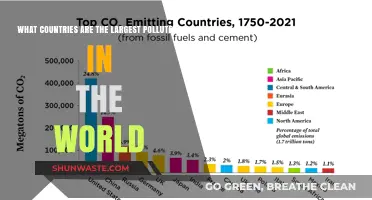
China is the world's most populous country, with a population of approximately 1.4 billion people as of 2019. It is the fourth-largest country by area, with a total land area of 9.6 million square kilometres. China's rapid population increase, rapid economic growth, and lax environmental oversight have resulted in severe water shortages and severe water pollution. The country's immense urban growth has substantially increased the need for consumer goods, vehicles, and energy, leading to increased burning of fossil fuels and smog. China's agricultural sector is also a significant source of waste, with farms generating more pollution than factories. However, China has made improvements in environmental protection in recent years, and some cities in China are known for their relatively better air quality, including Sanya, Guilin, Kunming, Lhasa, and Xiamen.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cities with the worst air quality | Anyang, Xingtai, Shijiazhuang, Handan, Linfen, Tangshan, Taiyuan, Zibo, Jiaozuo, Jincheng, Beijing, Urumchi, Lanzhou, Chongqing, Jinan, and Shanghai |
| Causes of air pollution | Burning of fossil fuels, agricultural sector, electronic waste, plastic bags, Styrofoam containers, light-colored materials, and factories |
| Effects of air pollution | Heart, lung, and stroke problems, respiratory and cardiovascular diseases |
| Cities with the best air quality | Sanya, Guilin, Kunming, Lhasa, Xiamen, Shangri-La, Lijiang, and Tibet |
| Efforts to reduce pollution | Ban on free plastic bags in supermarkets, department stores, and shops; encouraging the use of cloth bags; legislation banning the importation of electronic waste; smog alert system |
What You'll Learn

China's least polluted cities
China has made some improvements in environmental protection in recent years. The Chinese government has invested heavily to combat pollution, pledging over $277 billion in 2013. This has led to a reduction in the levels of PM2.5 and sulphur dioxide (SO2) in several cities. Despite these efforts, China ranked as the 11th dirtiest country in the world in 2019, and air and water pollution continue to cause hundreds of thousands of premature deaths each year.
Some of China's least polluted cities include:
- Sanya: Sanya is located in the southernmost part of China and has the best air quality in the country. Its PM2.5 measurements are around 20 μg/m³, which is well below the acceptable limit of 100. Sanya enjoys more than 300 sunny days a year and has an annual average temperature of 24.5 °C.
- Kunming: Known as the "spring city", Kunming has moderate temperatures and an abundance of colourful flower blossoms year-round. Popular destinations in Yunnan Province, such as Shangri-La and Lijiang, are known for their high air quality and lack of PM2.5 records.
- Lhasa: Lhasa, the capital of Tibet, is known for its high-quality air conditions. The PM2.5 levels in Lhasa are typically around 50 or below. Tibet is often associated with blue skies, Tibetan monasteries, and clear lakes.
- Xiamen: Xiamen won the UN Habitat Award in 2004 and is the most sought-after place to live for Chinese people. It has a temperate climate with an annual average temperature of 21 °C. Mount Wuyi and Taining Danxia Landform offer picturesque landscapes for visitors to enjoy.
- Guilin: Guilin is renowned for its clear air and picturesque landscapes, making it a popular tourist destination.
While these cities have relatively better air quality compared to other parts of China, it is important to note that air pollution remains a significant issue across the country. Even in less polluted cities, the air quality may still exceed the recommended limits set by the World Health Organization.
Microvelia: Pollution-Tolerant Bugs or Nature's Water Purifiers?
You may want to see also

