pollution. Additionally, early preparation and response assistance are vital for areas with weak health infrastructure, mainly in developing countries, to cope with the challenges posed by climate change.
In conclusion, while automobiles contribute significantly to pollution and climate change, it is important to recognize that homes and other sources also play a role. The impact of climate change on health is undeniable, and immediate action is necessary to mitigate its effects and protect the well-being of people worldwide.
Makeup's Impact: Environmental Contamination and Pollution
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Automobiles and homes both contribute to pollution. While it is difficult to say exactly what percentage of air pollution comes from cars, they are a major source of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, benzene, and formaldehyde. In typical urban areas, cars, buses, trucks, and other vehicles produce at least half of the hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides. Additionally, the production and distribution of electricity used to power electric vehicles can also contribute to pollution.
Pollutants from vehicle exhaust pose significant health risks, including adverse effects on nearly every organ system in the body. Fine particles from exhaust can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory problems and increasing the risk of asthma, heart disease, and eye irritation. Climate change, driven by heat-trapping emissions, also affects people's health, leading to more frequent and intense heat waves, sea level rise, flooding, droughts, and wildfires. Marginalized communities, including low-income households and communities of color, are often disproportionately exposed to higher levels of air pollution.
There are several ways to reduce pollution from automobiles:
- Choose cleaner vehicles: Electric, hybrid, and fuel-efficient vehicles typically produce fewer emissions than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Maintain your vehicle: Ensure that your vehicle's emission controls are functioning properly and keep your tires properly inflated to improve fuel efficiency.
- Drive efficiently: Observe speed limits, accelerate gradually, and avoid idling.
- Reduce vehicle usage: Opt for walking, biking, carpooling, or public transportation when possible to decrease vehicle miles traveled.