Impact of pollution on health
China has been facing severe air pollution, which has had adverse impacts on society. The impact of pollution on health in China has been significant, with up to 760,000 people dying prematurely each year due to air and water pollution. Air pollution alone causes more than a million deaths, while another million die from household air pollution from cooking with polluting fuels. The high levels of air pollution in Chinese cities cause 350,000-400,000 premature deaths, with an additional 60,000 dying from poor water quality.
A study from 2012 showed that fine particles in the air, which cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, were key pollutants that greatly damaged the health of Chinese citizens. The water resources in China are also affected by severe water shortages and pollution, further impacting public health. The rapid population increase, economic growth, and lax environmental oversight have resulted in increased water demand and pollution.
The health effects of air pollution vary across different regions of China. For example, the population health in Central and Western China was found to be more sensitive to air quality, possibly due to the relative lack of medical resources in these areas. In contrast, Eastern China had more medical resources and better climate conditions, particularly in coastal regions. However, the average health score for eastern areas was not significantly higher than that of the central/western regions.
Recent studies have also found associations between air pollution and deaths from cardiovascular and respiratory causes. Long-term exposure to air pollution and household air pollution from solid fuels is linked to various chronic diseases, including stroke, ischaemic heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer. The levels of air pollution exposure, background rates of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, and population density vary across China, influencing the impact of pollution on health in different regions.
Despite the challenges of pollution, some cities in China have been noted for their relatively better air quality. Sanya, Guilin, Kunming, Lhasa, and Xiamen are considered the top five high-air-quality tourist cities in China, offering fresh air and picturesque landscapes. These cities have lower PM2.5 measurements, indicating better air quality. Additionally, destinations in Yunnan Province, such as Shangri-La and Lijiang, have never suffered from air pollution, and Tibet is also known for its high-quality air conditions.
CFL vs LED: Which Lighting is Greener?
You may want to see also

Water pollution
China's rapid economic growth, industrialization, and urbanization, coupled with inadequate investment in water treatment infrastructure, have resulted in widespread water pollution. Over half of China's population consumes drinking water contaminated with animal and human excreta, with levels exceeding maximum permissible amounts by up to 86% in rural areas and 28% in urban areas. The country's rivers have suffered significant water quality impairments, with excess nutrients from rivers transported to lakes and oceans, resulting in blooms and red tides that endanger human and aquatic health.
The Lowy Institute estimates that 80-90% of groundwater in China is unsuitable for drinking, and 50% is too polluted for agricultural use. Additionally, 75% of lakes and reservoirs are too polluted for fishing and human consumption. Eutrophy, caused by pollution runoff from agriculture, industry, and urban sewage, is a significant issue for many lakes in China. The country's rapid population growth and economic development have increased water demand and pollution, with severe water shortages affecting China's water resources.
China has taken steps to address water pollution, with the Law of the People's Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Water Pollution enacted in 2008, tightening water environmental protection regulations. The Total Amount of Pollutants Control Plan, proposed in 2000, has achieved remarkable results in reducing key pollutants. From 2003 to 2017, inland water quality across China improved or was maintained at favorable levels. However, nutrient concentrations are expected to continue rising due to human activities and climate change.
While water pollution is a severe issue in China, some cities are known for their high-quality air. Sanya, Guilin, Kunming, Lhasa, and Xiamen are considered China's top five cities for air quality, offering fresh air and picturesque landscapes. These cities have PM2.5 measurements below 50, indicating excellent air quality.
Pollution and Pimples: Is There a Link?
You may want to see also

Plastic pollution
China has long been associated with severe air pollution, and plastic pollution is also a significant issue. China is the world's largest plastic producer and consumer, and this has contributed to it being the largest source of mismanaged plastic waste and the biggest offender of ocean plastic pollution. The Yangtze River, which supports nearly one-third of the population, has been identified as one of the biggest sources of marine plastic pollution.
China's contribution to the global plastic crisis is substantial, and it has earned an international reputation as one of the largest contributors to ocean plastic pollution. The country's massive local plastic production also contributes to its high greenhouse gas emissions, which are already driven by coal production. China's plastic pollution has led to environmental damage and degradation, with studies finding that all 21 species of sea fish and freshwater fish from Chinese waters examined had ingested plastic. This means that people consuming fish are inadvertently consuming plastic as well.
However, China has been making efforts to address plastic pollution. Since 2000, the number of plastic-related policies has increased from four to 41 as of mid-2021, representing a 925% increase. China's serious efforts to govern plastics gained momentum in 2016, with a focus on prohibitive bans and information campaigns. China banned imports of plastic waste in 2017, which had a notable impact on global plastic trade flows. Additionally, China has transitioned from a mixed-waste collection system to a source-segregation collection system to improve waste management.
While China's plastic pollution remains a critical issue, the country has demonstrated a commitment to tackling it through regulatory frameworks and policy changes. The future impact of these efforts will determine whether China can successfully mitigate its plastic pollution crisis and contribute to global efforts to reduce plastic waste.
Despite the challenges posed by pollution, some cities in China are known for their relatively better air quality. Sanya, Guilin, Kunming, Lhasa, and Xiamen are considered the top five high-air-quality tourist cities in China. These destinations offer fresh air and picturesque landscapes. Kunming, known as "Spring City," boasts moderate temperatures and colourful flower blossoms. Shangri-La and Lijiang in Yunnan Province have never suffered from air pollution, and Tibet is also known for its high-quality air. Xiamen, a coastal city with a temperate climate, won the UN Habitat Award in 2004 and is sought after as a place to live by Chinese residents.
Delhi's Polluted Air: Reasons and Concerns
You may want to see also

Efforts to reduce pollution
China has gained a reputation for being one of the most polluted countries in the world. However, it has made significant progress in reducing pollution in recent years. Here are some key efforts and initiatives undertaken by China to combat pollution:
National Air Quality Action Plan
China implemented the National Air Quality Action Plan in 2014, which set targets to improve air quality and reduce pollution. The plan included measures such as prohibiting new coal-fired plants in three target regions and requiring existing coal plants to reduce emissions or switch to natural gas. By 2018, several coal mines and coal-fired power plants had been shut down, and plans for new plants were canceled. This shift towards renewable energy sources contributed to a quarter of China's energy generation in 2017, surpassing the US.
War Against Pollution
In 2014, China announced a "War Against Pollution," demonstrating its commitment to tackling the issue. This campaign has yielded positive results, with a 39.8% reduction in particulate pollution. By 2021, China had sustained its efforts and witnessed remarkable progress, dispelling its reputation as one of the top five most polluted countries since 2016.
Plastic Bag Ban
In 2008, China implemented a ban on supermarkets, department stores, and shops from providing free plastic bags to customers. This initiative encouraged the use of cloth bags and reduced the prevalence of plastic bags in the garbage, contributing to a 10% reduction in plastic bag waste.
Electronic Waste Management
China has recognized the challenge posed by electronic waste, with domestic production and imported waste contributing to the issue. Legislation has been enacted to ban the importation of electronic waste, and proper disposal methods are being promoted. The city of Tianjin successfully disposed of 38,000 tons of electronic waste in 2010, showcasing the potential for effective local initiatives.
Incentivizing Environmental Protection
China has linked government officials' incentives to environmental performance. Provincial and local officials are now incentivized to improve the environment within their jurisdictions, fostering a culture of environmental responsibility and encouraging proactive measures to address pollution.
Public Awareness and Behavior Changes
Reducing pollution requires a collective effort, and China has witnessed growing individual initiatives to decrease air pollution exposure risk. Personal behavior changes, such as adopting green lifestyles, play a crucial role in minimizing exposure risk. Additionally, tools like the China Air Pollution Map, released by Ma Jun in 2007, empower individuals to monitor air quality and make informed decisions.
While China continues its battle for blue skies, these efforts demonstrate a commitment to improving environmental conditions and enhancing the quality of life for its citizens.
Ending Plastic Pollution: Actionable Steps to Take Today
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, there are places in China that are not polluted. According to IQAir.com, the cleanest air in China is found in Tibet, specifically in the city of Linzhi. Other places with good air quality include Sanya, Guilin, Kunming, Lhasa, and Xiamen.
The immense urban growth of Chinese cities has increased the need for consumer goods, vehicles, and energy, leading to the burning of fossil fuels and resulting in smog. The agricultural sector is also a significant source of waste, with Chinese farms generating more pollution than factories.
High levels of air pollution in China's cities cause premature deaths, with an estimated 1.6 million people dying annually from heart, lung, and stroke problems due to polluted air. Fine particles in the air contribute to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, posing a threat to the health of Chinese citizens.
The Chinese government has implemented a ban on free plastic bags in supermarkets and shops, encouraging the use of cloth bags. China is also increasing its forest cover and has made improvements in environmental protection in recent years.
Yes, Shangri-La and Lijiang in Yunnan Province are known for their high-quality air, with no records of PM2.5 pollution. Nyingchi in Tibet is also renowned for its fresh air and natural beauty.